

How Fast Do Catamarans Go? 5 Examples (With Pictures)
A catamaran is generally more balanced on the water and can be faster than a multi-hull vessel.
Unless you compare them to foiling monohulls like the new America’s Cup boats that sail at over 50 knots, they are not recreational vessels.
In this article, we will look at how fast each type of catamaran will go.
Table of Contents
Here are the numbers before we dive into the details:
Average Speed For Sailing Catamarans
Catamarans can vary in size from 14 ft to over 100 ft. Catamarans can come in a wide variety of design types.
Sailing Catamarans have been attempting to make advancements over their mono-hulled counterparts.
These advancements include:
- Foils that assist with lifting the vessel out of the water.
- Stability advancements.
- Racers that can maintain their speed while out in the ocean.
3 Different Types of Sailing Catamarans:
1) sport catamarans.

One type of sailing catamaran is a sport catamaran, which is otherwise known as recreational. These are typically supposed to have a small crew and launch and land on beaches.
Sport catamarans do not normally have living quarters and are ideal for day trips. Resorts or other rental services often use these.
These can also be used for racing.
Sport vessels have been known to travel over 30 knots but can speed over 40 knots in the proper conditions.
2) Cruising Catamarans

Another type of sailing catamaran is a cruising catamaran. These often come with complete living accommodations, so they sacrifice speed over their sportier counterparts.
They can average between 9 and 10 knots, depending on the conditions. The top speed is typically around 15 knots.
It would be best if you were careful with catamarans that have living quarters. The more you weigh it down, the less speed you will have.
3) Racing Catamarans

The final type of sailing catamaran is an ocean racing catamaran.
These boats are large and can reach over 100 feet in length.
The top speed of this type of catamaran is around 45 knots.
Because of the prize money for entering these in races, much research goes into their advancement.
Average Speed Of Power Catamarans
Catamarans with power motors fill a different type of boating category.
These are commonly used when speed and smoothness are favored over space or capacity.
Because of their stability, catamarans are good vessels for combating seasickness as well as transportation. We have a separate article here with all you should know about catamarans and (how to overcome) seasickness .
On a commercial level, these can be used for ferries for both people and vehicles. They are used for short term travel, often to or from islands.
Like sailing catamarans, there are a few types of power catamarans.
1) Power Cruising Catamarans

Similar to sailing cruising catamarans, they also have power cruising catamarans. These also have living quarters and are stable while out on the water. The speed of these vessels highly depends on the motors equipped and the size of the boat itself.
Like passenger transport or ferries, catamarans have a high speed of about 40 to 70 miles per hour.
These are made to travel at great speeds to allow their commuters the shortest possible ride to their destination.
The military also utilizes power catamarans. They use power catamarans to transport military cargo. These ships are ideal because of their speed, holding capacity, and ability to venture into shallow ports.
2) Swath Catamarans

They also have small-waterplane-area twin-hull vessels. These are called SWATHs.
These differ from the average catamaran because they also have submarine-like hulls that stay completely under the water.
Due to the hulls being submerged, they are not normally affected by waves. These are used most often in the ocean as research vessels. They can also be used for certain types of yachts. Because of their stability, they are good vessels for furniture that will not require as much securing.
These often travel between 20 and 30 knots.
Some catamarans are designed for wave piercing. These are made to pierce through waves rather than sail over them, causing them to be faster. These can be used as passenger ferries, yachts, and military vessels as well.
3) Whitewater Catamarans

There are also recreational catamarans made for whitewater travel. These are sometimes called “cata-rafts.”
They are made using two inflatable hulls connected with a scaffold. These are lightweight and perfect for whitewater sports.
They are even able to be packed away in a backpack. They can take up to 20 minutes to assemble, including inflation.
They have high speeds on white water rivers and can be most compared to a canoe, kayak, whitewater raft, or other white water vessels.
Performance Characteristics Of Catamarans
Catamarans require four times the power to double their speed. A mono-hull vessel, however, would require eight times the power to double their speed.
This is because a Catamaran has less resistance in the water.
This is also good for conserving and using less energy.
Catamarans are also more stable in the water. This stability is effective at resisting heeling or capsizing. A multi-hull vessel would require four times the force to capsize as a similar-sized mono-hull vessel.
The general sailing in a catamaran is smoother and allows for activities that are not always possible on a mono-hull sailboat.
Are Catamarans Faster than Mono-Hull Vessels?
Because catamarans have less water resistance, they are generally faster than mono-hull vessels.
This is because their hulls are smaller, which means they have a smaller bow wave to fight.
A bow wave is a wave created by the displacement of water by the bow of a ship. After a certain speed, a boat has to start hauling itself over its own bow wave.
The larger hull a ship has, the larger its bow wave will be and the more power required to fight it.
Catamarans have two small and narrow hulls, so they do not have much of an issue with their bow wave. This is one reason they are usually faster than a similar-sized mono-hull vessel.
Catamarans can be between 20-30 percent faster than their monohull counterparts.
Issues with catamarans over mono-hulls are that they can take more time to turn.
How Is The Speed Measured?
Boats commonly measure speed using GPS tracking devices to measure distance traveled. Speed while sailing is measured in knots. A knot is one nautical mile per hour, which equals about 1.15 miles per hour.
How Fast Are Catamarans Compared To Other Boat Types?
- Sailing catamarans typically average about 10 knots.
- Pontoon boats average about 20 mph.
- A powerboat cruiser can average anywhere between 30 and 50 mph.
- Cigarette boats can even reach close to 90 mph in the proper conditions.
- Sailboats average between 6 and 12 mph depending on wind conditions. This includes mono-hull between 6 to 8 mph and catamarans and trimarans between 9 and 10mph
Two different factors can determine the speed of sailing ships:
1) The hull type as listed above.
Different hulls rest in the water more or less than other types. The less of the hull that is underwater, the faster it can go.
This is because the less of the hull in the water, the less drag created while sailing.
2) The length of the boat
The longer the boat, the faster it can go. Every boat has a maximum hull speed that cannot be exceeded unless the boat can plane on the water’s surface or be lifted on hydrofoils. For most boats, the longer the boat, the higher the maximum hull speed is.
Speed Vs. Comfort Considerations For Catamarans
If you are looking for a catamaran, you have a lot of options.
You can choose to prioritize speed or comfort.
After deciding to purchase a catamaran, the type of catamaran you should look at depends on where and what you are using it for.
You will want to make sure that you look at what type of water you will be traveling in, how many people you are traveling with on average, and what type of speed you hope to achieve.
One thing you will want to keep in mind before the purchase of a catamaran is storage. If you intend to store your boat in a marina, you are often charged for two slips due to the beam, or width, of a catamaran versus the standard mono-hull vessel.
Catamarans can be beneficial for those who get seasick because they offer a steadier ride and the ability to have more open air space. Because the living quarters are not inside the hull and under the water’s surface, you have more windows and visibility.
Both sailing and power catamarans are viable options. Also, sailing catamarans can come with back-up power engines for low winds or situations such as docking in a marina.
Catamarans that have twin engines can offer more control and precision than those on a mono-hull vessel. This is good for tight and busy areas or navigating marinas.
Overall, there are plenty of options for you, and they offer many benefits over their mono-hull counterparts.
Click to share...

6 Best Performance Cruising Catamarans (Buyer’s Guide)

As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. We may also earn commissions if you purchase products from other retailers after clicking on a link from our site.
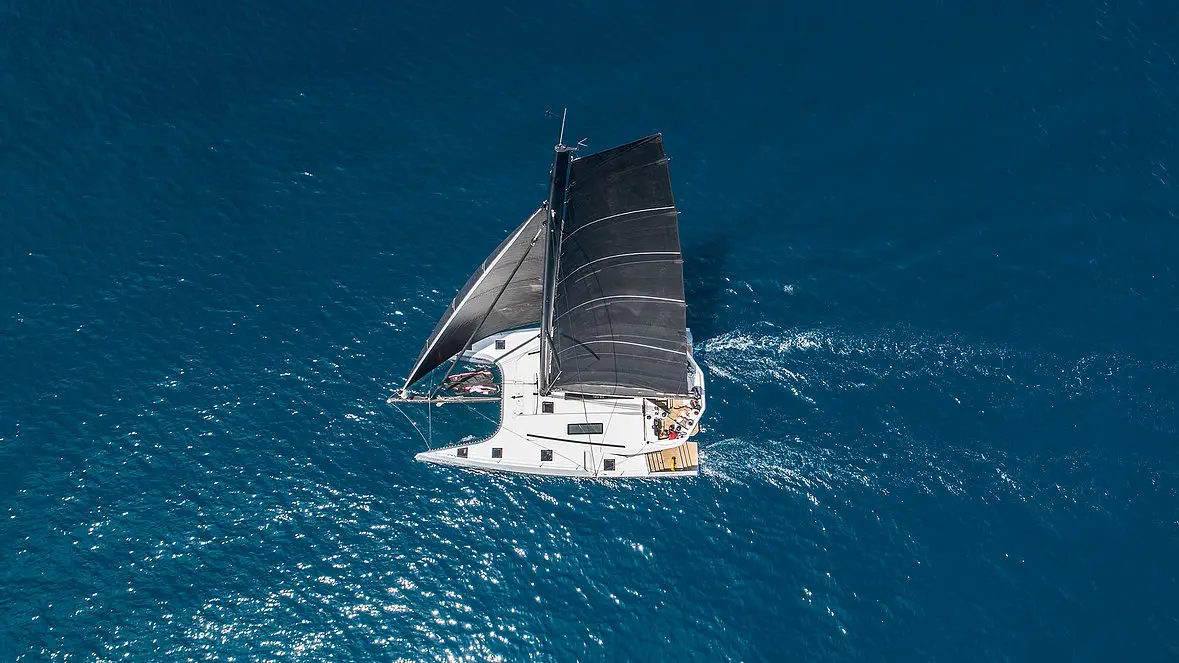
Performance cruising catamarans are impressive-looking vessels that focus on speed above comfort. These fast boats are ideal for racing and long cruising vacations. But with the numerous brands and models on the market, how do you know which is the best one?
The best high-speed performance cruising catamarans are the Outremer 4x, McConaghy MC50, Nautitech 44, Gunboat 62, Balance 526, and Marsaudon Composites ORC50. All these boats deliver outstanding speeds and are light in weight, relatively comfortable, and incredibly safe.
This article will explore the brands and models that I believe have the best combination of performance and comfort . We’ll look at their speeds and what makes them cruise so fast. We’ll also examine the factors to consider when shopping for a performance cruising cat.
Table of Contents
How Fast Are Performance Cruising Catamarans?
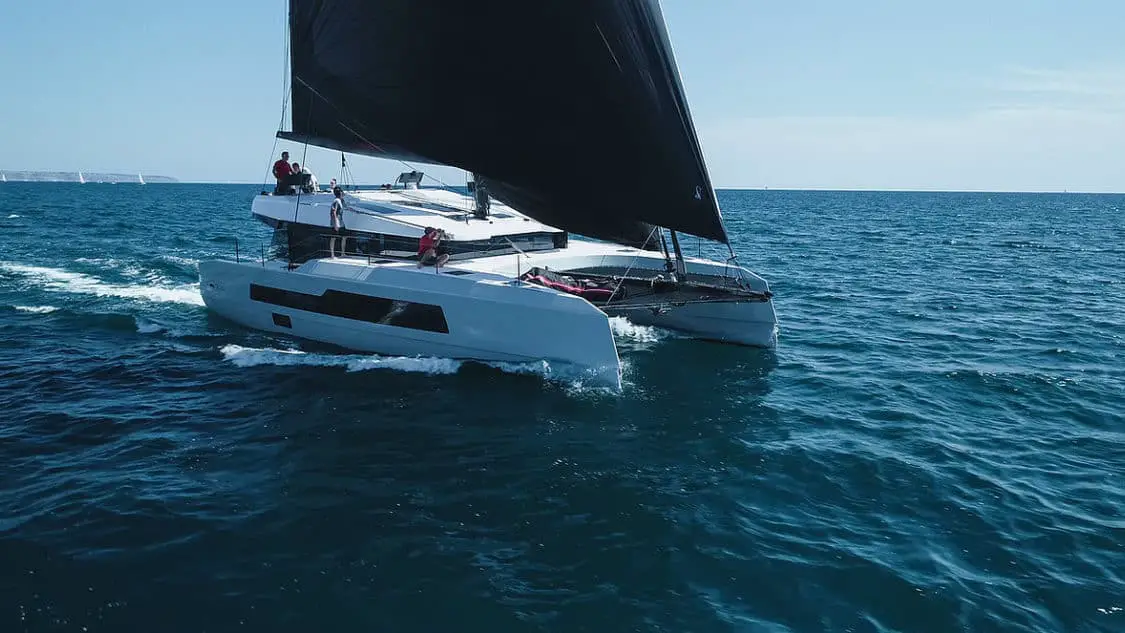
Cruising catamarans are generally faster than monohulls of similar lengths. This means most well-built and well-balanced cats will arrive at their destination much sooner, and the cruise is much more comfortable. Performance cruising cats like the Nautitech include deep daggerboards and rudders, narrow waterline beams, hull chines, and big sail plans that allow for faster sailing than a standard cruising cat.
Outremer 4X
Outremer Catamarans are well-known for their high speeds. These exciting cats sport brilliant designs, narrow bows, and large rigs. Built in Southern France, the vessels are strong and long-lasting since their structures feature materials such as carbon, glass, and vinyl ester.
The Outremer 4x is a stable and comfortable high-speeding cruising catamaran that performs ocean crossings and confronts any weather with remarkable ease. Named the European Boat of the Year in 2017, this 48-foot (14.6 m) bluewater cruiser sails faster than wind speed and attains maximum cruising speeds of 20 knots.
The 4x is an upgrade of the extremely popular Outremer 45, thus retaining Outremer’s core values of speed, safety, and comfort. It’s built for maximum performance and enjoyment, with the lightweight, carbon fiber structure allowing for additional speed under sail .
Featuring comfort typical of much larger vessels, the Outremer 4X features 4 double cabins, hot water showers, a full kitchen, spacious storage, and excellent ventilation. There’s also an expansive deck, an unobstructed cockpit, and large trampoline areas. Most importantly, your safety is assured through the cat’s unique features including a robust structure, offshore design, stability, and unrivaled speed potential.
The 4x’s cutting-edge design makes it ideal for competitive racing or blue water cruising, and it does both without compromising your comfort, safety, or onboard livability. However, to sail at maximum speed, the boat must remain lightweight, requiring your interior to be fitted out quite minimally. The other downside is the high price tag; the Outremer 4X commands a price between $912,322 and $1,202,945 .
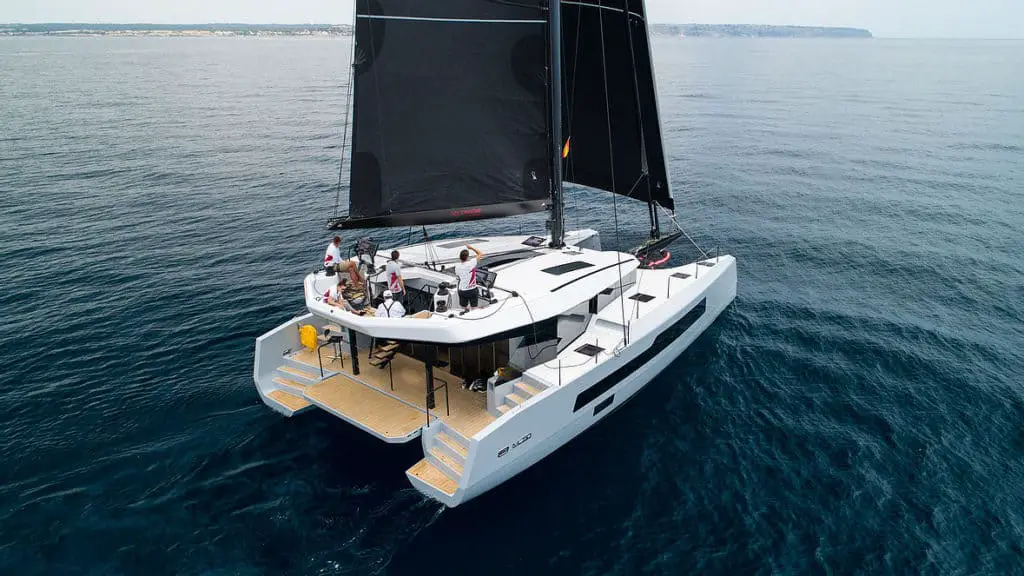

McConaghy MC52
The McConaghy MC52 is a performance luxury cruising cat reflective of McConaghy’s 50 years of experience in building high-tech composite projects. The luxurious boat features a flybridge, retracting centerboards, optimized hulls, and an open space bridgedeck combining the salon with the cockpit. You can also customize the boat to your specifications.

