Save 40% off! Join our newsletter and get 40% off right away!

Sailboat Life
Sailboat Cruising and Lifestyle Magazine.

Sailboat Solar Systems and How-To

Solar on a sailboat goes together like hands and gloves, but sailboat solar systems can be installed in a variety of ways. The solar components themselves create an infinite combination of possibilities for off-grid sailing. Victron Energy chargers, Renogy Panels, Sunpower Yachts, BlueSea Systems, and many more brands have entered the marketplace, and that’s not including the lithium battery companies.
To simplify things, we’ve compiled three sailboat solar systems videos to give you an overview of what’s possible. And to help you decide on your own simple solar panel setup for sailing.
How-To Install Solar Panels on Your Sailboat
This system from Zingaro shows flexible panels summing 300w of power on a 38′ catamaran.
300W Solar System:
- Three 100w solar flexible panels
- 1 MPPT Solar charger controller
View on Amazon >>
100W HQST Flexible Solar Panels $100-$200
20amp Solar Charge Controller by Victron Energy $150-$200

Simple Sunpower Solar System
This simple solar system from The Fosters shows a quick and easy setup with limited space on top of a bimini.
Sunpower Solar Panels are considered by most in the industry as the gold standard. They use the highest-efficiency solar cells and have top-notch build quality. In this simple installation, three 50w panels are just enough to get you started. Plus, it’s the most affordable installation!
150w Starter Solar System
- Three 50w Flexible Solar Panels
- A Single 15amp solar charge controller
50W Sunpower Solar Panels $150-$200
75v/15amp Solar Charge Controller by Victron Energy $100-$124

Off-Grid on a DIY Solar Powered Sailboat
Here’s a special installation that turned a derelict sailboat into an off-grid sailing machine!
Simon has transformed this derelict sailboat into an epic off-grid solar-powered and fossil-fuel-free cruising catamaran. He’s been living aboard and renovating the boat for the past 3.5 years We’re excited to show you the transformation as well as how he plans to propel the boat without the use of diesel or fossil fuels!
5280w Solar System for Electric Powered Catamaran
- 16 Rigid solar panels (330w each)
- 20kwh of Lithium Batteries
240W Rigid Solar Panels $250-$300
200AH Lithium 4d Battery $1200-$1200

Share this post!
Throw in your two cents, start a discussion cancel reply, related articles.