This hi-tech cat comes with sizeable sliding salon windows and frameless doors that provide fantastic views. Its wave-piercing bows can cut through waves, thus helping to increase performance by minimizing pitch resistance, while still retaining a smooth ride. Also, the saloon offers spacious dining space for up to 8 people, and the galley area is more like a penthouse.
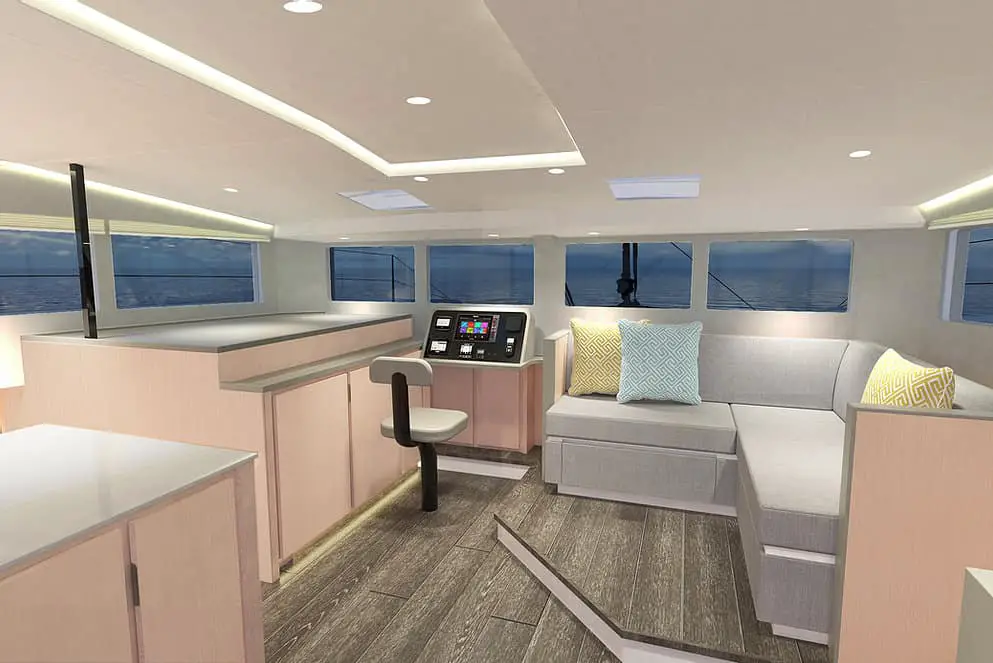

The manufacturer’s background in building high-end racing yachts has resulted in an incredibly strong and lightweight vessel capable of reaching 22 knots (40.7 km/h or 25.29 mph). The main downside to this boat is the boom placement on the mast, which is much higher than other high-performance cats. This makes accessing the mainsail somewhat challenging. It also increases the MC50’s center of gravity and center of effort.
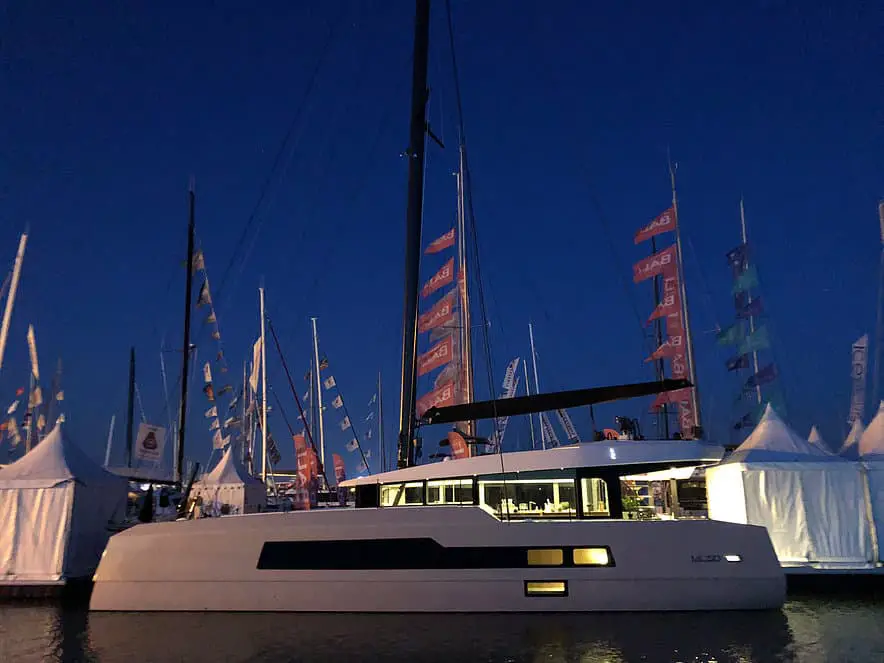

You can get the MC52 for about $1.6 million.
Nautitech 44
The Nautitech 44 easily blends comfort and fun to deliver an impressive sailing performance, whether you take short trips or long ocean crossings. The boat offers a good balance under sail, and it features helming stations on each hull. Plus, there’s an integrated hardtop bimini complete with sunroof opening. Slim hulls translate to higher speeds, with the vessel reaching up to 17 knots (31.4 km/h or 19.51 mph).
The well-laid-out interior boasts a functional design, ample storage space, plus all the equipment you require for ocean cruising, such as a fridge, watermaker, and solar.
Nautitech 44’s twin helms give you the real sailing experience with a fantastic view of the sails and great visibility when maneuvering into port. However, you might not appreciate being stuck in the aft helm position without protection in lousy weather or during hot days.
Nevertheless, the boat’s responsiveness makes sailing more pleasurable. Plus, it’s affordable; the price is between $236,000 and $334,000.
Marsaudon Composites ORC50
Marsaudon Composites vessels are ideal for both racing and cruising. The sporty-looking ORC 50 comes with large inverted bows, an angular coachroof, a high freeboard, and a sturdy rotating carbon mast. In addition, the vessel is light which allows it to accelerate quickly, while the angular coachroof offers lots of space and excellent visibility.
The ORC50 can attain 23+ knots (42.5+ km/h or 26.41+ mph) and is among the fastest high-performance livable multihulls. It’s capable of doing more than 350 miles (563.27 km) per day.
The downside to the ORC50 is it’s a bit technical to sail, thus requiring a skilled sailor. Furthermore, its immense power and speed can be intimidating to less experienced sailors. Solely designed for speed, the ORC50’s interior is simple, less roomy, and somewhat spartan; hence the boat might not be all that comfy. Still, it’ll get you where you want to go pretty fast, and it’s an excellent value for money at approximately $787,751.25.
Gunboat 62
The Gunboat 62 is a true high-speed catamaran capable of sailing at 20 knots (37 km/h or 23 mph) over true wind speeds and known to notch up speeds of 36+ knots (66.7+ km/h or 41.45 mph) on a surf. The initial 3 Gunboat 62 boats featured epoxy, E-glass, and carbon fiber construction, but the fourth vessel was all carbon, sported a taller rig and a more expansive sail area.
These structural features made the Gunboat 62s extremely light, and they formed the original luxury high-performance cruising cats.
This multihull sailboat boasts a carbon mast, round hull sections for a minimized wetted surface area, high-aspect rudders, and retractable daggerboards. The steering station offers 360-degree visibility and sports overhead hatches that you can use to monitor the mainsail trim. The boat also contains 3 private cabins with queen berths, 2 spacious heads with showers, an aft cockpit, galley, and lounge.
On the downside, Gunboats are pricey cats; hence they’re also expensive to maintain. The Gunboat 62 isn’t that spacious either as it’s more focused on speed, but it’s extremely comfortable, plus there’s plenty of space for hanging out. You can buy this catamaran starting from $2 million .
Balance 526
Built with a combination of carbon fiber, E-glass, epoxy, closed-cell foam, and composite bulkheads, this boat is strong, light, and can withstand terrible weather. The retractable daggerboards allow for good upwind performance. All high load areas contain carbon fiber, while furniture and cabinets feature cored sandwich construction, producing the lightest yet most robust catamaran.
A Balance 526 will reach speeds of up to 20knots without stressing the rig too much.
The boat is available in various layouts and comfortably accommodates 6 people. The spacious aft cockpit and saloon provide panoramic visibility. And since Balance 526 can handle the extra weight, you get performance plus all the creature comforts you desire.
Still, Balance 526’s pricing is on the higher end, beginning at $1,440,000 . Also, the slender hulls result in less space down below. Nevertheless, the boat lives up to its name, achieving the perfect balance between superb performance and comfort.
What Makes Performance Cruising Catamarans So Fast?

Performance Cruising Catamarans Have Narrow Hulls
Performance catamarans contain two small narrow hulls, which cause them to have less water resistance. Smaller hulls mean the vessels have much smaller bow waves to fight, allowing them to move extremely fast. In addition, the less hull area is underwater, the faster the boat is capable of moving since there’s less drag.
Having said that, it’s important to note that a narrow hull is more prone to burying its bows in rough seas. The wider the hull, the more buoyancy it offers, but only up to a given point. After which, the excessive width becomes unmanageable and performance suffers. The key lies in finding the right balance.

Performance Cruising Catamarans Have Considerable Length
The longer a cruising cat is, the faster it’ll move. While each vessel bears a maximum hull speed, in most cases, the lengthier the boat, the higher the speed it can reach. The length of the hull (length on the waterline) also has a significant impact on the speed performance. Thus, the cat attains maximum speeds when the wavelength is equal to the length on the waterline (hull speed).
Therefore, the longer the length of the hull, the better the performance of a high-speed cruising cat. You can also compare two cruising cats’ speeds based on this measure.
Performance Cruising Catamarans Have Quality Builds
Modern cat manufacturers continue designing more innovative high-performance cruising cats that deliver a new blend of performance and cruising features. They achieve this by using advanced construction materials, better daggerboard designs, and creative weight allocation. They also keep a keener focus on onboard amenities. For instance, asymmetrical daggerboards placed midships in each hull can help achieve proper balance and hull trim.
The overall goal is to design cruising cats that offer high speeds, outstanding performance, and enough offshore comfort.
Here’s an article if you are wondering what daggerboards and centerboards are and why they impact performance so much.
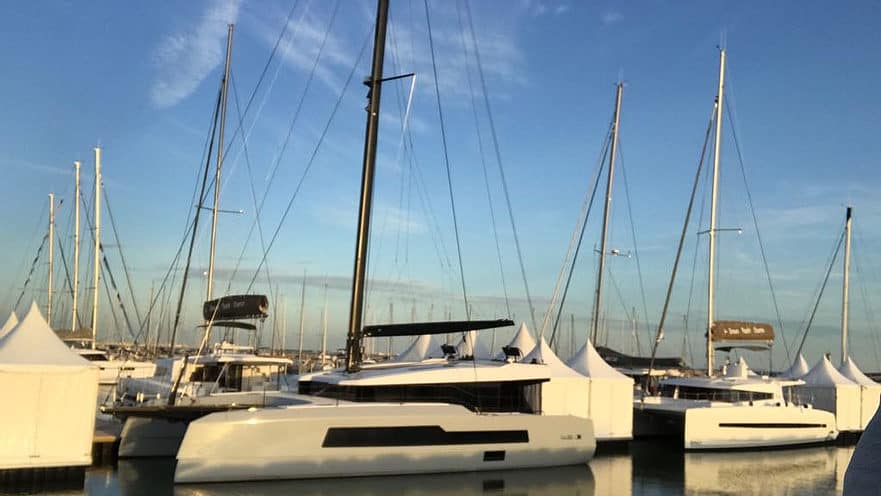

Performance Cruising Catamarans Are Light-weight
The lighter a cruising catamaran, the greater its performance. And some of the most popular high-performance catamarans find an optimal balance between performance and comfort. As a result, modern performance-based cruising cats have embraced the use of carbon composite construction for hulls, daggerboards, and rigging, instead of the somewhat heavier glass fiber materials.
A weighed-down cat produces less speed, which means excess immersion of the hulls renders the boat sluggish . The hull submersion also reduces the bridge deck clearance, promoting uncomfortable hull slamming.
You won’t find much difference in top speed between performance catamarans bearing similar lengths because they all have displacement hulls and mostly sail to hull speed with occasional surfing. This means that under skilled hands, these cats should exhibit roughly the same performance. A cruising cat’s performance is also highly dependent on the state of the sea, wind direction, and speed, amongst many other factors.

What To Consider When Choosing a Performance Cruising Catamaran
Speed is the number one consideration when choosing a high-speed cruising cat. Yet there are other factors just as important since they contribute to the overall cruising performance, including:
- What you’ll use the vessel for and where. Are you planning on doing coastal cruising or serious offshore cruising? Consider the number of people that you’ll be sailing with and the activities you’ll engage in. This also helps determine the size catamaran you’ll need.
- Comfort. While some racing enthusiasts might prefer spartan accommodation plans, most enjoy relative comfort on the high seas. In any case, modern high-speed cruising cats are designed to provide a certain level of creature comforts. And since most performance cats are custom-made, new boat owners may decide precisely which features to include in their cats.
- Quality. To produce light boats, builders employ the use of fine resins, carbon, epoxies, foam cores, and fiberglass. They build using a combination of vacuum-bagged techniques, foam cores, foam composite bulkheads, and make furniture and cabinetry with cored sandwich construction .
- Livability. One cannot underrate the appeal of sailing in a vessel with no heeling, not to mention the high privacy attained from separate living and sleeping areas. Panoramic views and exceptional deck space for lounging and entertaining are also essential in ensuring maximum cruising comfort. Fortunately, most high-speed cruising cats offer all these features and more.
- Equipment. Sailing upwind is a challenge for cruising cats since they tend to make lots of leeway. To make things easier, high-speed cruising cats come equipped with bigger rigs and either daggerboards or centerboards. However, this also means skilled sailors are required to operate them.
- Cost. Catamarans are generally expensive, but a cat built with longer, leaner hulls and less costly materials can still give an outstanding performance. Such materials include foam cores, epoxy bulkheads, and epoxy resins. Furthermore, it’s not necessary to use only carbon to build a lightweight boat.
Final Thoughts
Performance cruising catamarans are built using exotic, high-tech, lightweight materials to deliver an electrifying sailing experience. And as we’ve seen from the above list, these boats deliver performance plus much more. They’re not only speed cruisers, but they also provide a smooth, comfortable, and enjoyable cruising experience.
So, whichever option you go for – from the luxurious Gunboat 62 to the much more affordable Nautitech 44 – you’re sure to get a boat that suits your needs.
- Wikipedia: Spinnaker
- Wikipedia: High-Performance Sailing
- Yachting World: Fountaine Pajot Elba 45 Review
- Aeroyacht: Catamaran Speed
- Cruiser’s Forum: Nautitech 44…
- Nautitech Catamarans: Nautitech
- Katamarans: Marsaudon Composites ORC50 (TS5) Review
- Outremer USA: New Outremer 4x Performance Catamaran
- Dutoit Yacht Design: Balance 526 Review
- Go Downsize: How Fast Do Catamarans Go?
- Catamaran Guru: The Cruising Catamaran Performance Debate
- The Boat App: The Fastest Cruising Catamarans of 2020
- Sail Magazine: Performance Cruising Cats Set New Standards in Sailing Speed
- Cruisers Forum: Fast Cruising Catamarans – How Fast?
- Lagoon – Inside: The Secrets of a Catamaran’s Performance
- Sail Magazine: 10 Great Cruising Cats
- Cruising World: 40 Best Sailing Catamarans and Trimarans, Cruising Catamarans…
Owner of CatamaranFreedom.com. A minimalist that has lived in a caravan in Sweden, 35ft Monohull in the Bahamas, and right now in his self-built Van. He just started the next adventure, to circumnavigate the world on a Catamaran!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Must-Have Boat Gear for Catamaran Sailors!
Sailing is probably the most gear-intensive activity I've ever done; there are so many decisions to be made about what gear to buy now, for tomorrow, and what to definitely never buy. The gear on...
6 Best Trailerable Trimarans For Bluewater and Coastal Sailing
Having a boat costs a lot of money, even when you are not using it, marina fees, etc. And once it is in the water most sailors never go very far from their "home marina" and sailing will be somewhat...
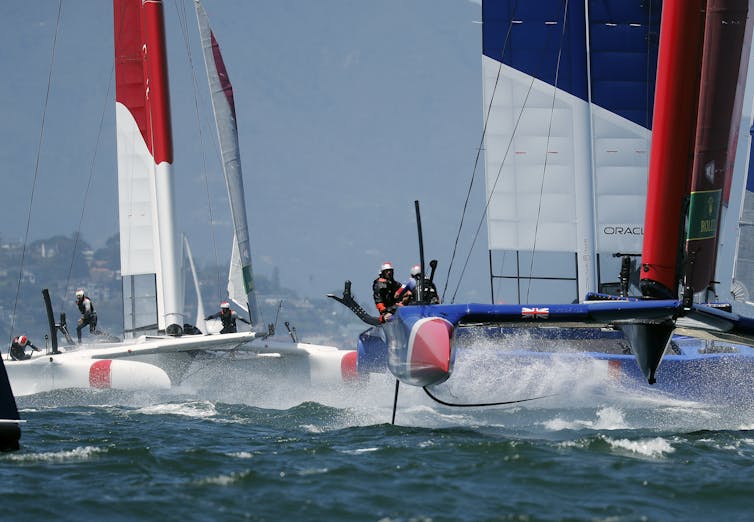
'Bloody scary' but 'a hell of a load of fun': On board the 'mind-blowing' 60 mph F50 catamaran
If you have ever travelled in a car, that most typical of daily tasks, the chances are you will know what moving at 60 miles per hour feels like..
But do you have any idea how it feels to be out on the waves on one of SailGP’s cutting-edge F50 catamarans, hitting nearly 60 mph as the elements do all they can to win this battle of nature vs technology?

For the lucky few, those elite athletes on the SailGP roster, the answer to that question is yes.
But for the rest of us, we can only watch on with envy; we jealously observe, awestruck at the speed of these miraculous creations, and just try to imagine how it feels to fly one of the most revolutionary racing machines ever designed.
Unfortunately, we cannot fulfil that dream of yours – to live first-hand the on-board F50 experience.
We can do the next best thing, however; we can hear from those who have been aboard these remarkable boats as they hit breakneck speeds as part of SailGP’s cutting-edge sail racing league.
Episode two of the new docuseries SailGP: Racing on the Edge in partnership with Rolex focuses on the race to 50 knots, with the athletes involved having their say on this record-breaking achievement.
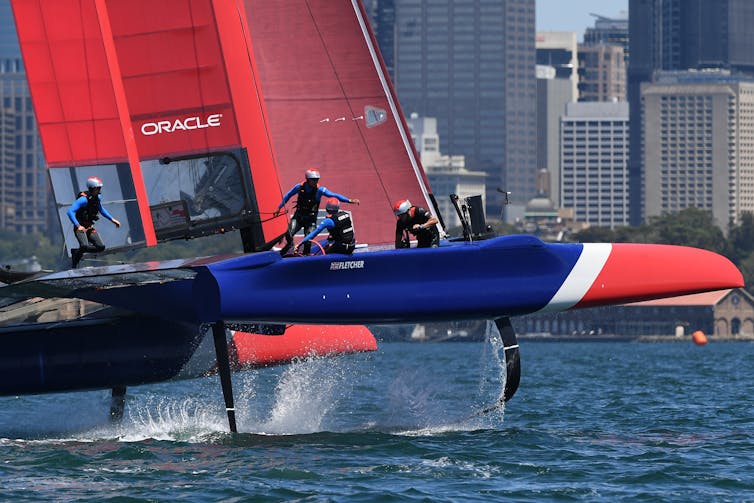
THE F50 CATAMARAN
First things first, let’s take a tour of the F50 and learn just how much goes into flying one of these state of the art creations.
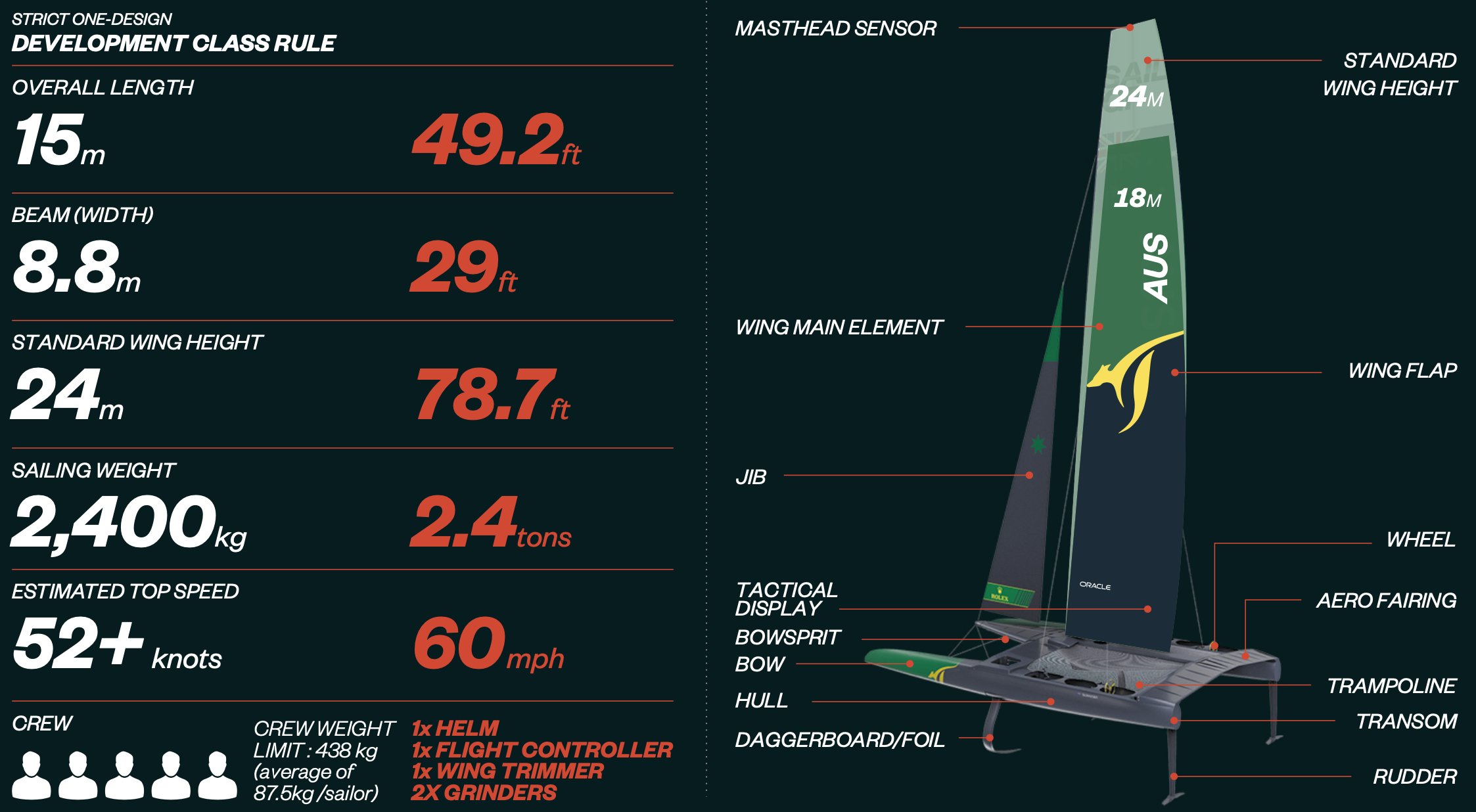
The F50 is a technological marvel, boasting cutting-edge technology to make it a remarkably fast boat in the annals of sailing history. The standard wing is 24m, though it can be altered to suit wind conditions, while the foils are constructed with high modulus carbon fiber and the lower section of the rudders are manufactured using high-strength stainless steel to reduce drag.
Not only is SailGP the most cutting-edge sail racing league in the world, we also strive to accelerate change to a cleaner and more inclusive future through our Race for the Future initiative. The F50s are front and centre of this vision, as they produce thrilling racing at each SailGP event while being Powered by Nature.
BREAKING THE 50-KNOT BARRIER
The F50 has an estimated top speed of 52+ knots (60 mph), and the Australia SailGP Team holds the honour of becoming the first crew to break the 50 knot barrier in sail racing, doing so at Cowes, UK in August 2019.
“I was surprised actually, as I thought the 50 knot barrier would be broken in San Francisco,” says SailGP CEO Sir Russell Coutts in episode two of SailGP: Racing on the Edge . “And then when we got strong winds again in Cowes, I was pretty certain it would be broken.”
All the build-up to Cowes was focused on hitting 50 knots, and the Great Britain SailGP Team managed it in practice - only to later see Tom Slingsby claim the official record as he helmed the Australians to 50 knots while crossing the finish line of the first race.
“We had a day’s practice racing on the Wednesday,” begins Dylan Fletcher, ex-helmsman for the British team. “That was actually my fondest memory of Cowes, because we did two practice races and won both comfortably and there were thousands of spectators who came out to watch.
“To be honest, we nearly pitchpoled the boat on the way in trying to hit 50 knots, but we just did it and hit 50 knots - and we didn’t even realise at the time. We weren't looking at the speedo, we were just heads down, focusing, and holding on for dear life!”
Fletcher certainly made the most of the achievement - by ‘winding everybody up’ in Nathan Outteridge’s words - and he even signed his name on the Brits' F50.
This elicited various responses from the rival teams, including a slightly salty Slingsby.
“We’re sitting here on shore and it’s not really a fair playing field as we’re not allowed to be out there training with them,” says the Australian helm. “They are given all the tools to break it and we are not, so that’s the way I think of it.”
Slingsby and the Aussies got the last laugh though, winning the first race in Cowes and hitting 50 knots to set a new speed record for sail racing - and celebrations were even sweeter as the previously jubilant Brits capsized and coudn’t race again for the remainder of the day!
This was a stark reminder that the F50 can truly reward those who sail it perfectly, but punish those who make even the slightest of errors.
THE F50 EXPERIENCE
When the Australians hit 50 knots in Cowes, the team's F50 was travelling at a remarkable 57.5 mph.
But how did it feel to be on board the F50 as it broke the 50 knot barrier? Slingsby made clear his feelings shortly after the race.
“I was definitely s---ing myself,” said the Australia helm in post-race footage highlighting the incredible achievement.
Phil Robertson, helmsman for Spain SailGP Team in Season 2 , has been similarly forthright with his description of flying an F50.
“It’s bloody scary, to be honest," admitted Robertson.
Saskia Clark, the British Olympian, got her chance on the F50 in the build-up to Sydney SailGP in February 2020.
“It’s mind-blowing,” said Clark of her F50 experience. “When you turn the corners, you feel like your head might fall off and you have to hold it on! When you do the turns up and the tacks it is a totally different sensation.”
The F50 might be ‘mind-blowing’ and ‘bloody scary’, but Sir Ben Ainslie could not contain his excitement at helming one of these technological marvels ahead of his SailGP debut with the British team on Sydney Harbour last year.
“It’s a real privilege to sail these boats,” said Ainslie. “Sometimes you have to pinch yourself. It’s a pretty wild ride, and a hell of a load of fun.”
The second episode of SailGP: Racing on the Edge in partnership with Rolex is available to watch BELOW, as well as on the SailGP YouTube channel and SailGP Facebook page.


The Cruising Catamaran Performance Debate
Which Cruising Catamaran Performs Better…And Does It Really Matter?
A client recently alerted us to a YouTube video posted by a catamaran dealer that is blatantly misleading and inaccurate. If you listen to this dealer, every catamaran manufacturer, other than the Fountaine Pajot brand, is slow, unsafe, not seaworthy and not fit to be a cruising catamaran.
While we agree that the Fountaine Pajot brand is an excellent product (we sell a lot of them), it certainly is not the ONLY good cruising catamaran in the world. There are many products available that are as good and like so many things, when it comes to choosing a cruising boat, it often boils down to personal preference, especially in this category of cruising catamaran.
2022 UPDATE: You will still find some great information below regarding cruising catamarans, especially if you are in the market to buy one. But lots has happened in the Performance Cruising Catamarans category since this post was written a few years ago, like Catana is back in the game with tons of innovation and a fresh new look. In addition to reading this article, be sure to read:
- 2022 Performance Cruising Catamaran Comparison
- We Bought a Performance Cruiser Catana OC 50
Cruising Catamarans Performance
The dealer in the video our client mentioned to us specifically focused on the superior performance of the Fountaine Pajot compared to some of the competing brands in the cruising category like Leopard Catamarans , Nautitech Catamarans , Bali Catamarans , Lagoon Catamarans , and Catana Catamarans .
The fact is that there is very little difference in speed between similarly lengthed cats in this category. All these catamarans are displacement hulls and they pretty much sail to hull speed with intermittent surfing. Therefore, when sailed efficiently, these cats should have very similar performance.
We hear terms such as power-to-weight ratio (sail area to displacement) bandied about a lot by yacht salespeople of the various boat brands as an indicator of performance. While this is definitely a factor and certainly has an effect on acceleration and light wind performance, it is not the only factor. Some catamaran brands will be faster around the cans in a regatta while others will be better when making long passages.
What one should also consider is that when cruising is that a catamaran’s performance will be dictated by sea state as well as wind speed and direction. In light winds, there will probably be a screecher or asymmetrical spinnaker deployed and in strong winds the sails will probably be reefed. This means that in cruising mode, most sail plans are optimized to the conditions. Therefore, when evaluating a cruising catamaran’s performance, there are many factors to be taken into consideration. This is not a simple cut-and-dried argument.
Catamaran Performance Factors & Calculations
To display the different factors and calculations which are relevant when it comes to catamaran performance, we went to Multihull Dynamics for data and pulled some numbers on the two boats most mentioned in this dealer’s video, namely Lagoon and Fountaine Pajot. Here is what we found on the Multihull Dynamics site:

- Base Speed – An empirically derived indicator of the speed a given boat could average over a 24-hour period (best days run) under a variety of conditions. Here again the Lagoon had better numbers with 9.82 knots versus 9.46 knots for the FP Helia 44 – this explains why the Lagoons are so successful on the long Ocean races like the ARC
- KSP – Kelsail Sailing Performance number is a measure of relative speed potential of a boat. It takes into consideration Sail area, Displacement and length at Waterline. The higher the number the higher the speed predicted for the boat. Here the FP Helia 44 at 6.06 had better numbers than the Lagoon 450 which comes in at 6.02 – the Helia is the lighter boat.
- TR – Texel Rating provides a handicap system for widely varying boats sailing together in a race. The formula is essentially the inverse of the Base Speed formula with constants applied to make the results useful. The Texel rating system permits the calculation of time to sail a given distance. Thus a boat with a higher TR can be expected to take longer from start to finish than a boat with a lower TR. The Lagoon 450 came in at 141 versus the FP Helia 44 at 144.
- Interestingly the Leopard 45 came in with better numbers than the Lagoon and the FP as follows: Bruce number – 1.25; Base Speed 10.65; KSP 7.68 and TR 122.
- The numbers for Antares PDQ44 are very similar to the Helia 44 and Lagoon 450.
- Unfortunately there was no data available for the Bali or current Nautitech designs.
*Disclaimer: All data quoted here was derived from Multihull Dynamics. Catamaran Guru offers the details in good faith and does not guarantee or warrant this data.
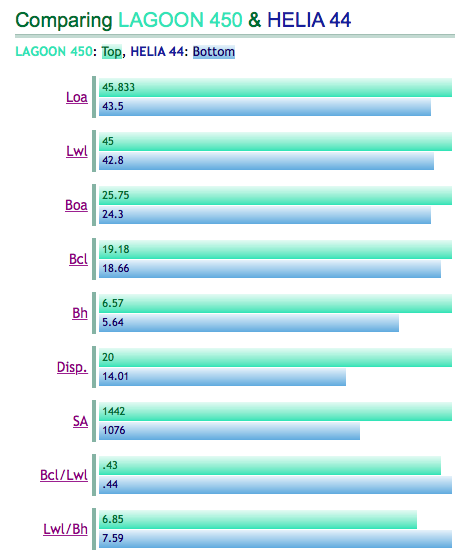
>>Click on the pictures above or go to Multihull Dynamics website for a full explanation of the graphs.

While the Fountaine Pajot dealer touts the superior performance of their brand, actual data shows that the Lagoon brand has won more ARC cruising rallies than any other brand of cruising catamaran. These are hardly the statistics of “just a charter catamaran that sails in 50-mile circles and lacks performance”, as is claimed by this dealer. As an example, check out these ARC and ARC+ rally results in which Lagoon consistently features well:
- Spirit, Lagoon 450 Flybridge – 1st Multihull
- Cat’Leya, Lagoon 52 Sportop – 2nd Multihull
- Sea to Sky, Lagoon 450 – 3rd Multihull
- Dreamcatcher, Lagoon 52 – 4th Multihull
- Sumore, Lagoon 570 – 5th Multihull
- Opptur, Lagoon 500 – 6th Multihull
- Lea, Lagoon 52 – 10th Multihull
- 2015: 380 Havhunden, first in ARC+ Multihulls Division in corrected time
- 2013: 620 Enigma, first in ARC+ Multihulls Division in corrected time
- 2012: 560 Feliz, first in ARC Multihulls Division in real time
- 2011: 560 Blue Ocean, first in ARC Multihulls Division in corrected time & third in ARC Multihulls Division in real time
- 2010: 620 Lady Boubou, first in ARC Multihulls Division & 11th overall in real time
This is NOT an indication of how good or bad one boat over another is, but rather an indication of dealer bias ! We are sure this debate will continue but it is our considered opinion that one should look at the overall boat and not be blinded by issues that might or might not be manufactured by over-zealous sales people. As we have said before, it often comes down to personal preference.
Performance Cruising Catamarans

High-performance cruising cats are becoming more popular and there are a lot more on the market than even just five years ago, but it’s not for everyone, especially if you are not a skilled sailor. Daggerboards and bigger rigs require more skill and are not for the average sailor.
We’ve been racing on and off for years on different catamarans and we’ve always had great fun sailing and surfing at speeds of 15+ knots. But as fun as that is, it can be a white knuckled, wild ride in bad conditions and can leave the crew tired and tense because one has to really pay attention. At these speeds any mistake could be catastrophic since there is so much load on the rig. So, make no mistake, sailing fast in less than good conditions is hard work, particularly when you sail shorthanded.
When only the two of us cruise along on our own boat, we really appreciate the pleasure of gliding through the water at 8-10 knots, relaxed and comfortable. Would we love to be able to coast along at a good clip in very light winds? Sure, we would love to own an Outremer or Catana! But that type of performance cat will cost us probably twice the price of a regular cruising catamaran. Is it worth the money for the average cruiser? Debatable.
With the advancement of technology, more people will eventually be able to sail these performance cats skillfully and will be able to afford them as costs come down but until such time, we believe that the average sailor can very happily sail at fair speed toward their destination, safely and relaxed on an average cruising catamaran as discussed above. The fact is, one or two knots of speed, which is what the difference between these cruising cats MIGHT be, will not make or break your passage.
2020 Update: At the time of writing this article, we owned a Lagoon 450 SporTop , not a rocket ship by any means, but a fair sailing boat. We now own a Bali 5.4 catamaran that is significantly lighter and faster in general as a cruising catamaran and we love the extra speed. However, I have to say that this boat is less comfortable underway than the heavier Lagoon. It is more buoyant, a little more skittish and tend to surf much quicker. So one has to pay more attention in more vigorous conditions. It can be tiring on a long passage, but it sure is fun!
Stephen says, “I personally like the Bali because it is a more lively boat and sails very well – when we picked our boat up in France it was completely empty and bobbed like a cork which we were not used to because our Lagoon was a much heavier boat. Since we have now equipped her with all the world cruising equipment as well as big dinghy, etc. she is a little heavier and a lot more comfortable. It is a fact that weight affects performance – the lighter the boat the better performance one can expect. We flew across the Atlantic when we were nice and light but the boat still performs well now that she is at full cruising weight”.
The Bottom Line
So, to conclude this argument, dealers are always somewhat biased about the products that they represent. Manufacturers go to great lengths and spend a lot of money training their dealer networks to be knowledgeable about their products and represent them well with the buying public. They rightfully expect loyalty from their dealers and expect them to present a positive image to the consumer. We all get that. However, when dealers trash and misrepresent their competition with manufactured issues in order to sell their own products, they do a disservice to the buying public and the industry in general.
We want to hear what you have to say! Tell us about performance on your cruising catamaran and also check out our article on why we chose our own catamaran .
Reminder! Check out these fresh updates on performance catamarans:
Contact us if you have any questions regarding catamarans, Fractional Yacht Ownership or our Charter Management Programs .
Estelle Cockcroft
Join our community.
Get the latest on catamaran news, sailing events, buying and selling tips, community happenings, webinars & seminars, and much more!
13 thoughts on “The Cruising Catamaran Performance Debate”
Thanks for a sober writing. I am the owner of the Lagoon 380 Hahunden, and agter with you. I have a spreadsheet with 75 different cruising cat models and the elapsed times in 29 races, and there is not much difference in perforfance. Can send it if uou want. Greetings.
I would like to see that spreadsheet for sure!
I own a Venezia 42′ and if my boat is part of your spreadsheet I would especially love to see it! Could you please send me a copy even if it’s not on there?
To discuss performance and Lagoon or FP in the same sentence is crass. These are not performance Catamarans, purely floating caravans. They have no pretence to performance only cruising capacity, any indicator of performance is purely coincidental.
I own a Privilege 495 and wouldn’t trade it for any other cat.
Hi Jack, I am interested in the performance of your boat. I understand that mini keels decrease performance considerably. Thanks Di
I would like to point out that the data that you use from Multihull Dynamics is completely flawed due to an inaccurate displacement value. Multihull Dynamcis inexplicably lists the Helia at 14 tons, while Fountaine Pajot and your site list the boat at 10.8 tons. This is quite a big difference and skews all the metrics calculated by the site. The Helia is obviously a lighter boat and performance in catamarans starts with weight, so it is undoubted that the Helia will be more lively than the Lagoon. I totally get your point that that does not mean that it will be more comfortable. Second, on the ARC data front: my father sailed twice across the same route in the Atlantic in the last 10 years and I’m very familiar with the conditions. The trade winds there tend to be rather lively and in those conditions weight will matter less. I would expect to see different results in lighter conditions. All that said, the dealer in question is undoubtedly doing their marketing with an agenda.
Hi Ivan, thanks for your input regarding the Helia 44 weight discrepancy. We are aware of this and it holds good for both vessels. You will note that the Helia 44 shows a displacement UNLOADED of 10.8T while the Lagoon 450 shows an UNLOADED displacement of 15T. In order to get accurate performance numbers we assume that Multihull Dynamics have used a number that represents the LOADED weight of both vessels. This means that for the Helia 44 it went from 10.8T to 14.1T (an increase of 3.3T) and in the case of the Lagoon 450, it went from 15T to 20T (an increase of 5T), since it a larger boat overall with more capacity. Based on the above I think we can safely say that we are looking at a fair and accurate comparison. Your input is really appreciated and we are always open to comment and correction to ensure the information we put on the site is accurate and fair.
Thank you for the clarification on displacement.I do see that they have bumped up the Lagoon 450 displacement as well so that’s a fair comparison. I wish they published that clearly because it changes numbers quite a bit as all manufacturers typically post the weight of their boats unloaded.It looks like the Lagoon makes up for the greater weight with a bigger sail area, so that will probably add up to greater effort needed to manage those larger sails but with modern systems, all these things can be managed. Thank you for the clarification and your insight overall.
I think the misconception people have about “performance” catamarans, is that the reason sailors gravitate towards them is not their speed, it is their ability to sail in light air. If you have a catamaran that will sail at windspeed or close to it in 5-8 knots, you’ll actually sail instead of cranking up the diesel. Those true performance catamarans capable of this that also have all the creature comforts of the Helia/Elba45 or Lagoon450/46, are 50+ feet long, and twice the price unfortunately.
You are so right! Well said.
Good article! For me, the weight includes all the stuff you are taking on a month long (or longer) journey (Full fuel +extra cans, 2 sups, dive tanks and compressor, 4 cases of wine…). My opinion is that the performance cats hull design suffers more when loaded to the gills. Ride quality is also very important and is often glossed over by the performance cat advocates.
You are completely right and that was part of strategy when we raced across the Atlantic with the ARC rally. We knew that all the cats would be loaded to the max for the crossing which no doubt makes them less efficient sailing cats. Fortunately on the Bali 5.4 the buoyancy calculations is for a fully spec’d and loaded boat. So we left and sailed like a bat out of hell right off the bat and we were sailing very efficiently, making 200+ NM distances every day. We figured that as the other cats start using their fuel, water and supplies, they would sail a little more efficiently but by then we would be well ahead of the pack, and it worked. We surprised even the very fast performance cats and all the while eight of us onboard were sailing in complete comfort and were eating gourmet meals three times a day! LOL- Of course the TS’s beat us but it is hardly a fair fight. LOL
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts

First-Annual Virgin Islands Boating Exhibition (VIBE)
VIBE – It’s a Destination Boat Show! Join us May 10 – 12 at

BALI Catamarans Unveils The New Bali 5.8 Flagship
CATANA GROUP launches its 14th BALI CATAMARAN model, the BALI 5.8, for the brand’s

Love Stories At Sea…because it’s valentine’s day
Because it’s Valentine’s day, we wanted to celebrate all the couples that we helped

Your Go-To Resource for all your Catamaran Needs!
Check out our brochure to learn about all we have to offer and why
For more than 30 years, we have been a part of the catamaran community and created Catamaran Guru™ to encourage and educate all the aspiring sailing out there. We understand the dream of traveling the world by catamaran and created a one-stop-shop to make that dream a reality for you.