The Voyage of the Sea Star – 35ft Sloop to Bermuda

Living Aboard a 30-36ft Sailboat: A Guide for the Curious and Adventurous

Summer Sailboat Video, Bikinis, Sails, and Fun

Saved Up For This Dream
- BOAT OF THE YEAR
- Newsletters
- Sailboat Reviews
- Boating Safety
- Sailing Totem
- Charter Resources
- Destinations
- Galley Recipes
- Living Aboard
- Sails and Rigging
- Maintenance
Adding Solar Power to a Sailboat
- By Emily Fagan
- Updated: October 18, 2019
During our nearly four-year cruise of Mexico, my husband, Mark, and I lived almost exclusively on 555 watts of solar power charging a 640-amp-hour house battery bank. We anchored out virtually every night aboard our 2008 Hunter 44DS, Groovy , and relied on the sun for power. During one 10-week stretch, while we waited for a replacement engine alternator to arrive, our boat’s solar panels were our sole source of power. We had no backup charging system to turn to, and yet we lived and sailed comfortably the entire time. Mounting solar panels on a sailboat was not difficult, but a few key decisions made a huge difference in how effective our panels were.
A solar-power installation on a sailboat is made up of two independent systems: one system to charge the batteries, and another system to provide 120-volt AC power for household appliances. In the charging system, the solar panels convert sunlight into electrical current and deliver it to the batteries via a solar charge controller. Similar to a voltage regulator, the charge controller acts as a gatekeeper to protect the batteries from receiving more current than they need as they are being charged. In the AC power system, an inverter or inverter/charger converts the 12-volt DC power in the battery into 120 volts AC whenever it is turned on.
Panel Positioning and Wiring Considerations
One of the biggest challenges for sailors installing solar power on a sailboat is finding a place on the boat where the panels will be shaded as little as possible. Just a few square inches of shade on one panel can render that panel all but inoperable. Unfortunately, between the mast, radome, spreaders and boom, shadows cross the deck all day long, especially as the boat swings back and forth at anchor.
What’s worse, if the panels are wired in series rather than in parallel, this little bit of shade can shut down the entire solar-panel array. When we installed solar power on Groovy , we had already lived exclusively on solar power in an RV for over two years. Our RV solar panels had been wired in series, and we had witnessed the array shutting down current production when just half of one panel was shaded.
Choosing whether to wire the panels in series or parallel on a boat affects the wire gauge required, which is why many solar-power installers lean toward wiring the panels in series. Panels wired in series can be wired all the way to the solar charge controller with a thinner-gauge wire than those wired in parallel. This is because the voltage of panels wired in series is additive, while the current remains constant, so the current flowing is just that of a single panel. In contrast, the current flowing from panels that are wired in parallel is additive, while the voltage across them is not. This means that in a parallel installation, the current going to the charge controller is several times higher and requires much thicker cable to avoid any voltage loss over the length of the wire.
Not only is thinner-gauge wire less expensive, but it is also more supple and easier to work with, making the job of snaking it in and around various crevices in the boat and connecting it to the solar charge controller much less of a struggle. Thus the choice between series and parallel wiring boils down to a trade-off between system performance, expense and ease of solar system installation.
Luckily, the size of the wire can be reduced if higher-voltage solar panels are chosen. Since watts are determined by multiplying volts by amps, a higher-voltage panel that generates the same watts as a lower-voltage panel will produce less current. Therefore, selecting nominal 24-volt panels instead of 12-volt panels allows for the use of thinner wire sizes no matter how they are wired.
Our Marine Solar Panel Design Choices
In our installation, we decided to mount three 185-watt, 24-volt (nominal) Kyocera solar panels high above the cockpit, well aft of the boom, as far away as possible from potential shade. Our Hunter came with a big, solid stainless-steel arch, and we turned to Alejandro Ulloa, a brilliant metal fabricator at Baja Naval Boatyard in Ensenada, Mexico, to build a polished stainless-steel solar-panel arch extension onto the existing structure. He designed the arch extension with integrated telescoping davits to hoist our dinghy as well as support the solar panels. These davits were strong enough — and the lines and blocks had enough purchase — that either of us could lift our light Porta-Bote dinghy with its 6-horsepower outboard without a winch.
We spaced the panels about a half-inch apart and wired them in parallel. Using two twin-lead wires, we snaked the three positive leads and one common ground down through the inside of the arch tubes so they wouldn’t be visible, and placed wire loom over the exposed wires under the panels.
The junction points for the three parallel panels were on positive and negative bus bars inside a combiner box, all mounted in a cockpit lazarette. Inside the combiner box, we installed three breakers, one for each panel. This gave us the ability to shut off any or all of the panels if we needed to (we never did).
We mounted a Xantrex solar charge controller (model XW MPPT 60-150) in a hanging locker, as close to the batteries as possible, in a spot where it was easy to monitor and program. We ran twin-lead wire from the combiner box to the charge controller and from there to the batteries.
Our boat came with three new 12-volt Mastervolt 4D AGM house batteries, all wired in parallel, for a total of 480 amp-hours of capacity. We wanted a bigger house battery bank, and because it is best for the age, type and size of the batteries to be matched, we added a fourth new Mastervolt 4D AGM house battery, which brought our total to 640 amp-hours. Our batteries were installed at the lowest point in the hull, below the floorboards, and they ran the length of the saloon, from just forward of the companionway stairs to just aft of the V-berth stateroom door.