- Stephen & Estelle
- Testimonials
Get Started
- Yacht Sales
- Used Yachts
- Charter Management
- Boat as Business Programs
- Seminars & Events

A Trusted Source For Boating Information Since 2019
A complete catamaran guide.
- Post Written By: Boater Jer
- Published: January 26, 2020
- Updated: November 27, 2020

Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product.
We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end.
Advertisement

There you are, out on the water when a strange craft approaches. Is it a sailboat? It sure looks like one until it turns to face you. That’s when you notice this boat doesn’t have just one hull. It has two hulls and it’s called a catamaran.
Catamarans are unique, and highly stable watercraft. We’ll explore all the ins and outs of sailing the waters in one of these weird, and awesome multi-hulled craft. Join me as we explore the wild world of sailing catamarans.
A History Of The Catamaran
It is believed that the first people to use a catamaran design were those living in Australasia.
The succession of boat design in this region was actually very interesting. The beginning of boats in the area was simple, albeit conventional rafts. These were fashioned from logs strewn together with plant fiber lashings such as those formed using bamboo fiber.
Catamaran Evolution
The conventional raft gave way to a minimal raft. This design was basically a conventional raft with two cross beams added in the form of logs. These would be eventually hollowed out to improve buoyancy.

The next step in the evolution of boats in the Australasian region was the double canoe. This proved to be the first real catamarans.
After some time, the form evolved further into the asymmetrical double canoe design. In this design, one canoe was large and the other attached canoe was smaller.
The asymmetrical design quickly evolved into the single-outrigger boat like the one shown in the photo below.
The final stage of the evolution of the catamaran in the region was to gain a second outrigger. This in effect created the trimaran with the single central hull and dual outriggers.
Eye Witness Accounts Of Catamarans
In 1697, William Dampier wrote of witnessing a type of seafaring vessel off the coast of Coromandel. He noted how the locals called the type of boat a catamaran. He also noted that it had multiple hulls (logs) and that they were small vessels that the person operating would have to hang partway into the water, straddling the hull (log).
The name catamaran came from the Tamil. And yet, it was easily applied by the European visitors to the two hulled sailing vessels that sped across the water in the region.
Although Dampier may have described the catamaran in the 1690s, the type of boat was actually used as early as the 5th century by the Tamil Chola dynasty. They used boats to move their troops from one island to another. Using this design of boat allowed them to travel heavy, travel quickly and was partially responsible for the conquering of neighboring Burma, Malaysia, and Indonesia.

Building A Boat – Basics Of Catamaran Construction
A boat is usually thought of as being a single-hulled vessel that travels along the surface of the water. It can have multiple types, shapes, and designs of the hull. However, it is often only thought of as having a single hull. But, what if it had two hulls? Would that be like taking two separate boats, and making a raft over both of them? In essence, that is exactly what a catamaran is: two boats made into one.
Advantages Of Multiple Hulls
- More stability than a monohull
- Wide supporting base allows for larger sails than monohull craft of the same length
- Hull does not require the deep-running keel of a standard monohull sailboat
- Less hull drag in the water than a monohull
- Less power required to drive a catamaran forward than a monohull boat
Disadvantages Of Multiple Hulls
- Due to multiple hulls, construction is more expensive than a monohull design
- Catamaran speed relies on lightweight materials to make a lightweight craft. This also drives up the cost of construction.
- Extra engineering requirements for multi-hull craft also increase the cost of construction.
Conclusion? Well, it looks to me like everything about catamarans points towards superiority over monohulls in nearly every way. But, you get what you pay for. I think the same thing likely applies to cars too. For instance, I have a performance car that cost me about 10k more than the equivalent non-sports car within the same class.
Yet to drive the vehicle, it performs so much better than the normal version of the car, it really speaks volumes to the difference between a common vehicle, and a performance one.
Speaking of performance vehicles, let’s take a look now at the different kinds and uses of a catamaran.
Catamaran Types
Commercial catamarans – ferries.
One of the most common uses for a catamaran is the commercial use of the vehicle design when it comes to ferries. This is likely due to the wide, flat deck possibilities of a catamaran versus a monohulled boat. Not only that, but the catamaran is also a much more stable bodied vessel. This again makes it a superior design for transporting larger land vessels like trucks and so forth. They can easily drive on the ferry without fear of the ferry tipping over.
Some ferries are designed for taking vehicles, like the one you might find in the city of Toronto. Where it transports cars from the mainland to Toronto Island. Others are designed specifically with the sole purpose of transporting people. I took a look at one such ferry that operates in Germany. Take a look at the following case study.
Commercial Use Case Study – The Ferry
The FRS Helgoline is a ferry catamaran operating out of Flensburg, Germany, close to the Danish border.

According to the ferry company’s website, the ferry runs using four main engines which are run to a capacity of 12,182 hp combined. This blasts this ferry at a speed of 35 knots or 65 km/hour. This is equivalent to 40 miles per hour. That’s pretty good considering the size and weight of the ship body this catamaran can carry.
Speaking of capacity, the ship can carry 680 passengers. At 56.4 meters long (185 feet) by 14 meters wide (45.9 feet), that’s a decent passenger capacity.
Catamaran Passenger Capacity Versus Monohull Boat Passenger Capacity
The general rule for calculating passenger capacity for a boat is as follows.
Length x Width / 15 = Passenger Capacity
Therefore, the FRS Helgoline should have a calculated capacity calculated as follows.
185 x 45.9 / 15 = 566
But it actually has a capacity of 680 which is a 20% increase in capacity over a standard monohull.

For comparison, let’s look at a superyacht. A 48.5m (159 feet) long by 10.7m (35 feet) beam (width of the boat) Palmer Johnson Supersport 48 (valued at about $28.5 million dollars) should have a capacity calculated as follows.
159 x 35 / 15 = 371
In short, 26 feet of difference in length equates to 309 fewer passengers. It is almost half of the capacity of the catamaran at 26 feet longer length.
Photo courtesy of https://sysyachtsales.com/
Commercial Catamarans – Service Vehicles
Although Catamarans are typically used as ferries due to their stability and ability to carry wide loads on their flat decks, there are many different service catamarans out there as well. From a support vessel to a crew transfer or search and rescue, catamarans are a solid and stable platform to build a ship on.
This is the Ardea which is a 20 meter (65.6 feet) catamaran to be used for crew transport and as a support ship. This ship was built by the Echo Marine Group and delivered to Western Australia in early 2019. This particular vessel is in the service of the Cape Preston Sino Iron Project.
Catamarans are used all around the world, for a variety of tasks, not just ferries or support craft.

Commercial Catamarans – Cruise Lines
Now these are the catamarans we all want to be aboard, aren’t they? Due to the wide stance, these ships can feature massive halls and wide-open interior areas. These ships are stable, and some would say even more stable and safer than monohull design ships.
There are many cruise ship catamarans in use today around the world. Some of the more ‘famous’ catamaran cruises are those which investigate the Galapagos Islands. There are several high-end, small fleet, cruise lines operating to the Galapagos which utilize catamaran design vessels as their primary ship type.
These ships can be extremely comfortable and stable and often offer some reprieve to those who may otherwise feel seasick. It won’t stop the feeling, but the more stable the hull, the less the boat rocks around.
Military Catamarans
Catamarans make excellent military transport vessels. They are stable and the potential to have a large, flat and wide deck for transporting land craft, troops or acting as a landing pad for vertical take-off aerial craft. The stability of the two hulls makes the vessel an excellent candidate for military use, and thus it is used for said purpose.
As you can clearly see in the image of the USNS Spearhead, the rear of the vessel has a moveable ramp that can be used for loading and unloading land vehicles. The interior bay of the craft is visible in the image as well, a large area for storage of vehicles, supplies and more. The crane arm on the back of the ship also shows how it is a versatile craft, set up to act as an excellent support craft with a helicopter landing pad and ample storage and freight capacity.
Recreational Catamarans
Catamaran Personal WatercraftThe wind is in your hair, the warm spray from the hull cutting over the edge of each wave as you skip over the water. That is life, let me tell you. Personal watercraft have come a long way over the years and the small one, two, three and four-person catamarans have come a long way as well.
Depending on the options, you can get a small one or two-person catamaran for as little as $1500 new. That might be an inflatable though. There are some very nice, rigid hull designed catamarans for 1-4 people that range from $3500 to $15000. And these are basically open, personal watercraft like that shown in the image below.
Using a small catamaran can be quite challenging to learn at first. Sailing is not for the faint of heart. It requires skill, technique, knowledge of the wind and sea, and a bit of hard work. But it can be fun, rewarding and a great way to catch some sun and fresh air out on the water. It’s a relatively GREEN sport as well. Given the use of sails over gas-powered motors that is.
‘Sailing Cats’ – Sailing Catamarans – Yacht & Luxury Class
Here’s where we get into the dreamy boats of the rich and famous. I priced out a small 43’ luxury Leopard 40 sailing catamaran. Even before I added any extras at all, the base price was $399,000 USD. I imagine if I added a few of the multiple extras available, and some tax, freight and that sort of thing, I’m easily in half a million dollars. And that’s the smallest base model.

There are all kinds of luxury catamaran shipbuilders across the world. From Asia to Europe and The Americas, it seems any major boating country has at least one company building luxury catamarans. It’s weird that you don’t see more of them on the water though, don’t you think?
Being sailing vessels, these luxury cats require some training in sailing before you get behind the wheel. And considering the price point, I would definitely want to be at least a semi-decent sailor with some good few years experience under my belt before I would comfortable at the helm of a half-million-dollar sailing cat. It’s all relative I suppose. I imagine a billionaire might bat an eye at the prospect of wrecking a half-million-dollar boat. But to me, and most of you reading this, that’s likely a lot of money.
‘Power Cats’ – Powered Catamarans
The powered catamaran is one of my favorite boats. They have sort of a muscle car appearance with the wide and often tall front end of the boats. I find it to be reminiscent of a large air intake on the front hood of a rally race car like the Subaru WRX, for instance. These boats are fast, they are stable and handle very well. Catamarans are often considered the boat of choice for long sea voyages due to their stability.
A powered catamaran will definitely cost more than a powered monohull boat of the same length. Why? Well, the powered catamaran has one crucial downside. That is, it needs two engines. One for each of the two hulls. Otherwise, it’s off balance for propulsion. These two engines or motors have to be in sync with each other or again, the propulsion will be off-balance. Because they have two motors, they have double the maintenance when it comes to maintaining the propulsion system.
More components also means a greater chance of things breaking down. In essence, it doubles the chances of the ship having a motor break down. The saving grace is that should one motor break, they have a backup, even if it does mean very unbalanced propulsion. In contrast, a monohull vessel of the same length may only have half the chance of motor failure due to only having one motor, but if that one motor breaks, then what? Call for help, that’s what. A cat would have a struggling chance to get itself back to port. A monohull would be dead in the water unless it was carrying spare parts or another motor onboard somewhere.
Catamaran Frequently Asked Questions
What is a catamaran cruise.
A catamaran cruise is simply a cruise on a dual hull design boat. Often used for river cruises, the catamaran which is used as cruise ships are often considerably smaller than their giant monohulled counterparts.
What is the purpose of a catamaran?
A catamaran is a design for a boat that utilizes two hulls. Due to the flat, platform-like-potential for the deck of the boat, the catamaran is often purposed with transporting materials, vehicles, and people. For instance, catamarans are quite often used as ferries.
Is catamaran safe?
Catamaran are very safe water craft. The design of riding on two hulls separated by a gap in between, in essence is like giving a car a double-wide wheel base. The wider the stance, the more stable the craft, from side to side anyway. And if the length of the boat is proportional to the width, then it becomes an extremely stable craft. That is why catamarans are often considered the best to be used for long voyages. Yes, catamaran are safe.
What is the difference between a catamaran and a sailboat?
A traditional sailboat is a deep, monohull vessel that has at least one mast extending high into the air above the deck to hold sails. A catamaran refers to the design of a dual-hull boat and really has nothing to do with sails. Although, catamaran do make excellent sailing boats as well, they are quite capable of acting as power boats and do not require sails if they have the correct amount of powered motors to propel them. Sailboats, although also able to be powered if a motor is provided, are traditionally monohull and wind-powered exclusively.
Do catamarans have small interiors?
The size of an interior cabin on a boat is typically proportional to the size of the boat itself. If a catamaran has above-deck cabins, they will likely be able to be of a larger design than those you would find on deck of a monohull boat. This is because a catamaran has a much wider footprint than a monohull boat of the same length. This extra width would allow for larger on deck cabins.
How much does a catamaran cost?
A personal watercraft (1-2 person) inflatable catamaran will run you anywhere from $1500-$12000 USD, depending on the quality and features. The rigid hull catamarans of the same size start at about $4500 USD.

A small cabin cruiser type of catamaran will typically start at about $60000 for a small base model and the price just goes up and up depending on size and features.
For Instance, a 40’, 3 cabin with 1 washroom cat will cost you about $500,000 USD for the base model. They are considerably more expensive that a monohull of the same length. However, the trade-off is greater stability and a smoother, more comfortable ride.
Is a catamaran more work to maintain?
Technically yes. Due to having two hulls and if powered, two motors and likely also water jets, this means you have double the oil changes of a boat that would have a single motor. Once you get past the basic engine and hull maintenance, a catamaran is not that much more work than a monohull ship of the same length.
The trouble with catamarans in terms of maintenance, is that once they reach a certain length, the width becomes more than a standard lane on the road. That being said, if you ever need to transport the boat via land, it can be quite the challenge. Especially if you need to pay to have a police escort for an extra-wide trailer. And special licensing might be involved as well.
What is the difference between a catamaran and a trimaran?
A catamaran is a dual hull boat. In other words, it has two hulls. A trimaran has three hulls.
Is a catamaran considered a yacht?
According to Oxford dictionary, a yacht is a medium-sized sailboat equipped for cruising or racing. A catamaran, on the other hand, is a boat with two hulls. Therefore, a catamaran can most certainly also be a yacht. And likewise, if a yacht has two hulls, then it is a catamaran as well.
Can you get seasick on a catamaran?
Seasickness occurs when a person feels nauseous from the swaying motion of a rocking ship. These feelings may be lessened on a catamaran, due to their extra stability. However, a catamaran may be slightly more stable than a monohull of the same length, but it is still a boat. And it will still make someone who experiences seasickness continue to feel the ill effects.
Are catamarans more stable in rough seas?
Catamarans are known to be more stable than monohull ships of the same length. This is why catamarans are often the ship type of choice for long sea voyages due to their stability.
Why do catamarans capsize?
Catamarans are not known for capsizing. The larger vessels that is anyway. But, it does happen from time to time. Catamarans are known for their stability, so typically if a capsize event should occur, it is typical for them to be extreme circumstances.

Personal watercraft catamarans are a different story though. These are in fact known for tipping over. Not because they are less stable than their monohull counterparts of the same length. But instead, because they are able to go considerably faster than monohull personal watercraft of the same length (not including powered craft though). This is due to the sailing cats being able to have a larger sail than a small monohull sailboat of the same length.
Due to the extra sail, they are able to travel faster than monohull sailboats of the same length. This allows them to whip around on the water and at higher speeds, whipping your cat about quick can easily send it over sideways. Extra speed means fast turns carry momentum in the direction of travel and that extra speed equates to tipping over if turned too fast. To sum up, they capsize due to user error or extreme events.
Which is safer, a catamaran or a monohull?
Due to the extra stability of having a wider footprint than a monohull, a catamaran of the same length is the safer vessel.
Are catamarans safer than sailboats?
The same rule applies to stability versus the length of the hull. A cat will always be the more stable length for length. However, due to their ability to go much faster than a monohull sailboat, this kind of cancels out some of the added safety due to stability. With that in mind, they may just be about the same but there is one generalization we can make when comparing the safety of catamarans vs sailboats: At the same speed, and of equal length, sailing or power catamaran will be safer than a monohull sailboat.
How fast can catamarans go?
The speed a catamaran can go is entirely dependent upon the hull design, weight of the vessel, the strength of propulsion (be it wind or powered) and so on. The general rule is that in terms of sailing cats vs monohull sailboats, a cat of equal length can typically go faster than a sailboat.
In terms of powered cats vs powerboats, a powered catamaran will typically require less energy to move forward than a monohull of the same sort of hull design (but monohull of course) and thus a cat should, in theory, be able to go faster than a monohull when both are using propulsion that is equal in power.
Bibliography
- Wikipedia – Catamarans
- Mahdi, Waruno (1999). “The Dispersal of Austronesian boat forms in the Indian Ocean”. In Blench, Roger; Spriggs, Matthew (eds.). Archaeology and Language III: Artefacts languages, and texts . One World Archaeology. 34 . Routledge. pp. 144–179. ISBN 0415100542 .
- Wikipedia – Spearhead -class expeditionary fast transport
- https://www.tiki-toki.com/timeline/entry/169516/Origin-of-the-catamaran/#vars!panel=1620923!
- https://www.austal.com/ships/passenger-express-56
- https://www.adventure-life.com/galapagos/galapagos-catamaran-cruises
Boating Gear
Take a look at our Recommended page for a variety of items. Here are some of the things you can expect:
- GPS And Fish Trackers
- Hitch And Trailer Supplies
- Lifejackets And Specialty Clothing
- Boating Books And More!

Crab Island by Pontoon: A Fun Watery Boating Guide Destination in 2024

Upgrade Your Boating Experience: Adding a Third Pontoon Made Easy!

How Long Does It Take A Canoe To Go… (Canoe Calculator Here)

In-Depth Review of the Pelican Sentinel 100X Fishing Kayak: Pros, Cons, and Performance

How To Put A Kayak In The Water – The Ultimate Guide For New Kayakers

Best Cruising Catamarans For Couples
More from boating guide magazine.
- Pontoon Boat Basics
- The Complete Runabout Boat & Trailer Towing Guide
- Winterizing Your Boat
- Boating Gear Requirements For Canada And USA Waters
Aluminum vs. Fiberglass Bass Boats
- Better Boating At Night & How To Survive The Darkness
- Staying Safe On A Catamaran: 24 Essential Tips
- Can A Catamaran Capsize?
- 4 Common Types Of Propulsion For Boats
Return To Home * About Boating Guide * About The Author
fakewatches.is

Share this post with your friends
- Tags: boat type , catamaran , catamaran basics , catamaran essentials , sailing
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Join us in our love for all things water. And Adventure.

The Eyoyo Portable Underwater Fish Finder and Camera Review
Advertisement A fishing trip is something that can excite any man (and some women too). You get to enjoy good times outside with your friends. Nevertheless, the pain of being unable to catch any fish may be yet to come. If you’re one such unlucky person, who is having a hard time catching even a

Advertisement As the sun sets over the tranquil waters, the gentle hum of the engine and the soft lapping of waves against the hull create a symphony of serenity. Boating enthusiasts know there’s nothing like being out on the water, surrounded by nature’s beauty. But what if we told you you could take your boating


PowerRay Wizard Underwater Drone – Nothing Short of Awesome.
The PowerRay Wizard Underwater Drone is a feat of technology at a budget price. It’s no wonder this thing won so many awards. Find out how to get yours with extras.

How Much Does A Catamaran Cost? (Big Crazy $$$?)
Advertisement You’ll want to know the Catamaran cost if you find sailing on lakes and fishing exciting. Then, a catamaran boat is your best bet. A catamaran is a watercraft featuring two parallel hulls. The name ‘catamaran’ is from the Tamil word, kattumaram, which means logs bound together looking like the first fishing boat designs.

The Elkton Outdoors Cormorant 2-Person Tandem Inflatable Kayak Review (My First Impressions)
Advertisement I decided to share my tandem inflatable kayak review because I think there is a lack of transparency online about these products. Besides being the most affordable way to explore your favorite fishing spots, kayaking can help improve your mental and physical health. Fortunately, kayak manufacturers understand this, which is why they have produced

Looking for a good article about aluminum versus fiberglass bass boats? Look no further my friend.

Boat Information By Type
© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication.
Privacy Overview
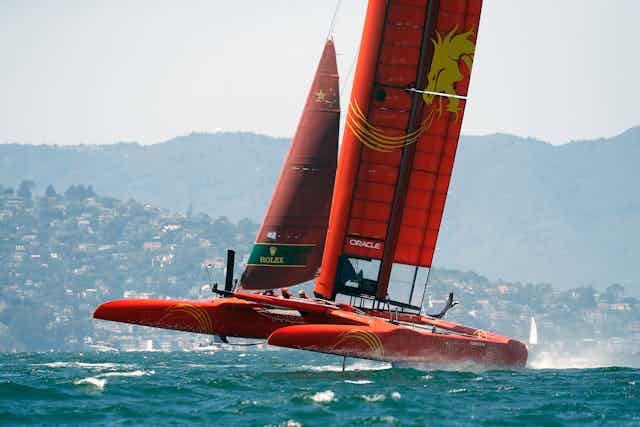

Sail GP: how do supercharged racing yachts go so fast? An engineer explains
Head of Engineering, Warsash School of Maritime Science and Engineering, Solent University
Disclosure statement
Jonathan Ridley does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
View all partners
Sailing used to be considered as a rather sedate pastime. But in the past few years, the world of yacht racing has been revolutionised by the arrival of hydrofoil-supported catamarans, known as “foilers”. These vessels, more akin to high-performance aircraft than yachts, combine the laws of aerodynamics and hydrodynamics to create vessels capable of speeds of up to 50 knots, which is far faster than the wind propelling them.
An F50 catamaran preparing for the Sail GP series recently even broke this barrier, reaching an incredible speed of 50.22 knots (57.8mph) purely powered by the wind. This was achieved in a wind of just 19.3 knots (22.2mph). F50s are 15-metre-long, 8.8-metre-wide hydrofoil catamarans propelled by rigid sails and capable of such astounding speeds that Sail GP has been called the “ Formula One of sailing ”. How are these yachts able to go so fast? The answer lies in some simple fluid dynamics.
As a vessel’s hull moves through the water, there are two primary physical mechanisms that create drag and slow the vessel down. To build a faster boat you have to find ways to overcome the drag force.
The first mechanism is friction. As the water flows past the hull, a microscopic layer of water is effectively attached to the hull and is pulled along with the yacht. A second layer of water then attaches to the first layer, and the sliding or shearing between them creates friction.
On the outside of this is a third layer, which slides over the inner layers creating more friction, and so on. Together, these layers are known as the boundary layer – and it’s the shearing of the boundary layer’s molecules against each other that creates frictional drag.

A yacht also makes waves as it pushes the water around and under the hull from the bow (front) to the stern (back) of the boat. The waves form two distinctive patterns around the yacht (one at each end), known as Kelvin Wave patterns.
These waves, which move at the same speed as the yacht, are very energetic. This creates drag on the boat known as the wave-making drag, which is responsible for around 90% of the total drag. As the yacht accelerates to faster speeds (close to the “hull speed”, explained later), these waves get higher and longer.
These two effects combine to produce a phenomenon known as “ hull speed ”, which is the fastest the boat can travel – and in conventional single-hull yachts it is very slow. A single-hull yacht of the same size as the F50 has a hull speed of around 12 mph.
However, it’s possible to reduce both the frictional and wave-making drag and overcome this hull-speed limit by building a yacht with hydrofoils . Hydrofoils are small, underwater wings. These act in the same way as an aircraft wing, creating a lift force which acts against gravity, lifting our yacht upwards so that the hull is clear of the water.

While an aircraft’s wings are very large, the high density of water compared to air means that we only need very small hydrofoils to produce a lot of the important lift force. A hydrofoil just the size of three A3 sheets of paper, when moving at just 10 mph, can produce enough lift to pick up a large person.
This significantly reduces the surface area and the volume of the boat that is underwater, which cuts the frictional drag and the wave-making drag, respectively. The combined effect is a reduction in the overall drag to a fraction of its original amount, so that the yacht is capable of sailing much faster than it could without hydrofoils.
The other innovation that helps boost the speed of racing yachts is the use of rigid sails . The power available from traditional sails to drive the boat forward is relatively small, limited by the fact that the sail’s forces have to act in equilibrium with a range of other forces, and that fabric sails do not make an ideal shape for creating power. Rigid sails, which are very similar in design to an aircraft wing, form a much more efficient shape than traditional sails, effectively giving the yacht a larger engine and more power.
As the yacht accelerates from the driving force of these sails, it experiences what is known as “ apparent wind ”. Imagine a completely calm day, with no wind. As you walk, you experience a breeze in your face at the same speed that you are walking. If there was a wind blowing too, you would feel a mixture of the real (or “true” wind) and the breeze you have generated.
The two together form the apparent wind, which can be faster than the true wind. If there is enough true wind combined with this apparent wind, then significant force and power can be generated from the sail to propel the yacht, so it can easily sail faster than the wind speed itself.
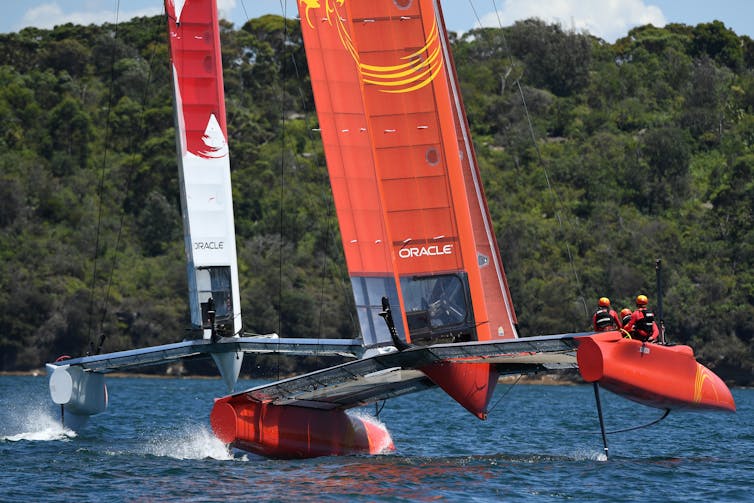

The combined effect of reducing the drag and increasing the driving power results in a yacht that is far faster than those of even a few years ago. But all of this would not be possible without one further advance: materials. In order to be able to “fly”, the yacht must have a low mass, and the hydrofoil itself must be very strong. To achieve the required mass, strength and rigidity using traditional boat-building materials such as wood or aluminium would be very difficult.
This is where modern advanced composite materials such as carbon fibre come in. Production techniques optimising weight, rigidity and strength allow the production of structures that are strong and light enough to produce incredible yachts like the F50.
The engineers who design these high-performance boats (known as naval architects ) are always looking to use new materials and science to get an optimum design. In theory, the F50 should be able to go even faster.
- Engineering
- Aerodynamics

Research Fellow in Tropical Climate Variability

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

Deputy Editor - Technology
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Blistering Speed of SailGP
The catamarans use wings, not sails, and hydrofoils help the boat fly over the water. It’s like a fast video game, with consequences.

By Kimball Livingston
A generation ago, sailing would not, could not have made the short list of team sports played at highway speeds. The boats that most people race are considered fast at nine knots; screaming at 15. That’s about 10 to 17 m.p.h.
Then came the F50 catamaran in 2019, with wings instead of sails and hydrofoils that lift the boats above the friction of the water, reaching speeds beyond 60 m.p.h., as they seemingly fly above the ocean. Indeed, the crew member helping make that happen is called the flight controller, who manipulates the elevations and angles of the left and right hydrofoils centered between bow and stern.
In SailGP lingo, the controller can fly the boat higher or lower. Higher is faster, but riskier because it also gets the boat closer to a nosedive.
The boats also require a new breed of helmsmen — they call themselves drivers — who direct the rapid-fire team choreography in which decisions must be made in fractions of a second.
The wing trimmer, a term from sail trimming days, shapes the wing — an airfoil — for speed and stability. Compared with fabric sails, a wing can provide more stability even while producing more speed. SailGP wings are built from carbon fiber with titanium fittings under a light plastic wrap. The old days of eyeballing sail shape are gone from these boats.
Data from racing and practicing is accumulated and analyzed to determine optimum wing shape for speed in different conditions, and the trimmer uses hydraulic controls to achieve the target settings.
With more moving parts than an airplane wing, an F50 wing has a larger menu of shape settings.
Given more wind, a sailboat tips over farther and farther until it spills wind out of the sails or loses control. Up to a point, SailGP catamarans just keep going faster. The British team hit a record 53.05 knots. or 61.05 m.p.h., during practice last summer.
“Compared to traditional boats, what is striking in SailGP is the complexity of the control systems,” said Nathan Outteridge , a two-time Olympic medalist who drives for the Japanese team. “I should say that driving is pretty easy, until things go wrong.”
Jason Waterhouse , an Olympic medalist who is flight controller for the Australian team, manages the hydrofoils that go up and down at precise angles with precise timing. Get it wrong, and the boat can nosedive.
“I have to have muscle memory,” Waterhouse said about operating the buttons and dials. It’s like a fast video game, with consequences.
Waterhouse also controls the rake, or angle, on the horizontal flaps on the two rudders the driver uses to steer. The flight controller contributes to level flight by dialing in as much as seven degrees of differential rake between the rudder flaps. The flap on the side being pushed down by the wind is angled to push up, and the flap on the opposite side is angled to push down.
“It adds an extra 300-400 kilos [650 to 900 pounds] of righting moment,” Waterhouse said, referring to the forces working to keep the boat from tipping over.
Paul Campbell-James, the wing trimmer for the U.S. team, said that because much of the boat’s hydraulic power was generated by a battery instead of by a crew member turning a grinding pedestal, his team had given that grinder a second job.
“We set up our forward-facing grinder to also be a tactician,” Campbell-James said. The grinder spins the pedestal’s handles to generate power for the hydraulics but also looks for wind shifts.
Wing shape on these boats has taken over most of the trim-in, trim-out of normal sail control, while contributing to level flight. The key is negative camber, shaping the upper wing to pull opposite to the lower wing, countering the forces trying to tip the boat over. Negative camber adds to the effect of the rudder flaps to make for level sailing. Old school it is not.
In turning maneuvers, the crew switches sides and Campbell-James crosses the boat first to take over driving duties before others follow him across. As they come, if he wobbles the helm, the motion could flick his teammates off the deck.
At the same time, he has to keep the boat level in a dynamic turn, press a foot button to raise a hydrofoil, respond as the wing loads up on the new side and hang on against “G-forces that are unbelievable because, remember, you might be going 50 knots. That’s a lot going on.”
Your source for the latest news on yachts, boats and more. Read through our articles to find out how to compare boats and find the right fit for you!
How fast are catamarans
Oct 26, 2020
less than a min

Catamarans are multi-hull vessels composed of two hulls. This geometry allows them to be balanced on water and in turn gain a great deal of speed. Compared to single-hull boats, catamarans are regarded as much faster. But how fast are catamarans actually ?
Catamarans come in various types and sizes. They start from 14 feet up to 100 feet. Each one can reach a different speed limit. Typically, a cruising catamaran sails at 15 knots . A sport cruising catamaran can reach 30 knots . A racing catamaran is somewhat faster and can sail at 45 knots . The power cruising catamaran is probably the fastest vessel and can travel at 70 knots .
One of the main features that make catamarans so fast is the integration of assisting foils that lift the boat off the water. In addition, catamarans are equipped with stability advancements that allow them to gain speed in the ocean.
To better understand how fast catamarans are , they are divided into three groups:
- The sport boats
- The racing ones
- The cruising catamarans
The sport catamarans are recreational vessels designed for a small crew. Their interior is limited as well. Most of them have no living quarters as they are only used for short trips. Some sport catamarans are also used for racing, however, the maximum speed they reach in ideal conditions is 40 knots .
Racing catamarans are used in ocean races and rallies. They are large yachts that can go up to 100 feet and sail at a maximum of 45 knots .
Cruising catamarans on the other hand are more comfortable vessels used for ocean crossing as well. They are equipped with luxurious living quarters. Because of their size, load and volume, these catamarans usually sail at 10 knots , with a maximum speed of 15 knots in ideal conditions.
Some catamarans on the other hand are fitted with powerful motors that favor speed over space. The most common catamaran of this category is the power cruising catamarans . These boats have living quarters and offer the same stability as sailing catamarans. However, the integration of a powerful motor allows these vessels to reach about 70 miles per hour . These catamarans are typically used for passenger travels to shorten the trip between two relatively close destinations such as the mainland and a not-so-remote island.
Power catamarans are also used by the military to transport items. They are particularly on-demand as they can sail in shallow waters as well.
In terms of their performance, catamarans have less resistance to water. Their hulls are smaller so they also have a smaller bow wave created by water displacement to fight. In addition, catamarans only need 4 times the power to double their speed, which is much less power than a monohull would require. Apart from using less energy, catamarans are also good at conserving energy.
Moreover, they are stable and can resist capsizing more than other vessels. They have twin engines that provide more control over speed and stability. Last but not least, catamarans offer smoother voyages and are great for entertainment.
All in all, catamarans can achieve a 30% faster speed than monohulls. Learn more interesting facts about catamarans with TheBoatAPP . Compare these vessels at TheBoatDB . Follow our blog for more interesting facts!
You might like these too

Electric and Hybrid Boats – The Future of Sailing lg ...
Aug 23, 2022

Boat navigation light types and functions lg ...

How Long does it Take to Sail Around the World lg ...
Oct 04, 2021

What are some Fun Things to Bring on a Boat lg ...
Oct 01, 2021

The Proper Term for the Forward End of a Boat lg ...
Sep 30, 2021

Regular Boat Maintenance Tasks You Should Always Do lg ...
Sep 17, 2021

Catamaran Vs. Speedboat (What’s the Difference)
Posted on May 30, 2022

Catamarans are fast, especially long ones. Most of them are even twice as fast as a monohull vessel that is about the same size.
Some cats operate with only sails and then some cats operate with both sail and motor. You have sports, cruising, racing cats, and more. So, is a racing cat or cats, in general, the same as speedboats?
Unlike catamarans that get a lot of assistance from the wind and have two hulls, sowed oats operate only by motors, whether inboard or outboard. Cats require a more hands-on strategy. However, they provide more stability than speed oats. There are also speedboat cats, which outclass the rival monohulls.
We’ll take a look at this and a myriad of other differences as you continue reading.
Catamaran Vs. Speedboat
The catamaran.

A catamaran has two hulls of the exact size that run parallel to each another. Instead of being stabilized by a ballasted keel like a monohull boat, it is a geometry-stabilized craft that relies on its broad width.
For the same length of the boat, catamarans often have a smaller hull capacity, less displacement, and a shallower draft (draught). Because of their lesser hydrodynamic resistance, two-hulled vessels frequently require less propelling power from either their sails or their engines than comparable monohulls.
Compared to a monohull, a catamaran’s wider stance on the water reduces both heeling and wave-induced motion, as well as the wakes it leaves behind.
The Speedboat

A speedboat is a vessel whose propulsion is solely derived from an engine. There are two types of motorboats: those with inboard engines and those with outboard motors put on the back, which include the engine and transmission.
The engine and transmission are located on the outside of the boat, while the propeller and gearbox are housed inside. This configuration is known as an inboard-outboard.
Why Get a Powerboat?
Powerboats are quick, exciting, and roomy all at the same time. Motorboats make it simple to get out on the water, even if you don’t know how to operate one.
With the right boat, you can go tubing, waterskiing, wakeboarding, or fishing with your family. It’s also possible to take a relaxing boat ride around the canals.
Due to the smaller amount of equipment in a sailboat, powerboats often have more deck space. To make things easier for people with large families or who want to take a large number of people out with them, you can carry out more passengers at once.

A motorboat’s galley and stateroom often have greater room. Long-distance offshore fishing expeditions benefit from the extra deck space provided by motorboats, which is why many anglers opt for them. As an added benefit, motorboats can navigate in shallower waters than sailboats because of their shallower hulls.
There is less training involved in operating a powerboat than a sailboat if you’re just getting started in boating. Sailboats require a significant amount of time and practice to become comfortable. A GPS and a boating license are all you need to get started with a motorboat.
To run a speedboat, you must rely solely on the sun’s rays for power. It’s not necessary to wait for ideal wind conditions. Getting up and going whenever you want is completely up to you. When you’re on a boat, you’re not affected by the weather or the tides, unlike when you’re out sailing.
Speedboat Cons
Even though powerboats are simpler to handle and provide more living areas, they are more costly to run. You have to rely on the motor to get about, and it can rapidly amount up to a lot of money. In addition, it consumes more fuel than a catamaran, which is far more eco-friendly.
Powerboat engines are also more pricey. You should plan to pay a lot of money if you need to fix or replace the boat’s engine. This is why it is essential to get your engine checked and maintained regularly.
In addition, the motor itself becomes loud and odorous, which some may argue diminishes the experience of sailing. It doesn’t help seasick folks, but it doesn’t help everyone else either.
Expect to spend more for a powerboat trip and have an excursion that is more centered on the water activities, rather than the pleasure of being on the waterway.
Why Get a Catamaran?