The best way to charge a bank of batteries that are wired in parallel is to span the entire battery bank with the leads coming from the charge controller. We did this by connecting the positive lead from the charge controller to the positive terminal of the first battery in the bank, and the negative lead from the charge controller to the negative terminal of the last battery. By spanning the entire bank, the batteries were charged equally rather than having the charging current focused on just the first battery in the bank.
We feel that AGM batteries are superior to wet cell (flooded) batteries because they can be installed in any orientation, don’t require maintenance, can’t spill (even in a capsize), and charge more quickly. Our Mastervolt batteries, like almost all AGM batteries on the market, are dual-purpose, combining the very different characteristics of both deep-cycle and start batteries. Our batteries work well, but if we were doing an installation from scratch today, we would consider the new Trojan Reliant AGM batteries. These batteries are engineered strictly for deep-cycle use and have been optimized to provide consistent current and maximize battery life.
Our boat came with a Xantrex Freedom 2,500-watt inverter/charger wired into the boat’s AC wiring system with a transfer switch. The inverter/charger performed two functions. While the boat was disconnected from shore power, it converted the batteries’ 12-volt DC power into 120-volt AC power, allowing us to operate 120-volt appliances, like our microwave. When the boat was connected to shore power, it charged the batteries.
Because this inverter/charger was a modified-sine-wave inverter, mimicking AC current with a stair-stepped square wave, we also had a 600-watt pure-sine-wave inverter to power our potentially more sensitive electronic devices. We chose Exeltech because its inverters produce an electrical signal that is clean enough to power medical equipment, and they are NASA’s choice for both the Russian and American sides of the International Space Station. For simplicity, rather than wiring the inverter into the cabin’s AC wiring, we plugged ordinary household power strips into the AC outlets on the inverter and plugged our appliances into the power strips. Like the charge controller, the inverter must be located as close to the batteries as possible. Ours was under a settee.
Shade’s Impact on Sailboat Solar Panels
Once our solar installation was completed on our sailboat, we closely observed the effects of shade on our solar-panel array. We were often anchored in an orientation that put the panels in full sun. Just as often, however, we were angled in such a way that shade from the mast and boom covered portions of our panels. It was fascinating to monitor the solar charge controller’s LCD display whenever the sun was forward of the beam — the current from the panels to the batteries fluctuated up and down as we swung at anchor.
Taking notes one morning, we noticed that the charging current was repeatedly creeping up and down between 9.5 and 24.5 amps as the boat moved to and fro. When the entire solar-panel array was in full sun, it generated 24.5 amps of current. When we moved so the mast shaded a portion of one panel, the array generated 15 amps. When it shaded portions of two panels and only one was in full sun, the array produced just 9.5 amps. Of course, it would have been preferable to see a steady 24.5 amps all morning, but this sure beat watching the current drop to zero whenever a shadow crossed a panel.
We discovered that shade makes a huge impact while sailing, too. Surprisingly, it is far worse to have the panels shaded by the sails than to have the panels in full sun but tilted away from its direct rays. One afternoon, we noticed that while we were on a tack that tilted the panels away from the sun, they generated 24.5 amps of current, whereas on a tack where the panels were tilted toward the sun but two of the three were partially shaded by the sails, the current dropped to a mere 10 amps.
Reflections On Our Solar Panel Installation
A wonderful and surprising side benefit of our large solar panels and arch system was that the setup created fabulous shade over the jumpseats at the stern end of the cockpit. Our metal fabricator, Alejandro, placed a support strut at hand-holding height, and sitting in those seats feels secure and comfortable while sailing, no matter the conditions.
After living on solar power for eight years of cruising and land-yacht travel, we’ve learned that you can never have too much solar power. Groovy’s 555 watts was enough to run all our household appliances as needed, including our nearly 4-cubic-foot DC refrigerator, two laptops, a TV/DVD player, and lights at night. However, it was not quite enough power to run all that plus our stand-alone 2.5-cubic-foot DC freezer during the short days and low sun angles of the winter months without supplemental charging from the engine alternator every few days. For the 10 weeks that we did not have a functioning alternator, our solution was to turn off the freezer, which enabled our batteries to reach full charge every afternoon.
Solar power made a world of difference in our cruise. Not only did it allow us to live comfortably and with ample electricity for weeks on end when our engine alternator went on the blink, but as a “set-it-and-forget-it” system, it also gave us the freedom to anchor out for as long as we wished without worrying about the batteries. In our eyes, the solar-panel arch enhanced the beauty and lines of our boat, giving her a sleek and clean appearance. It was true icing on the cake to discover that the panels and arch system also provided much-needed shade over the cockpit and helm from the hot tropical sunshine. If you are preparing for a cruise, consider turning to the sun for electricity and outfitting your sailboat with solar power.
The Installation:
Emily and Mark Fagan offer cruising tips and share their stories and photos on their website, roadslesstraveled.us . They are currently enjoying a land cruise across America aboard an RV.
- More: DIY Sailboat Projects , green sailing , How To , installations , Refits , Sail Green , solar , solar panel , Upgrades
- More How To
How To Prioritize Your Sailboat’s Spring Checklist
How to protect your spars from corrosion, sailing totem refit series: the forward head makeover, fatty goodlander: dealing with chafe while cruising, tradewinds debuts 59-foot twe6 smart electric yacht, good bread for good health, center of effort, the halfway point: sailing to bermuda.
- Digital Edition
- Customer Service
- Privacy Policy
- Email Newsletters
- Cruising World
- Sailing World
- Salt Water Sportsman
- Sport Fishing
- Wakeboarding
Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition

Sailing with solar power: A practical guide
- Duncan Kent
- November 13, 2020
The latest solar technology makes self-sufficient cruising much more achievable. Duncan Kent gives the lowdown on everything you need to get your boat sorted

SOLAR POWER ON BOARD
Solar power is fast becoming the most popular and economic method of keeping the batteries charged on a boat.
Particularly now that the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) panels, charge controllers and batteries is improving every day.
Furthermore, the latest technology in regulators and charge controllers has brought about a noticeable increase in useable power output, so the problems of shading and non-alignment can be compensated for more easily.
Not only has PV equipment become more efficient and cost-effective, but many of the modern devices we want to use on a boat have become less power hungry.
This means it is now far easier to provide your entire yacht’s electrical needs, both 220Vac and 12/24Vdc, from natural energy resources – particularly solar power, even if you are planning on a fully electric boat .

Thinking carefully about how much power you need and how much your boat can accommodate is key to planning a solar array. Credit: Graham Snook
WHAT DO YOU NEED?
For instance, a boat with two new, good quality, deep-cycle house batteries of 100Ah each would supply 100Ah of energy to consume between charges, if you only use the recommended 50% of available charge between each charge cycle to protect the batteries.
From this you could run:
- a modern 12Vdc fridge (approx. 1.5Ah, or 36Ah over 24hrs),
- all LED lighting (say 20Ah per day),
- various small device chargers (20Ah)
- and a number of other items such as water pumps, TVs and stereos (25Ah/day)
- Totalling around 100Ah.
- For this you’d need 400W of solar capacity.
Of course, if you like to run a lot of AC devices off-grid such as hair dryers, microwaves, toasters and the like, then you’re going to need a DC/ AC inverter, which will take you to another level in power consumption terms.
But even then, with careful planning, solar could provide a large portion of the power you need before resorting to engine charging or a generator.
THE AVAILABLE SPACE
In practical terms, a modern 40ft monohull would have the space for around 1,200W of PV panels (cockpit arch, sprayhood top, deck), maybe 1,500W with the addition of a few portable panels for use at anchor.
The 1,200W of fixed position solar array could produce around 360Ah on a sunny summer’s day (zero shading) or more likely 250Ah on the average UK summer’s day.
So that’s enough for your 100Ah general DC consumption plus another 150Ah of AC consumption via the inverter.
Of course, to do this you’ll most likely need to increase your battery capacity to around 400-500Ah for maximum flexibility (you’ll need to store as much as possible during daylight hours), a typical figure for a 40-50ft offshore cruising yacht these days.

Get your solar charging right and you may never need to hook up to shore power
Typical daily inverter loads for a cruising yacht off grid might be:
- induction cooking plate (20min) 60Ah
- microwave (15min) 30Ah
- coffee maker (20mins) 25Ah
- hair dryer (5min) 15Ah
- laptop charger (2h) 10Ah
- or around 140Ah in total.
The trick is to monitor the batteries’ state of charge (SOC) at all times and vary your use of the inverter to suit.
For example, you might want to cook supper mid-afternoon, when solar is in abundance, and then reheat it in the evening when you want to eat it.
In some cases, when you’re cruising in warm climates such as the Med, you might end up with excess charge from your solar panels .
In this situation, many long-term cruisers devise a method of ‘dumping’ the extra energy by heating water for showers.
Do bear in mind if you’re planning to live aboard full time , then it’ll be a whole different story on cloudy days and during the winter, when inverter use might need to be knocked on the head entirely.
Continues below…