Catamaran cruises are preferred because of their size and stability. We pick the number of individuals we’d want to bring along, and then head out on the lake whenever and wherever we want. On and underneath the deck, a catamaran’s dual hulls plus extra room between them provide greater room for entertaining and relaxing.
Renting a boat is a popular way to spend a holiday , and cats are popular pets. There’s plenty of room for more things and people. Because the two hulls stabilize the boat, it will not heel like a monohull; rather, it sits generally level. Sailing is less tiring since you’re not against gravity.
Catamarans can sail in shallower waters because they use less water to glide than monohulls. Individuals onboard can enjoy greater privacy because of the ship’s two distinct hulls, which are completely independent of one another.
Cons of a Catamaran
The slamming of a low bridgedeck clearance catamaran in choppy seas upwind can be a severe problem. When you first hear this pounding, it can be a little unnerving.
Spreaders on a monohull are angled at 90 degrees to the mast, whereas spreaders on a catamaran must be swept backward . Since the backstay is present on a monohull, the intermediates can be used to create a lovely pre-bend in the mast (the pre-bend is to flatten out the mainsail and allow for better performance).
Due to its wide beam, a catamaran is more difficult to dock , whether temporarily or permanently. This, however, is rapidly transforming and will cease to be an issue shortly. Generally, dockage is billed by the length of the vessel in feet, but this is not the case in the US, where dockage is charged by the length times one and a half because of the greater beam.
Catamaran haulouts are more difficult to obtain a travel lift with a suitable beam, but monohulls have no issues whatsoever. There are fewer facilities that can haul out cats because of their wide beam.
Catamarans have a lot of windage . If you’re trying to fly in tight confines against a strong wind, this could be a problem. However, I’ve discovered that having twin engines negates this issue if the engines are strong enough for the catamaran’s size . Adding a bow thruster is becoming increasingly common on large modern catamarans as well. The docking process is a breeze.
Catamaran boarding is significantly more expensive than monohull boarding . A substantial hole in your cruising fund, or perhaps the need to delay your dream, could result from this. The supply of pre-owned monohulls, on the other hand, greatly outweighs the demand at this time.
High-Speed Catamarans vs V-bottom Speedboats

When go-fast boats first appeared, they were all the same design: a V-bottom monohull with a high deadrise and upward of three engines, based on the vessel’s length as well as beam.
Today’s go-fast boat market provides consumers with more options than ever, and practically any builder that has fast boats for sale may customize them to match particular needs.
High-performance cats are becoming increasingly popular. Catamarans are better able to exploit their horsepower than V-bottoms since they have more air under their hulls and a smaller wetted area.
The greater the surface area that is submerged, the more hydrodynamic drag is generated. As a result of the sticky nature of water, more hydrodynamic drag equals a greater demand on the engine.
Boat engines are subjected to a much harsher load cycle than automotive engines. At 50mph in second gear, imagine driving up a steep hill with a trailer. Every time you run a boat engine, it’s kind of like that.
Because of this, catamarans are the quickest and most powerful high-performance boats available. With the same amount of power, a catamaran will always be quicker than a V-hull boat of the same length. Always.
Over 150 mph is possible on modern offshore catamarans. You can get them with two 1,550-horsepower inboard sterndrives or a phalanx of 450-horsepower outboards lashed to the back. There has never been a better time to be a performance boater.
The emergence of the center console as a high-performance powerboat is one of the Great Recession’s few silver linings. Traditional offshore V-bottoms are being outsold in larger numbers by high-performance boat manufacturers. Some people have completely given up on classic performance boats.
Are Any Fast Boats Fuel-efficient
Sadly, this is not the case. Though catamarans are more economical than V bottoms, no vessel can be considered fuel-efficient. There is good news, though, in that today’s motors are far more environmentally friendly than their ancestors, and hence pollute less.

My Cruiser Life Magazine
Sailing Catamaran Speed
You’ve probably heard that one of the best reasons to get a catamaran is because they’re fast. After all, there’s a race any time there are two sailboats on the same waterway.
But like all things in boating, speed is a relative term. Catamarans seem fast to those coming from slow and heavy monohull sailboats, but cruising catamarans are still pretty slow vessels. There are indeed high-tech racing catamarans breaking speed records all the time. Still, the vessels that most liveaboard cruisers venture out on are only slightly faster than their monohull counterparts.
For this article, we will look at the types of catamarans people live on and cruise on. Forget about those fantastic America’s Cup yachts or those multihull go-fast fishing boats for a few minutes.
I have had experience cruising and living aboard both catamarans and monohulls. For five years, my wife and I enjoyed catamaran sailing on a Lagoon 380. We then switched—for many reasons—to a Cabo Rico 38. The Cabo Rico is a traditionally-designed monohull with a full keel and a heavy displacement. In other words, it’s about as far away from a “speedy” catamaran as one can get.
Table of Contents
How fast can a catamaran go, measuring catamaran speed, catamaran speeds vs monohull speeds, sailing cruising catamarans, performance cruising catamarans, racing catamarans, power cruising catamarans, catamaran top speed, faqs – how fast are catamarans.

There’s no doubt that catamarans are some of the fastest sailboats around—but there’s also a lot of misinformation and misunderstanding online about how fast they really are.
Realize that not all catamarans are created equally. There are cruising catamarans built to carry their passengers in comfort. And then there are racing catamarans built for nothing but speed. Somewhere in between, there is a poorly-defined category of “performance cruising” catamarans that stir passions.
So, are catamarans fast? Well, it’s all relative. But, if you compare them to monohull sailboats of similar sizes and capabilities, the catamarans are usually faster for several reasons.
The speed difference is even harder to measure in the cruising catamaran category. One of the reasons catamarans beat monohulls during races is because they are built light with no ballast. But a heavily-laden cruising cat ready for an ocean crossing is hardly “lightly loaded.” Will it still beat a similarly heavily-laden monohull? Sure! But probably not by as much as you might think.
Boats measure their speed in knots. Traditionally, this was measured by a tool known as a knot log. The modern equivalent is an underwater instrument with a spinning wheel that effectively measures the speed of the water passing over the hull. So long as no currents are present, that speed will equal the boat’s speed over the ground (SOG).
Satellite navigation allows us to measure our SOG more accurately, but this isn’t a great indication of boat performance since it will be affected by tides and ocean currents.
For landlubbers, one knot is equal to about 1.15 statute miles. So, in other words, when we say that a sailboat cruises at 6 knots, it means it’s going about 7 mph.
But before going any further, consider this—the maximum speed that a sailboat makes is generally a pretty meaningless number. Maybe the knot log pegs to 13 knots for a few seconds, thanks to a strong gust of wind while you’re headed down a large swell. Does this mean you’re driving a 13-knot boat?
A voyaging sailor who has made a long passage will have little interest in this sort of number. When you’re crossing oceans, what really matters is how many miles pass under the keel each day. The more miles you tick off, the shorter the passage. So most sailors learn quickly to look past the “fastest speed in knots” number and find real-world stats on passage miles.

Comparing speeds between radically different sailing vessel hulls is like comparing apples to oranges. Even seemingly similar boats, like “cruising sailboats,” the differences between one and the other are endless.
For example, let’s say you wanted to compare 38-foot monohulls to 38-foot catamarans. The speed of a monohull is limited by waterline length, which means you’d have to look at a hull that is significantly more than 38 feet in most cases. On the other hand, the catamaran is known for long swim platforms on inverse transoms and plumb bows—meaning most 38 foot cats have nearly 38 feet of waterline.
Then, what sort of hull design makes a fair comparison to a catamaran? Would it make sense to compare a transitional, salty 38-footer with a full keel? Probably not. Most sailors interested in the cruising catamaran lifestyle would more than likely be comparing it to a modern monohull with a flatter bottom, fin keel, and spade rudder.
What about the catamaran? There’s a lot of variation in the catamaran field regarding performance. If speed is your goal, you likely want to compare the high-end performance brands—Outremer, Gunboat, HH, and the like. These boats are becoming more popular, but most cruising cats you see on the water are not performance models. Instead, they are the big and comfortable cruisers made by Lagoon, Leopard, or Fountaine Pajot.
Finally, how can you fairly compare the stats? Boats sail differently in different wind speeds and at different points of sail. In other words—there are a lot of variables that make it hard to answer the question, “How fast can a catamaran go?”
Polar charts for each vessel can provide some clues to make a somewhat fair comparison. Polar charts are graphical plots of a sailboat’s performance in different wind conditions and at different points of sail. Manufacturers seldom publish since no two are ever perfectly alike. They are less of a boat specification and more of one sailor’s results for a particular boat. Most owners make their own polar diagrams, but they’re still a tool for those looking to get an idea of a model’s performance in the real world.
Speeds of Various Types of Sailing Catamarans
There are several distinct catamaran classes, and predicting speed means understanding what the designers were building the craft to do. You might be surprised to learn that the first “modern” catamarans popped up in the New England racing circles in the late 1800s. Nat Herreshoff’s Amaryllis is particularly famous from the time .
Since then, catamarans have been synonymous with speed. But in today’s world of many different multihull designs, it’s important to set your expectations accordingly. As you would not buy a Ferrari for its cargo space, don’t expect your minivan to win any races at the track.
Examples of cruising cats include popular models made by the big-three catamaran makers—Lagoon, Fountaine Pajot, and Leopard. However, there are dozens of other companies making these boats. The market and industry for cruising catamarans have never been larger.
Most of these boats are engineered to provide comfortable accommodations for voyaging. They first became famous as vessels for sail charter holidays, where their huge cockpits and private cabins made them much more popular than the smaller and cramped monohull options.
As a result, they’re not built with high-tech components or super lightweight performance rigs. Instead, they’re the catamaran equivalent of a Hunter or a Catalina sailboat—mass-produced on an assembly line. That keeps prices lower than other types of catamarans, but it also means that they’re not winning any races. The makers use traditional layups with end-grain balsa-cored fiberglass to keep costs down. In addition, they usually feature stub fin keels, which are foolproof to sail but will not provide the upwind performance of a lift-making daggerboard.
Still, without ballast and when lightly loaded, cruising catamarans can move. They show their colors in light air when heavy displacement-hulled sailboats usually make their poorest showing. Since these moderate conditions also make for great cruising, these boats can provide a lovely ride in smooth weather.
Cruising catamarans can’t plane or anything, but their narrow hulls create an effect that means they can beat the hull speeds of a similarly sized monohull. Of course, it’s not a precise number since every boat and crew is different, but generally, you could expect speeds to be about one and a half times that of a same-sized monohull.

These catamarans are still rigged for comfort, but they’re built using the highest-quality and lightest-weight materials. While their hulls are rigged for comfortable living, they are generally designed much sleeker than regular charter-style cruising catamarans. The hulls are narrower, and you’re unlikely to see tall flybridges or forward lounge seating.
Several companies are making these boats. But in the world of catamarans, a performance cruiser is the upper end of the market. If you want a car comparison, Lagoons are something like a Chevy sedan, whereas an Outremer is like an M-series BMW. A Gunboat would be even more exotic, like a Ferrari. Not only are they more fashionable brands, but they’re also made to higher standards with cutting-edge designs .
It’s also worth noting that the category of “performance cruising cat” is a sliding scale. Some companies make vessels with better materials and craftsmanship than the cruising cats but aren’t designed for speed. Others build cats that are all about performance with few amenities.
With every new model, companies building these cutting-edge boats are attempting to boost the “performance” and the “cruising” aspect of their vessels. As a result, amenities and speed continue to get better and better.
Any racing sailboat is not designed for comfort. Especially on a catamaran, accommodations take up space and weigh the boat down. True racing vessels are designed to not worry about the crew but optimize every element for speed. Once the boat is designed for the desired performance, they’ll squeeze in bunks and storage wherever they can.
As such, there’s not much point in comparing them to liveaboard or cruising sailing vessels—they are too different. Some modern racing catamarans even fly above the water on foils. This makes for a high-speed boat and a considerable risk for sailors traveling for pleasure. Gunboat tried to make a foiling cruising cat in the G4 model, but it didn’t go so well for them.
Power cats run the same gamut of designs that sailing catamarans do. Power catamarans and sport catamarans designs are popular in powerboat circles for the same reasons they are in the sailing world–their hull designs allow for smaller underwater profiles and high speeds. There are many fast catamarans out there with twin engines and average speeds of well over 70 knots. Most recreational vessels cruise at about 20 knots, however.
Power catamarans also offer a smooth ride, making them a popular choice for large vessels like passenger ferries. There are even military vessels that use two hulls, like the stealth M80 Stiletto .
As you can see, catamaran speeds vary from just slightly better than monohulls to extraordinary flying machines. But cats are about much more than just speed. Their open and bright living space makes living aboard an entirely different experience than living on a monohull. Their cockpits flow into their salons for a full-time outdoor living feel that no other type of vessel can match. There are many reasons to choose a catamaran as a liveaboard sailboat.
How fast is a catamaran?
The answer depends on many other questions, like what sort of catamaran is it? And if it’s a sail cat, how fast is the wind blowing?
Sailing catamarans come in all different shapes and sizes. Some are optimized for living space and comfort, while others are designed with fast cruising speeds being the sole goal of the boat. The Gunboat 68, one of the fastest cruising sailboats currently made, can exceed 30 knots.
The world of power cats is much the same. Some power cats can do well over 70 knots, while most cruising boats top out at around 20 knots.
Do catamarans have a hull speed?
A hull speed is a characteristic of traditional displacement-hulled sailing vessels. The properties of the hull shape under the water create drag that limits the overall speed that the vessel can achieve. Even if you keep adding more power (or more wind), the vessel cannot exceed its designed hull speed for any length of time. Hull speed is a factor of waterline length.
Multihulls, however, have an entirely different underwater profile than monohulls. Their narrow hulls and shallow keels mean that drag is not the limiting factor. With this in mind, designers can tweak catamaran hulls to plane and cruise well above the hull speed of a similarly sized monohull.
What is the fastest cruising catamaran?
The market for fast-moving cruising cats has never seen more innovation than in the past decade. This type of boat has taken off, spurred in part by new designs and the overall popularity of multihulls for cruising. The industry leader in fast multihulls is generally considered the French-based company Gunboat . After all, one of the company’s mottos is “Life is too short to sail a slow boat.”
The company’s largest boat to date is the Gunboat 90 Sunshine . However, the delivery of the company’s current flagship, the Gunboat 68 Condor , from France to St. Maarten, provides some real-world numbers. In the delivery crew’s words, “Our max speed exceeded 30 knots a couple of times, and the max 24-hour run was 328 nm.” To save you the math, that works out for an average speed of 13.7 knots for their best day.
Matt has been boating around Florida for over 25 years in everything from small powerboats to large cruising catamarans. He currently lives aboard a 38-foot Cabo Rico sailboat with his wife Lucy and adventure dog Chelsea. Together, they cruise between winters in The Bahamas and summers in the Chesapeake Bay.
Better Sailing

How Fast Do Catamarans Sail? Average Sailing Speed of a Catamaran
In most aspects, sailing a catamaran is very similar to sailing a monohull. If you learn to sail on a monohull then most of the skills are transferable. But, there are a couple of subtle differences that we will analyze further in this article. A catamaran is generally more balanced on the water and can be faster than a multi-hull vessel. And, cruising on a sailboat with a cat hull will be much faster than cruising on a sailboat with a monohull. Therefore, a catamaran hull is able to achieve the speeds of a racing monohull and is also more comfortable to sail on.
A tri-hull is even much better as they’re designed towards the performance end of the spectrum. And that is why they double the speed of a racing monohull. So, let’s analyze this subject further in this article and see what’s the average sailing speed of a cat. Follow me!
Catamaran Vs Monohull Speed: Are Cats Faster than Monohulls?
Not all cruising cats are always faster than an equivalent length monohull. But, many well-designed and balanced multihulls can easily surpass the speed of their monohull cousins. And, it’s not fair to mass all cats into one example, but performance cruising catamarans like the Nautitech or Neel trimarans distinguish from others. Their narrow waterline beams, hull chines, deep and fine keels, and rudders as well as efficient sail plans will typically be faster than the average cruising monohull.
“The fun of sailing is proportional to the speed of sailing”, as an American designer, L. Francis Herreshoff, said. And, it’s basically true because when we sail and see another boat heeling in the breeze, we also feel we want to do the same. This is because for many sailors speed means much more than just fun. You should, however, consider keeping your cat as light as possible if you want to maximize speed. I know that keeping your sailboat light is difficult but it’s of importance if speed is your main goal.
Keep in mind that a boat’s speed has won wars and has also been a contributor to safety. In the past, a fast warship was able to outmaneuver its adversary or escape from a boat with more firepower. And just as proven in history, the speed of a sailboat is important and provides a faster boat with more options.
Monohull VS Catamarans Differences
- When tacking, you must work hard to keep your speed consistent in the tack and always ease the mainsheet to avoid “windvaning.” When the larger mainsail on a catamaran attempts to turn the boat back towards the wind, this is known as windvaning.
- On a monohull, you must be extremely cautious about an unintended gybe. Meaning that you must gybe much more slowly. On a catamaran, you can take advantage of the increased speed and sustain it while gybing to help depower the main.
- On a monohull, and when winds increase, the boat starts heeling. This automatically informs you that you have too much sail up and it’s time to reef. And, as catamarans don’t heel, you have to be very careful when to reef the massive main. Most of the time, you will throw in the first reef at 18-20 knots of wind speed. The second reef will be put as the wind gets closer to 23-25 knots. The above-mentioned always depend on the size and type of your vessel.
Wind as a Main Factor for Speed
Thanks to tech evolutions in radar, satellite, and computer technology, a five-day forecast is as accurate as a two-day forecast was back in 1980. A multihull’s higher speed also contributes to easier and safer planning of ocean passages around weather windows since exposure time will be less. Moreover, meteorological prediction for shorter periods is far more accurate. Keep in mind that when sailing faster you also introduce the concept of apparent wind to the strategy of efficient sailing.
Multihull speed upwind? Sailing upwind, the catamaran usually experiences more apparent wind across the deck since it’s sailing faster. Therefore, the sails will feel more pressure, which will make the boat perform even better. And, of course, the concept of apparent wind contributes to the joy of sailing, as it adds another dimension to it. When sailing towards a downwind destination, fast multihulls are able to sail at smaller wind angles. Subsequently, this brings the apparent wind forward of the beam, hence optimizing the angle of attack on the sails.
While cats will fly gennakers, code-zeros, or asymmetric spinnakers, monohulls mostly set symmetric spinnakers to the poles. And most importantly, their boat speed will often cancel out the true wind and will reduce the apparent wind and performance. The faster the multihull is the more it is able to take advantage of the apparent wind and tack downwind towards its destination. Although it might be sailing twice the distance, it will arrive at the downwind mark quicker because its Velocity Made Good (VMG) will be faster.
>>Also Read: How Fast is a Laser Sailboat? Laser Sailboat Top Speed
Performance Characteristics
Bear in mind that cats require four times the power to double their speed. But, a mono-hull vessel requires eight times the power to double the speed. This is due to the fact that a cat has less resistance in the water. However, this is great in terms of conserving and using less energy. Catamarans are also more stable in the water. This stability is effective at resisting heeling or capsizing. In other words, a multi-hull vessel requires four times the force to capsize as a similar-sized mono-hull vessel.
Most of the time, sailing in a catamaran is smoother and facilitates activities that are not always possible on a mono-hull sailboat. In addition, as catamarans have less water resistance, they are generally faster than mono-hull vessels. As their hulls are smaller, this means that they have a smaller bow wave to fight. The bow wave is a wave created by the displacement of water by the bow of a ship. After a certain speed, the boat has to start hauling itself over its own bow wave. Meaning that the larger hull a boat has, the larger its bow wave will be and the more power will be required in order to fight it.
Since catamarans have two small and narrow hulls, they don’t have much of a bow wave. This is one of the reasons they are normally quicker than a monohull vessel of comparable size. Catamarans can travel at speeds of up to 30% faster than monohull boats. Catamarans have the disadvantage of taking longer to transform than monohulls.
Lastly, the thing that makes monohulls harder to sail is heeling and smaller spaces. In stronger winds, monohulls tend to heel. This results in making most tasks a bit more difficult to perform. Whether you’re heading forward to reef, trying to winch in a sail, or move about the boat, sailing on a heeling boat is always more difficult. However, cats have extra stability and room, and this allows for much easier movement around the boat as they do not heel. And, for this reason, catamarans are often considered easier to sail.
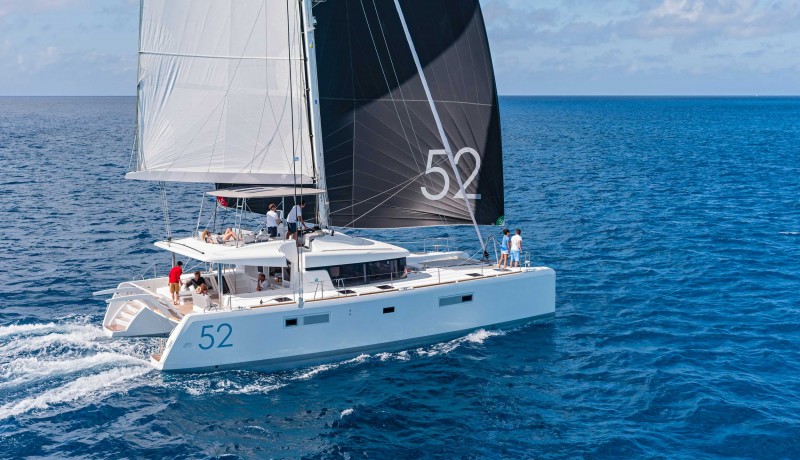