Eco friendly sailing: Best practice for green yachting
How easy is it to go eco friendly sailing? We look at the steps cruisers can take to minimise their…

How and where to go wild cruising in the UK
Planning to spend the night away from crowded waters can be truly rewarding but preparation is essential before you go…

Solar-powered boat crosses Atlantic
Then heads to UN climate conference
POWER DISCREPANCIES
There’s often confusion as to how much power you can harvest from a solar installation.
A PV panel is nearly always advertised stating its theoretical peak output power (Pw).
But in reality, on a yacht where there are limited areas in which to mount them, they will more likely produce a maximum of 60% of their peak output if mounted horizontally, increasing to 80% if tilted towards the sun and regularly adjusted.
The latter is rarely achievable on a boat, however, as even at anchor it can swing through an arc of 180° in wind or tidal shifts .

Flexible panels can be mounted on sprayhoods or awnings to add power when it’s needed at anchor or in harbour
INSTALLATION
Having trawled through hundreds of ‘deals’ to get the best price on the most efficient panels you can afford you now need to know how to install them to best fulfill your energy generation needs.
The output, even from the highest quality photo-voltaic array, will only be as good as the installation itself.
So following our guidelines should ensure you extract every last drop of energy from your investment.
PANEL MOUNTING
Sailing boats are not the ideal structure on which to mount wide, flat PV panels.
So before you go ahead and purchase what looks like the biggest and best, take a few minutes to decide on exactly where you can mount them, as this will affect what size and type of panels you should buy.
In many cases the first choice would be on an arch, davits or gantry aft, especially if you already have, or plan to fit one.

Dinghy davits, particularly on multihulls, can support a huge solar capacity
These allow a solid metal framework to be constructed that will be strong enough to take the heavier, more productive rigid PV panels.
You can also build in some form of adjuster to the framework that will allow the panels to be orientated towards the sun for the best performance.
With luck (or careful planning) a gantry will also keep them aft of the boom, thereby eliminating loss of output caused by boom shading.
The next most popular position for mounting the panels is on a cockpit sprayhood or bimini, although this will often mean using the flexible or semi-flexible panels, which are generally less efficient than the rigid ones for the same area.
ELEVATED MOUNTING
Alternatively, there are kits available for mounting panels onto lifelines, which can allow their elevation to be manually adjusted to a certain degree.

Pole-mounted panels can be used for maximum adjustability
Finally, panels can be fitted directly onto the deck by either gluing them down using mastic or attaching them onto a rigid support frame.
Once again you will probably need to use semi-flexible panels – especially if the deck surface is curved.
Rigid, glass-coated panels will obviously not be suitable for deck mounting in an area that is frequently walked over.
Don’t be tempted to drill through the panels, even along the edges, as this will invalidate the warranty and possibly damage the panel.