How Fast Are Catamarans Compared To Other Boat Types?
There are two main factors that determine the speed of ships. The first one is the hull type. There are hulls that stay beneath the water more or less than others. But, keep in mind that the less the hull is underwater, the faster it can go. This is due to the fact that the less of the hull underwater, the less the drag created when sailing. The other factor is the length of the boat. And, reasonably, the longer the boat, the faster it can go. Every boat has a maximum hull speed that can’t be exceeded. This can only happen in case the boat can plane on the water’s surface or be lifted on hydrofoils. For most boats, the longer the boat, the higher the maximum hull speed is.
Sailing catamarans typically average about 10 knots while pontoon boats average about 16 knots. As for powerboats, they can average anywhere between 30 and 50 mph. Most average sailboats are designed with monohulls and they average from 6 to 9 knots depending on wind conditions. Generally, sailboats average between 8 and 12 mph, again depending on weather conditions. This includes mono-hull between 6 to 8 mph and cats or trimarans between 9 and 10mph.
Speed and Comfort Considerations For Cats
You have a lot of choices if you choose to buy a catamaran. You have the option of prioritizing speed or comfort. After you’ve decided to buy a catamaran, the type of catamaran you can consider is determined by where you’ll be using it and what you’ll be doing with it. In addition, make sure that you look at what type of water you will be traveling in, your crew members, and what type of speed you want to achieve.
Storage is an important consideration to make before purchasing a catamaran. Due to the beam, or width, of a catamaran versus a regular mono-hull vessel, you are often charged for two slips if you wish to store your boat in a marina. Moreover, catamarans are a great option for those who get seasick because they have a more stable ride and more open air space. You have more windows and visibility since the living quarters are not within the hull and below the water’s surface.
Sailing and power catamarans are both great choices. In addition, for low winds or conditions such as docking in a marina, sailing catamarans may be equipped with backup power engines. Twin-engine catamarans can have more power and precision than mono-hull vessels.
>>Also Read: How Fast Can Sailboats Go?
Main Advantages of Catamarans
- Space! If you want to opt for more interior and exterior space then the two separate hulls of a catamaran can often double the amount of social space than a monohull of the same length.
- Catamarans are far more stable than monohulls. For this reason, they don’t heel when sailing, and are less prone to rocking when at anchor. This factor also contributes to comfortable sailing.
- Catamarans have a shallow draft which allows them to enter shallower areas. Keep in mind that in the South Pacific, most lagoons are 6 to 8 ft in depth. This depth doesn’t allow for monohulls to enter, but a catamaran can easily enter these areas.
- Stability is another big plus of cats. A cat isn’t that susceptible to the effects of wave action and it also doesn’t heal the way a monohull does. Therefore, it’s much easier to walk around on deck and within the interior of the cat while underway.
- In terms of speed, and mostly for downwind sailing , cats are faster than monohulls. This particularly applies to downwind runs, reaches, and broad reaches.
- More light, customizable, and airy living area. On a catamaran, the living space is usually situated in the middle of the boat and built on the bridge deck. But, in a monohull you go down into the hull where it is darker and less airy.
- More storage space and room for extra systems, provisions, and general sailing equipment. These may include air conditioning, heaters, oven, watermakers, generators, larger fridges, and freezers, etc. And, if you’re a liveaboard, then living on a cat is far more comfortable than living in a sailboat. You have more interior, exterior, and storage space as well as stability and speed in terms of sailing performance.
- Many modern cats have flybridge helms. And of course, no monohull achieves this visibility from the helm provided on most modern catamarans.
- The galley, main salon, and cockpit are all located on one level , above the waterline.
- Because the majority of living space is above the waterline , there’s a better flow of ventilation on a cat making the need for air conditioning somewhat less important during the daylight hours.
- When you plan to set sail, you almost never have to rush around stowing stuff or using bungee cords to hold things in place. Except in relatively rough waters, most things stay put.
- Since catamarans lack a large, heavy keel filled with lead, they can float even if they’re holed. Production cats are constructed with so much buoyancy that sinking them is nearly impossible.
- Catamarans are usually easy to dock because you have two motors and two rudders. Additionally, there’s also no need for a bow thruster.
- Most catamarans are able to turn 360 degrees within their own length.
Average Sailing Speed of Catamarans
How fast do catamarans sail – the bottom line.
Bear in mind that not all catamarans are created equal. In other words, catamaran speed is relative. The most important benefit of the speed of a multihull is the ability to outrun bad weather. Meaning that you’re able to average 9-10 knots on a catamaran rather than 6-7 knots on a monohull. Subsequently, this will give you more options in your strategy to avoid bad weather. In general, sailing catamarans typically average about 10 knots. Higher maximum and average speeds are what makes cats distinguish as well as their stability. These are the most important characteristics which makes many sailors prefer cats rather than monohull boats.
Peter is the editor of Better Sailing. He has sailed for countless hours and has maintained his own boats and sailboats for years. After years of trial and error, he decided to start this website to share the knowledge.
Related Posts

Atlantic vs Pacific: Which is More Dangerous for Sailing?

Lagoon Catamaran Review: Are Lagoon Catamarans Good?

Best Inboard Boat Engine Brands

Are O’Day Sailboats Good? A Closer Look at a Classic Brand
- Buyer's Guide
- Destinations
- Maintenance
- Sailing Info
Hit enter to search or ESC to close.
- In the News
- Speed On The Water Videos
- Racing Reports
- Countdown To The 2024 Miami International Boat Show
- Coverage Of The 2023 Lake Of The Ozarks Shootout
- Coverage From The 2023 Key West Poker Run And Offshore World Championships
- Image of the Week
- Safe Boating
- New Products
- Featured Boat
- Latest Projects
- Year in Review Print Magazine
- Subscriber Login/Logout
- Subscribe to SOTW Magazine
- Buy Single Digital Mag Issues
- Magazine Archives
- Magazine Features
- Events Calendar
- Advertising Information
- Article Plaques
- Industry Partners

MTI At 25—Looking Back At Speed Racer
Of all the high-performance “theme boats” that were built in the 2000s, precious few stood the test of time, much less commanded top dollar at resale. That’s because no matter how well-executed—and no builder has been better at creating them than MTI in Wentzville, Mo.,—theme boats are hyper-personal expressions of a given owner’s tastes, sensibilities and imagination. As such, their appeal is inherently limited.

After purchasing Speed Racer in 2009, Bob Christie ran it in an array of poker runs and other go-fast boating events for several seasons. Photos by Tim Sharkey copyright Sharkey Images .
The greatest exception to this, though arguably so of course, is the 44-foot Speed Racer catamaran from Marine Technology Inc. Built for Missouri’s Randy Kent in 2005 (model-year 2006) and painted by Mark Morris at Visual Imagination , the MTI was themed to conjure the popular cartoon series, which was produced in Japan and originally aired in the late 1960s. For boys of the gearhead kind who grew up in that era, Speed Racer was “must-watch” television—to miss an episode was to be out of the adolescent-male loop.
Among those boys was Bob Christie of New Jersey, now a semi-retired businessman who worked on Wall Street and later in book publishing, as well as several other ventures during his long career. In 2009, Christie purchased the 44-footer without engines, though it did have surface drives, from Kent. Christie then tapped Ron Potter of Potter Performance Engines to build him a set of supercharged 1,100-plus-hp engines for the boat and also replaced the cat’s surface drives with Mercury Racing No. 6 units.

For go-fast boating fans of a certain vintage, the Speed Racer theme never got old.
Eventually, Christie stepped up the power to 1,300-plus-hp Potter engines. He also had the cat’s interior expanded from its original four-seat configuration to accommodate six people.
“Randy Scism of MTI flew in and tested the boat to 190 mph,” said Christie, who has owned multiple boats including an MTI 340X catamaran since selling the 44-footer. “He said if she had bigger props she would have topped 200 mph.
“ Speed Racer was my favorite boat,” he continued. “It handled rough water perfectly and cruised at 165 mph all day. My wife, Madelyn, and I have some great memories of that boat.”

Christie eventually upgraded the cat’s supercharged Potter engines from 1,100- to 1,300-plus-hp versions, and the boat became a rocket.
So, too, does this reporter, who Christie let drive in the Atlantic City and Miami Boat Show poker runs, though I’m not sure those count among his finer memories of Speed Racer . (What’s hosing down a boatload of pals behind you on New Jersey’s Barnegat Bay or cutting it a bit too close to a bridge in the Florida Keys among friends?) The catamaran was just one of those boats that made people smile—even those who had never seen the cartoon series that inspired it—when they saw it at the docks.

Though dash layouts have changed dramatically since Speed Racer was built, the boat’s command-center setup was state-of-the-art at the time.
“I’m not sure where she is now,” said Christie, who owned the boat for four years. “But I miss her like crazy.”
Editor’s note : “MTI At 25” is a new weekly series on speedonthewater.com celebrating the company’s 25th anniversary. A new installment will go live every Wednesday on speedonthewater.com through the end of the year.
Related stories MTI Celebrating Silver Anniversary All Year Michel Sells Cloud IX MTI Catamaran Image Of The Week: Happy Halloween From Mini Taylor Scism Scisms Set New Dam Challenge Record Scisms And Millers Plan Dam Challenge Record Attempt As Shootout Fundraiser New Video: In The Lead With Randy Scism Of Marine Technology Inc. Inside SOTW Mag: Women Of Substance—Cherell And Taylor Scism
Featured Boat: 2021 MTI 390X Catamaran
Featured boat: 2015 mti 48 catamaran.


What Is A Catamaran Sailboat? (And What It Looks Like)

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
August 30, 2022
Catamarans are increasingly popular for sailing and commercial use, but what sets them apart from monohulls and other multihulls?
A catamaran is a twin-hull boat with two equally-sized hulls placed side by side. They’re powered by engines, sails, or both—and they’re known for efficiency and speed. Catamarans are the most common kind of multihull boat.
In this article, we’ll go over the characteristics of catamarans and how to differentiate them from other types of boats. Additionally, we’ll cover the advantages and disadvantages of catamarans and compare them to trimarans and monohulls. We’ll also go over the most common types of catamarans and their uses.
We sourced the information in this article from marine design guides, boat identification resources, and the online boating community.
Table of contents
How to Spot a Catamaran
Spotting a catamaran is easy. Simply look at the hulls and count them. Catamarans have two hulls side by side and a relatively large gap between them where you can see light on the other end. Catamarans are distinct from trimarans, which have an additional hull between the two outer hulls.
How do Catamarans Work?
The principle behind the catamaran is simple. You can think of catamarans like cars and monohulls like motorcycles. Catamarans distribute their weight between hulls on either side, whereas monohulls utilize only one hull.
Evidently, cars are much more difficult to tip over and can hold much more weight. Additionally, cars are wider, as they have much more contact with the road. Catamarans work in a similar way, as they have a wide stance and contact with the surface on both sides.
Obviously, that isn’t the most precise comparison. But the basic principle is the same, and catamarans have a few notable benefits over monohulls.
Catamaran Vs Monohull
Catamarans are easy to distinguish from monohulls. A monohull is just a regular old boat with a single hull. The vast majority of boats and ships are monohulls. Catamarans have two hulls, which are usually sleek and narrow.
Here are some comparisons of catamarans and monohulls, along with the advantages twin-hull designs have over most single hull types.
Benefits of Catamarans
Catamarans have numerous benefits. The first is speed. Catamarans produce less drag than monohulls and thus can achieve excessive speeds both under sail and power. They don’t need to plane like monohulls to achieve these high speeds, and they use less fuel.
Catamarans are also much more stable than monohulls. They have a wide stance and shallow draft, and many waves and swells can travel between the hulls instead of below them. This effectively reduces an entire axis of movement and prevents catamarans from rolling excessively.
Drawbacks of Catamarans
Catamarans aren’t advantageous in every way, or else we wouldn’t bother building monohulls. The disadvantages of catamarans limit their use to niche commercial applications and high-end yachts. But what are the drawbacks of a twin-hull design?
Sailing catamarans don’t follow many of the traditional boat handling rules and characteristics that sailors pass down for generations. Some, such as hull speed limitations, are good to do away with—while others, such as responsiveness, are not.
Catamarans aren’t as quick to the helm or responsive as monohulls. There are some exceptions to this rule, but for the most part, you’ll get a lot more feedback from a single-hull vessel. Additionally, the large section of deck between the hulls of a catamaran is prone to pounding in rough seas, which is loud and uncomfortable.
Catamarans can sometimes be twice the width of an equivalent monohull sailboat, which can increase mooring fees and limit docking options.
The final major drawback of catamarans is a consequence of their stability. Traditional full-keel monohull sailboats have a very low center of gravity, which makes them roll in heavy seas but ensures a recovery.
Catamarans have a higher center of gravity, and they can’t right themselves after a knockdown. And though catamarans are less likely to roll, a severe list on a multihull is a much more serious concern than on a ballasted monohull.
Catamaran Vs Trimaran
Catamarans and trimarans are often lumped together, but they have very different design and performance specifications. Trimarans have three hulls, whereas catamarans have two.
Trimarans look a lot like catamarans from the side, but a quick glance at the bow or stern can set them apart. Trimarans are faster than catamarans, as they distribute their weight across three hulls instead of two. This helps them stay centered and reduces interference from pitching and rolling.
Catamarans are fast, but they lose out to trimarans when going head to head. However, catamarans are much less expensive to build and maintain and often have roomier cabins due to their larger hulls.
Types of Catamarans
There are numerous types of catamarans, and their uses vary widely. The catamaran is one of the oldest and most useful hull types, and some variants have been used for thousands of years. Here are the most common kinds of catamaran boats and their uses.
Sailing Catamaran
Sailing catamarans are probably what you think of when you hear the name. Sailing catamarans are sailboats with two identical hulls connected by a center deck. The largest sailing catamarans are spacious and stable vessels that are capable of serious offshore sailing.
Sailing catamarans have a number of notable advantages over monohulls. Monohulls, which are traditional sailboats with a single hull, are limited by a simple concept called hull speed. As the bow and stern wave of a monohull intersect, they cause drag which limits the top speed of the boat.
Catamarans are not bound by hull speed limitations, as they have two hulls. Catamarans can go twice or even three times as fast as similar monohulls and achieve excellent travel times.
Catamarans are also more stable than monohulls, as their wide stance and shallow draft reduce the effect of rough water. They don’t heel, as the force of the wind is counteracted by the double hulls. Additionally, modern sailing catamarans can ‘wave pierce’ by cutting through swells instead of riding over them.
Sailing catamarans come in many shapes and sizes. Small sailing catamarans, such as those used in races and regattas, are known for their speed and relative stability compared to light racing monohulls. Sometimes, they feature a smaller second hull for stability—these are called outriggers.
Sailing catamarans have spacious interiors thanks to the large cockpit between the hulls. This cockpit usually contains cooking and eating spaces, a place to sit, and a hallway between the hulls. The hulls usually contain living quarters and often mirror each other.
Power Catamarans
Power catamarans have an even greater variety than sailing catamarans. These vessels are used for everything from party platforms to ferries and patrol boats.
Power catamarans are a recent development, as engineers and marine architects now realize they have numerous hydrodynamic advantages over other hull types.
Catamarans are much more efficient than other hull types, as they have less drag relative to their size. Additionally, you can build a much larger catamaran with less material. This makes them popular for car and rail ferries, as builders can construct a very wide vessel with two small hulls rather than a narrower vessel with a large single hull.
Military and Commercial Catamarans
Even the military has found a use for the catamaran hull shape. The Spearhead class EPF is an expeditionary fast transport vessel designed for carrying capacity and speed. It has two sharp hulls and a huge cargo capacity.
The Spearhead class EPF is 337 feet long, which is about the same length as a WW2 escort destroyer. Yet despite having a similar length and displacement, these catamarans can travel more than twice as fast—43 knots, or nearly 50 miles per hour. Their great speed is a direct consequence of their catamaran hull type.
Power catamarans are also used as patrol and utility boats on a much smaller scale, with either outboard or inboard motors. The State of Texas uses catamarans to patrol shallow rivers and lakes. Texas Game Wardens utilize state-of-the-art aluminum catamaran patrol boats, which are fast enough to outrun most fishing boats.
There’s another form of power catamaran that you may not have considered. Pontoon boats are technically catamarans, and they’re enormously popular on lakes and rivers throughout the country. Pontoon boats aren’t known for speed, but they’re a great platform for a fun and comfortable outing.
Catamaran Houseboats
The final common type of power catamaran is the two-hulled houseboat. Houseboats don’t always use the catamaran hull type, but it’s common enough that most major manufacturers offer it as an option.
Catamaran houseboats have a few notable advantages over monohull designs. For one, they’re easier to build—especially when pontoons are chosen. Additionally, they’re better suited for navigating shallow water. These vessels can support more weight across their two hulls, offer increased stability, and they’re also efficient.
Why Aren’t Catamarans More Common?
With all the advantages listed in this article to consider, it may seem strange that the use of catamarans is still somewhat limited. At the end of the day, it comes down to economics—as monohull boats and ships are simply cheaper to build.
Additionally, catamarans have some distinct limitations. Monohulls have lots of storage space in their hulls and can carry thousands of tons of cargo safely in all weather conditions. Catamarans lack this space and low center of gravity, so they’re not ideal for transporting cargo past a certain point.
Additionally, monohulls work, and many people are reluctant to experiment with new designs when old designs work just fine. This rule applies to both large and small boats.
A large monohull sailboat can be constructed at low cost from stock plans and reliably sail almost anywhere. Very little complex structural engineering is involved, and looser tolerances reduce cost and maintenance requirements.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Learn About Sailboats
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

Affordable Sailboats You Can Build at Home
September 13, 2023

Best Small Sailboat Ornaments
September 12, 2023

Discover the Magic of Hydrofoil Sailboats
December 11, 2023
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley
June 15, 2022