With solid panels, the ability to adjust the angle can add significantly to output
It might seem obvious, but the key to an efficient system is to avoid shading wherever possible.
It’s no good fitting expensive, high-efficiency PVs right under the boom as they’ll perform little better than the cheaper types.
Saying that, in good quality panels each cell will be isolated from the next by a series of diodes (one-way electrical valves), so that if one cell is shaded at least it won’t drag down the other cells within the same panel.
Older panels often didn’t have these, so the slightest partial shading caused the output of the entire panel to cease.
OVERHEATING
Another important factor that is often ignored when installing the panels is that of overheating.
If a PV panel gets too hot, which is quite likely if mounted directly onto a flat surface without an air gap behind, its output will drop quite noticeably.
To allow for some air circulation behind the panels it’s best to apply mastic adhesive in numerous large dabs.
This is best achieved by placing wooden spacer strips between the dabs until the mastic has completely cured, after which the spacers can be removed.
You might need some form of trim around one or more of the outside edges, though, if they are positioned where sheets and other lines might get caught under them.
Raising the panels up will also help water to drain off and thereby helping to avoid possible delamination from sitting in water for too long.
CHARGE CONTROL
A PV module cannot supply an electrical device directly due to the changeability of the sunlight, which in turns varies the current it can produce.
Therefore, it has to be connected to a battery, which stores and smooths its output.
Whatever the size of your solar array you will need to fit a regulator, or charge controller as they are now more commonly known, to the system in order to control the output and to help extract as much power from the panels as possible.
There are two types of PV charge controller.
The older designs, called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) types, were fairly basic voltage regulators and simply output volts at just above battery level.
The latest controllers use Multi Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology and can accept much higher input voltages (up to 240Vdc).
MPPT controllers can be up to 30% more efficient as they use the peak output of the panels to charge the batteries, even compensating for partial shading.
BEWARE FAKE GEAR
If you buy online do be careful to ensure you’re getting what you pay for.
There are a huge number of fake MPPTs out there, which are simply the much cheaper PWM dressed up with fake labels.
It’s hard to tell which is which, but the old adage of ‘if it looks too good to be true, it usually is’ makes good sense.
MPPT controllers are usually bigger and heavier than PWMs, but if in doubt call or email the supplier to discuss the pros and cons of their kit before buying.
If they’re not happy to chat and advise you then I would steer clear of their gear.
Some good MPPTs are made in China, but unless they have a UK supplier, I wouldn’t bother with them as you’ll have no follow-up advice.
To calculate what size controller you need simply divide the panel’s peak power in Watts (Wp) by the battery voltage, which will give you the maximum current (Amps) they could theoretically supply.
For example 240W/12V = 20A. Although it’s unlikely you’ll ever get near the peak output from any PV panel, it’s best to go for the maximum possible.

Induction cooking is now a reality on board, even without shore power
PV panels come with a short length of cable, usually around 1m long.
Some are supplied with MC4 connectors already attached but most only provide bare wires.
The latter can be easily extended using proper waterproof connections but thought must be given as to the current rating and voltage drop (usually max 3%) for the size of cable you intend to use.
If in doubt, bigger is better!
Panels can sometimes be ordered with the wiring on the back so that the cable can go straight below deck through a hole under the panel.

You may need to fit extra battery capacity if you want to run an inverter from solar charging
SERIES OR PARALLEL?
A commonly asked question is ‘should I wire my PV panels in series or in parallel?’
The simple answer is, if there’s any danger of frequent shading to one or more of the panels then install them in parallel.
If wired in series the shading of a single panel will drag down the output from all of the others in the same series.
PARALLEL IS PREFERRED
Most commonly, multiple panels are wired together in parallel to a single charge controller, with diodes protecting each panel from discharging the others should one become partially shaded.
With the advent of MPPT controllers, however, there can sometimes be a benefit to wiring two or more identical panels into a series bank, thereby presenting a higher voltage to the controller.
It’s worth noting that, like batteries, wiring PV panels in series increases the voltage only – the current capacity of the array remains the same as for a single panel.
‘Where’s the benefit of wiring them in series then?’ you might ask.
Well, the higher the voltage fed into the MPPT, the more consistent it will be with its output, which could, in some cases, prove more efficient than a parallel installation with PWM controllers.
It’s also likely to be necessary if you have a 24V domestic system.
SERIES WIRING
Series wiring is usually only done when the cable runs are long, as it helps negate the voltage drop caused by the resistance of the cable.
While a decent controller will have no problem handling the output from four or even five panels wired in series, it is often inappropriate for sailing yachts as shading just one of the panels will reduce the output of the entire series array.
If you need to do so in order to reduce cable runs then it’s best to split the panels between each side of the boat – a series bank on each side.
If you do this, then you would ideally fit a separate controller to each series PV bank and then connect their outputs together in parallel to the battery bank.
Note, however, that panels wired in series must all be the same types with an equal number of cells per panel.
Furthermore, the charge controller needs to be sized for the total of all panel voltages added together and the current rating of one individual panel.
Differently rated panels can be connected together in parallel but only if each panel has its own controller.
The outputs of the individual controllers can then be joined together to go to the battery bank.
BATTERY BANK QUESTION
Another frequently asked question is ‘Can I connect another charging source to the battery bank while the solar array is charging?’
The answer is yes.
Any decent PV controller will be protected against feedback from other charging sources.

Think carefully about where shade from mast, boom and rigging will fall. Credit: Graham Snook Photography
CABLE SIZE AND CONNECTORS
A frequent cause of reduced output from PV arrays is wiring that is too small.
The resistance of a wire conductor increases in direct proportion to its cross-sectional area, so go as big as is practicable for the least cable loss.
Each panel should be supplied with the correctly sized cables for its own maximum output.
But if you’re combining panels, either in parallel or in series, you will clearly need to rate the single feed cable to suit the maximum current available at theoretical peak solar output and to minimise voltage drop.
Likewise, the cable from the controller to the batteries should be sized to suit the controller’s maximum output current and protected with a fuse.
For outside it’s important to use exterior grade cable, which is double- insulated and UV-proof.
WEATHERPROOF CONNECTORS
And wherever possible use compatible weatherproof connectors (usually MC4) to those found on the panels rather than cutting off the plugs and hard-wiring them.
Field- assembly MC4 plugs are available, so you don’t have to drill large holes in the decks or bulkheads when feeding the cables through.
When joining more than one panel together try to use the approved multiway connectors; not only do they keep the wiring neat and tidy, but they also offer a greater contact area than budget terminal blocks.
If you have to use screw-type connectors make sure to fit proper ferrules to the wire first to avoid any stray wires in the multistrand shorting across the terminals.
When feeding a cable from above to below deck, try to go through an upright bulkhead where possible to minimise ‘pooling’ of water around the access hole.
Also, use a proper watertight deck seal that matches the cable you’re using.
If drilling through a cored deck you need to drill a larger hole first, fill it with epoxy resin and then drill the required size hole through the epoxy to ensure no water gets into the deck core.
Ideally, the charge controller should be mounted no further than 2m from the battery bank.
If you need to go further, you’ll require larger cabling to reduce the voltage drop.

A generous solar array will keep you self- sufficient indefinitely. Credit: Graham Snook Photography
CONTROLLER LOAD TERMINALS
There is often confusion over the ‘load’ output of a charge controller (often depicted by a light bulb) and what can safely be connected to these terminals.
Rarely explained in the manual, the load terminals should be pretty much ignored in a marine installation as the output on these terminals is usually very limited (10A max).
Some attach an LED light to them to indicate the controller is operating, but all your usual electrical loads should remain connected to the batteries with the battery terminals on the controller connected directly to that battery bank via a fuse.
It is possible, though, to control a high-current switching relay in certain conditions.

Parallel installation is more resilient to shading, but a series installation will increase peak charging outputs. A combination of the two offers some of the benefit of both
CIRCUIT MONITORING
Unlike most cheap PWMs, the majority of good quality MPPT charge controllers come with an alphanumeric LCD screen to let you know what is going on.
This can either be a remote display or simply one on the front of the box.
It’s obviously a lot better to have a proper numerical display than to rely on a few flashing LEDs to tell you when something’s not right.
So if your chosen controller doesn’t have one be sure to fit a battery monitor (the shunt type) into your solar circuit between the controller and the batteries.
It doesn’t have to be a very ‘smart’ monitor, just one that can display the voltage and current being supplied by the panels.
For smartphone addicts there are several wifi apps that will do the job remotely on your phone or tablet.
DEVICE PROTECTION
All good quality PV panels feature built-in diode protection between each cell to prevent a shaded cell from dragging down the productive ones.
In addition, there will be internal blocking diodes on the final output to protect the panel from polarity reversal and to ensure that the batteries can’t discharge back into the panel during the night.
The latter can be added externally, the former can’t, so check before you buy.
A fuse, rated just above the maximum current available, should be fitted between each panel and the charge controller.
Another fuse should then be installed between the charge controller’s output and the batteries.
In the case of multiple arrays, this second fuse will be rated higher than the individual panel fuses and should match the maximum current rating of the cable.
With this protection installed other charging devices can be connected in parallel at the battery, meaning the solar can be left connected even when you are hooked up to shore power and the battery charger is operating.
In some circumstances, however, this arrangement can affect the sensing of the battery by the charger, causing it to fall back into float mode.
If this becomes apparent it can be overcome by installing a manual/auto switch to disconnect the solar array when on shore power.