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
New Zealand wins home leg of SailGP; takes series lead as Australia crashes
New Zealand SailGP Team helmed by Peter Burling leads the fleet at the start of racing on Race Day 2 of the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Chloe Knott/SailGP via AP)
Tom Slingsby, CEO and driver of Australia SailGP Team, looks over the damage sustained to the F50 catamaran after they hit a finish line marker during Race 1 on Race Day 2 of the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Ricardo Pinto/SailGP via AP)
The SailGP F50 catamaran fleet compete on Race Day 2 of the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Ricardo Pinto/SailGP via AP)
The New Zealand SailGP Team helmed by Peter Burling crosses the finish line on the final race and win the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Ricardo Pinto/SailGP via AP)
The New Zealand SailGP Team helmed by Peter Burling crosses the finish line to win the final on Race Day 2 of the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Iain McGregor/SailGP via AP)
New Zealand SailGP Team members spray champagne as they celebrate on the main stage in front of a packed crowd after winning the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Iain McGregor/SailGP via AP)
Peter Burling, Co-CEO and driver of New Zealand SailGP Team, and his crew lift the trophy as they celebrate winning the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Brett Phibbs/SailGP via AP)
New Zealand SailGP Team members hold the trophy during the presentation after winning the final race on Race Day 2 of the ITM New Zealand Sail Grand Prix in Christchurch, New Zealand, Sunday, March 24, 2024. (Chloe Knott/SailGP via AP)
- Copy Link copied
CHRISTCHURCH, New Zealand (AP) — New Zealand won its home leg of the SailGP series on Sunday to take the overall series lead from Australia who collided with a mark in the first fleet race of the day and took no further part in the event.
By winning the ninth leg of the series New Zealand moved one point ahead of Australia in the championship standings with only two events remaining in Bermuda and Halifax before the series final in New York in June.
The latest leg on Lyttelton Harbour near Christchurch on the South Island was condensed to three fleet races before New Zealand, France and Canada raced in the event final. Three fleet races were scheduled for the first day Saturday but none could be sailed because of the presence of endangered dolphins on the race course.
Lyttelton Harbour is a habitat of the endangered Hector’s dolphin and the event protocols prevented racing from taking place if dolphins were sighted on or near the course. No dolphins affected racng on Sunday.
New Zealand, France and Canada each won one of the fleet races sailed Sunday to qualify for the final in which New Zealand beat France by 12 seconds.
Australia sustained damage when it collided with a mark near the start of race one and was unable to continue in the event.
New Zealand sailed cleanly throughout the day, often choosing to race out of phase with the remainder of the fleet to avoid the danger of a collision.
There were multiple collisions in the first race which was won by New Zealand. New Zealand started at the back of field in the second and third races but showed speed to sail through the field into fourth place in the second race won by Canada and second in third race won by France.
The third race was thrilling as several teams vied for a place in the final. Only the top three teams contest the final and the winner is crowned the event champion, taking 10 points in the overall series standings.
France, Canada, Spain and Germany led early in the third race before New Zealand closed into fourth place at the fifth gate and finally moved up into second.
New Zealand won the start in the final and led around the course. Canada was second early but lost ground when it split with the fleet on the third of seven legs.
Racing was watched by more than 22,000 spectators in the viewing area on shore, making the event the largest ticketed sailing event in history.
“It doesn’t get any better than this, a race weekend win at home,” New Zealand wing trimmer Blair Tuke said. “Beautiful conditions, great crowd.
“After yesterday’s disappointment for everyone, we’re so stoked to put on a good show today. We said we’d do it and we’ve done it.”
The race win was the third in succession for New Zealand driver Peter Burling who steered the New Zealand boat into first placings in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. He missed the eighth leg in Sydney due to parental leave and New Zealand finished second in his absence in an event won by Australia.
The SailGP series is in its fourth year and involves 10 teams racing identical high-tech foiling F50 catamarans that can reach speeds of around 50 knots (57 mph).
AP sports: https://apnews.com/sports
Advertisement
The Fastest Fish in the Ocean Can Swim at Nearly 70 MPH
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email

While there are tons of fish in the sea, only a few hold the title of the fastest fish in the ocean. You might wonder how the fastest fish swim at such high speeds.
The key to a fish's speed is a streamlined shape. It's usually fish with a pointed snout and broad, propulsive tail that are able to move through the open with minimal resistance.
So, which fish are the fastest? Let's take a look!
- Atlantic Bluefin Tuna
- Striped Marlin
- Black Marlin
- Fourwing Flying Fish
1. Sailfish
The sailfish stands out as the fastest fish in the world, a title it proudly holds thanks to its remarkable adaptations and evolutionary prowess. In fact, the sailfish can reach top speeds of 68 mph (110 km/h).
Inhabiting the warm waters of the Indian and Pacific oceans, the sailfish features a streamlined shape that epitomizes hydrodynamic efficiency. Its powerful muscles that contract rapidly, propelling it through the water at velocities that top out during short periods of high-speed pursuit.
Fins Fit for Speedy Evasion
What really sets the species apart from other fish are its numerous fins arrayed with precision along its sleek body. The sail-like dorsal fin, from which it derives its name, along with dorsal fins projecting from the back and pectoral fins on the sides, play a crucial role in maneuverability and stability.
Meanwhile, the tail fin and anal fins provide the forward propulsion needed to reach top speeds.
Beneath its sleek exterior, bony spines add to its structural integrity, allowing for bursts of speed that captivate and intrigue marine biologists and enthusiasts alike.
These aquatic speedsters have an alternate use for their sail-like dorsal fin. While it helps them cut through water with minimal resistance, they also sometimes raise it to intimidate predators. Nature loves a multi-tool.
2. Swordfish
Diving deeper into the ocean, the swordfish emerges as another one of the fastest fish out there. The maximum speed of a swordfish is about 60 mph (94 km/h).
Known for its iconic elongated bill, resembling a sword, this species cuts through the water with precision and agility. The swordfish's large, powerful muscles enable quick bursts that propel the fish forward, allowing it to navigate through the water at speeds that leave observers in awe.
Swordfish can withstand particularly cold water temperatures because of a specialized organ located near their brain, known as a countercurrent heat exchange mechanism.
This special organ literally heats their brain and eyes, allowing them to think clearly in colder waters. It also helps them effectively see and hunt their prey.
In tropical and subtropical waters around the world, the wahoo is a name that evokes with speed and agility. This striking fish is celebrated for its ability to reach speeds that make it a formidable predator and a sought-after prize among sport fishermen. The maximum speed for a wahoo is about 48 mph (77 km/h).
The wahoo's slender, torpedo-shaped body is perfectly adapted for high-speed pursuits, allowing it to dart through the water with incredible acceleration. Its streamlined form minimizes drag, enabling the wahoo to slice through the ocean currents as it chases down its prey with ruthless efficiency.
One fascinating feature of the wahoo is its series of sharp, serrated teeth , capable of slicing through its catch (typically smaller fish and squid) with ease.
4. Atlantic Bluefin Tuna
Among the giants of the sea, the Atlantic bluefin tuna commands attention not only for its size but also for its ability to swim faster than many of its oceanic counterparts. In fact, it's the fastest tuna in the world, reaching top speeds of 44 mph (70 km/h).
This species combines brute strength with a hydrodynamic silhouette, and its muscular body is supported by a series of finlets on the dorsal and ventral sides, reducing drag and allowing for swift, efficient movement.
An intriguing aspect of the bluefin tuna is that they must keep swimming in order to get enough oxygen from the water. Like some shark species, Atlantic bluefin tuna must keep swimming forward with their mouth opens to keep their blood oxygenated; they don't have the ability while they're stopped.
Additionally, Atlantic bluefin tunas have a countercurrent exchanger that allows them to regulate body temperature in cooler waters. This allows them to hunt efficiently in cold water, much like swordfish.
5. Mako Shark
The mako shark, found in tropical and temperate waters around the world, is the fastest known species of shark, reaching a maximum speed of 46 mph (74 km/h).
The mako's sleek, streamlined body allows it to chase down swift prey, with its powerful caudal fin, shaped like a crescent moon, acting as a propulsive force. The endothermic system of this species also allows it to maintain a body temperature higher than the surrounding water.
Like the bluefin tuna, the mako shark must keep swimming in order to live. It needs water to constantly pass through its gills to create oxygen for in order to breathe. If make sharks stop swimming, they won't survive.
Additionally, mako sharks can remarkably see in the dark . Unlike many other sharks who rely on electroreception to navigate, the mako uses their smell, hearing and vision. These sharks have light-detecting cells and a tapetum lucidum (like cats!) that helps them to see in the dark. This trait combined with their strong sense of touch, allows them to sense tiny pressure changes and movements in the water.
6. Blue Shark
Gliding through the deep waters of temperate and tropical oceans (the Indian, Pacific and Atlantic ocean), this species can reach a maximum speed of 43 mph (69 km/h). Their speed and stamina allow them to traverse vast distances in their quest for food and mating grounds.
These slender, indigo-colored predators are designed for endurance and speed, with long, lithe bodies that cut through the water with minimal resistance.
Their elongated pectoral fins enable them to maintain stability and maneuver with precision, while their powerful tails provide the propulsion necessary for sudden bursts of speed.
Blue sharks' migratory patterns , which are among the longest in the shark world, reflect their search for food and warm waters. Blue sharks have been known to travel across entire ocean basins, a testament to their stamina, adaptability and efficiency.
7. Bonefish
In the shallow, clear waters where the ocean meets the land, the bonefish emerges as a silent sprinter, known for its ability to reach speeds of 40 mph (64 km/h).
The bonefish's torpedo-shaped body and large, powerful tail fin work in unison to propel it forward with bursts of speed, enabling it to escape predators and navigate through its complex, reef-studded habitats with ease.
Bonefish are capable of surviving in shallow, brackish backwaters because they have a special, lung-like air bladder. Essentially, bonefish can suck in air and then hold onto it, allowing them to breathe comfortably in low-oxygen waters.
You'll likely find them moving with the tide, taking advantage of deep water and increased oxygen at low tide and in the shallower flats during high tide where they can hunt for their food.
8. Striped Marlin
Navigating the tropical and temperate regions of the Indo-Pacific Ocean is the striped marlin. Recognized for its striking appearance and formidable speed (with top speeds reaching 50 mph (80 km/h)), the striped marlin is a creature of beauty and power.
Its sleek, streamlined body — equipped with a distinctive bill and pronounced dorsal fin — combines with a flexible spine, allowing it to propel itself forward at high speeds, making it one of the ocean's most efficient predators.
The striped marlin uses its sharp bill to stun prey, a technique that showcases its intelligence and adaptability. While you might think it would impale its victims, it actually stuns them by slashing sideways .
The marlin's speed, combined with this hunting strategy, makes it a master of the marine environment, capable of capturing a wide variety of prey.
9. Black Marlin
Though experts believe the black marlin's swimming speed is around 30 mph (40 km/h), they are capable of reaching much higher speeds in short bursts. The BBC even recorded one reaching 80 mph (128 km/h)!
This impressive species, with its robust, cylindrical body and spear-like upper jaw, is engineered for speed. The black marlin's powerful tail fin, split into two crescents, acts as a propulsive force. Its sleek physique minimizes drag, allowing the black marlin to dash through the water with remarkable efficiency.
This fish has a reputation as one of the most sought-after game fish. Sport anglers from around the world dream of hooking a black marlin, not just for the thrill of the catch but also for the respect earned from battling such a swift and formidable opponent.
10. Fourwing Flying Fish
Soaring above the surface of subtropical waters of the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, the fourwing flying fish represents hits top speeds of 37 mph (60 km/h) .
This species has evolved not just to swim but to glide over the water, using its uniquely developed pectoral and pelvic fins as wings.
These "four wings" enable the fish to escape predators by making powerful leaps out of the water, propelling themselves through the air at considerable speeds. The streamlined body of the fourwing flying fish reduces drag both in water and air, reaching impressive heights of nearly 4 feet (2 meters).
It can also glide for very long distances, typically up to 650 feet (200 meters). That said, records have shown that they're able to make consecutive glides of up to 1300 feet (400m).
11. Barracuda
Lurking in the shadows of coral reefs and seagrasses, the barracuda is an intimidating presence in the marine world, known for its sharp snouts and the ability to reach speeds of 36 mph (58 km/h) in short bursts.
With a sleek, streamlined body and a robust tail fin, the barracuda is built for rapid acceleration, allowing it to ambush prey. Its elongated body is perfectly adapted for slicing through the water with minimal resistance, and its large, pointed teeth are ideal for seizing and holding onto slippery fish.
That said, barracudas are curious and often misunderstood nature. Despite their fearsome reputation, they are usually not a threat to humans unless provoked.
We created this article in conjunction with AI technology, then made sure it was fact-checked and edited by a HowStuffWorks editor.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Gunboat 68 (+35Kts) Gunboat 68 is a cruising catamaran designed to reach the highest speeds possible. Made by Gunboat, the ship uses Grand-Prix racing boats' designs to develop the speediest cruising catamaran on the market. Gunboat 68 is made entirely from carbon composites, which keeps the ship lightweight and fast.
2) Cruising Catamarans. Another type of sailing catamaran is a cruising catamaran. These often come with complete living accommodations, so they sacrifice speed over their sportier counterparts. They can average between 9 and 10 knots, depending on the conditions. The top speed is typically around 15 knots.
August 30, 2022. Catamarans are known for their speed, and some vessels are fast enough to break world sailing speed records. Catamarans can go between 15 and 30 knots, with the fastest achieving speeds well in excess of 60 knots. Sailing catamarans are sometimes twice as fast as monohulls and cut through the water with greater efficiency.
Onboard sailing footage of the SIG45. The video shows how fast and smooth the boat is. Thanks to her intuitive deck layout and large rudders, she is very eas...
Outremer. Outremer Catamarans is one of the original makers of French performance cats, in business since 1984. According to their website, the company has made over 300 boats since then. A large-scale production boat maker they are not. These are custom-built fast catamarans of the highest quality, made for safety, comfort, and speed.
The Ice Cat 61 is a luxury catamaran. At 61 feet (18.60 meters) long, it is a large catamaran that has been designed with both speed and stability in mind. While its average cruising speed is 12 knots, it can achieve up to 25 knots. The ICE Cat 61 has been designed with carbon and glass fiber - materials that allow the boat to be lighter.
The Gunboat 62 is a true high-speed catamaran capable of sailing at 20 knots (37 km/h or 23 mph) over true wind speeds and known to notch up speeds of 36+ knots (66.7+ km/h or 41.45 mph) on a surf. The initial 3 Gunboat 62 boats featured epoxy, E-glass, and carbon fiber construction, but the fourth vessel was all carbon, sported a taller rig ...
Catamarans aka Tunnel Boats; Offshore V bottoms and catamarans between 35 and 50 feet are the most popular because they are seaworthy. Let's take a deeper look at both of these types of offshore powerboats. Offshore V-Bottom Monohull Speed Boats. The offshore monohull V-bottom is still the quintessential high-performance powerboat.
The F50 catamaran is the technological marvel key to SailGP, the world's most cutting-edge sail racing league ... The F50 has an estimated top speed of 52+ knots (60 mph), and the Australia SailGP Team holds the honour of becoming the first crew to break the 50 knot barrier in sail racing, doing so at Cowes, UK in August 2019.
While the Fountaine Pajot dealer touts the superior performance of their brand, actual data shows that the Lagoon brand has won more ARC cruising rallies than any other brand of cruising catamaran. These are hardly the statistics of "just a charter catamaran that sails in 50-mile circles and lacks performance", as is claimed by this dealer.
How fast can catamarans go? The speed a catamaran can go is entirely dependent upon the hull design, weight of the vessel, the strength of propulsion (be it wind or powered) and so on. The general rule is that in terms of sailing cats vs monohull sailboats, a cat of equal length can typically go faster than a sailboat.
An F50 catamaran preparing for the Sail GP series recently even broke this barrier, reaching an incredible speed of 50.22 knots (57.8mph) purely powered by the wind. This was achieved in a wind of ...
Choosing a catamaran offers increased speed at the expense of reduced load per unit of cost. Howard and Doane describe the following tradeoffs between cruising monohulls and catamarans: A long-distance, offshore cruising monohull may be as short as 30 feet (9.1 m) for a given crew complement and supporting supplies, whereas a cruising catamaran ...
The boats that most people race are considered fast at nine knots; screaming at 15. That's about 10 to 17 m.p.h. Then came the F50 catamaran in 2019, with wings instead of sails and hydrofoils ...
Catamarans come in various types and sizes. They start from 14 feet up to 100 feet. Each one can reach a different speed limit. Typically, a cruising catamaran sails at 15 knots. A sport cruising catamaran can reach 30 knots. A racing catamaran is somewhat faster and can sail at 45 knots.
Catamarans, including ferries or passenger transport, have a top speed of 40 to 70 mph. Military Catamarans. The catamaran hull shape has found application in the military as well. Designed for cargo capacity and speed, the EPF of the Spearhead class is an expeditionary fast transport vehicle (EPF). The ship has two pointed hulls and a large ...
Catamaran Speed Boats. Catamarans like this Outer Limits SC 46 can go even faster than a V-hull with similar power. Photo via Outer limits. Another popular type of high-performance powerboat is the power catamaran. Because they pack air under their hulls and benefit from less wetted area, catamarans capitalize on their horsepower more than V ...
Catamaran boarding is significantly more expensive than monohull boarding. A substantial hole in your cruising fund, or perhaps the need to delay your dream, could result from this. The supply of pre-owned monohulls, on the other hand, greatly outweighs the demand at this time. High-Speed Catamarans vs V-bottom Speedboats
For example, let's say you wanted to compare 38-foot monohulls to 38-foot catamarans. The speed of a monohull is limited by waterline length, which means you'd have to look at a hull that is significantly more than 38 feet in most cases. On the other hand, the catamaran is known for long swim platforms on inverse transoms and plumb bows ...
The most important benefit of the speed of a multihull is the ability to outrun bad weather. Meaning that you're able to average 9-10 knots on a catamaran rather than 6-7 knots on a monohull. Subsequently, this will give you more options in your strategy to avoid bad weather. In general, sailing catamarans typically average about 10 knots.
Editor's note: "MTI At 25" is a new weekly series on speedonthewater.com celebrating the company's 25th anniversary. A new installment will go live every Wednesday on speedonthewater.com through the end of the year. Few if any high-performance theme-boats have stood the test of time better than Speed Racer, a 44-foot MTI catamaran built ...
A catamaran is a twin-hull boat with two equally-sized hulls placed side by side. They're powered by engines, sails, or both—and they're known for efficiency and speed. Catamarans are the most common kind of multihull boat. In this article, we'll go over the characteristics of catamarans and how to differentiate them from other types of ...
The calculations for a catamaran are more complicated. The formula for catamaran hull speed is 1.34*(wetted length)1/2; however, this drag formula is generally not the limiting factor for catamaran hull speed. This is because boats with waterline length to beam ratios greater than 8:1 are not limited by hydrodynamic drag factors, whereas smaller boats need to plane to do so (planing requires ...
New Zealand started at the back of field in the second and third races but showed speed to sail through the field into fourth place in the second race won by Canada and second in third race won by France. ... The SailGP series is in its fourth year and involves 10 teams racing identical high-tech foiling F50 catamarans that can reach speeds of ...
The mako shark, found in tropical and temperate waters around the world, is the fastest known species of shark, reaching a maximum speed of 46 mph (74 km/h). The mako's sleek, streamlined body allows it to chase down swift prey, with its powerful caudal fin, shaped like a crescent moon, acting as a propulsive force.