Check the flex of the solar panel is sufficient for your deck
EXCESS POWER DUMPING
A solar charge controller works by disconnecting the supply from the PV panels when the batteries are fully charged.
But for some full-time liveaboards in sunny climates that can be considered a waste, when the excess power could be put to good use – heating water, say.
This is commonly done using an inverter to supply AC power to the heating element.
Alternatively, you can now buy a 12Vdc element for your calorifier (hot water tank) and supply this directly from your battery bank.
Both of these methods would require a voltage sensitive relay (VSR) to disconnect the element should the battery voltage drop below a pre-set level.
Don’t expect boiling hot water, as there will probably only be enough spare power to take the chill off it before your battery bank reaches its lower threshold voltage.
A 600W/12V element will draw some 50A, from the batteries, whereas a 1kW AC element run through an inverter will need close to 100A.

A small, semi-flexible panel will be sufficient for keeping batteries trickle charged, but not for heavy use
RIGID, FLEXIBLE, OR SEMI FLEXIBLE?
Despite massive recent improvements in semi-flexible panels in recent years, the solid glass panels still offer a higher power density.
That said, they are heavier, more awkward to mount and can’t be walked on, so unless you have a dedicated gantry aft, you’re better off choosing the more rugged semi-flexibles.
Modules incorporating monocrystalline cells also have a better output than those with polycrystalline cells (that’s cells made from a single slice of silicon as opposed to layers of smaller pieces).
Output voltage also depends on the number of cells on the panel.
In the past this has commonly been 32, but now some 36 and even 40 cell panels are available.
That said, they’re larger, of course, so an array of interconnected smaller panels might be a better solution.
Module efficiency is now more often around the 20% mark, as opposed to 12-15% for older models and semi- flexible (up to 20° bend) are usually better than flexible (up to 180° bend).

A rigid panel is more efficient, but less robust
There are a huge number of panels on the market, but many use the same cells.
Sunpower Maxeon cells are exceptionally good, as are the Panasonic HIT range and LG, but they are pricey.
If the maker is offering a 25-year guarantee instead of a 3-5 year one, you can be pretty confident they’re good.
When it comes to charge controllers it’s definitely worth paying a little more for a decent MPPT.
A cheap PWM might be okay just to keep a small starter battery charged with a 30W panel, but the MPPT will give you much more when it comes to heavy service.
Victron are probably top of the range, while cheaper brands like MakeSkyBlue and EPever are also good value – but treat imports of unclear origin with care.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Duncan Kent has been evaluating and reviewing yachts and marine equipment for the past 30 years
Enjoyed reading this?
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.

Service Locator
- Angler Endorsement
- Boat Towing Coverage
- Mechanical Breakdown
- Insurance Requirements in Mexico
- Agreed Hull Value
- Actual Cash Value
- Liability Only
- Insurance Payment Options
- Claims Information
- Towing Service Agreement
- Membership Plans
- Boat Show Tickets
- BoatUS Boats For Sale
- Membership Payment Options
- Consumer Affairs
- Boat Documentation Requirements
- Installation Instructions
- Shipping & Handling Information
- Contact Boat Lettering
- End User Agreement
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Vessel Documentation
- BoatUS Foundation
- Government Affairs
- Powercruisers
- Buying & Selling Advice
- Maintenance
- Tow Vehicles
- Make & Create
- Makeovers & Refitting
- Accessories
- Electronics
- Skills, Tips, Tools
- Spring Preparation
- Winterization
- Boaters’ Rights
- Environment & Clean Water
- Boat Safety
- Navigational Hazards
- Personal Safety
- Batteries & Onboard Power
- Motors, Engines, Propulsion
- Best Day on the Water
- Books & Movies
- Communication & Etiquette
- Contests & Sweepstakes
- Colleges & Tech Schools
- Food, Drink, Entertainment
- New To Boating
- Travel & Destinations
- Watersports
- Anchors & Anchoring
- Boat Handling
- ← Technology
What You Need To Know About Boat Solar Panels
Advertisement
Sunshine and boats are a natural together, so why not use all that free energy? Here’s the lowdown on solar panel selection and installation
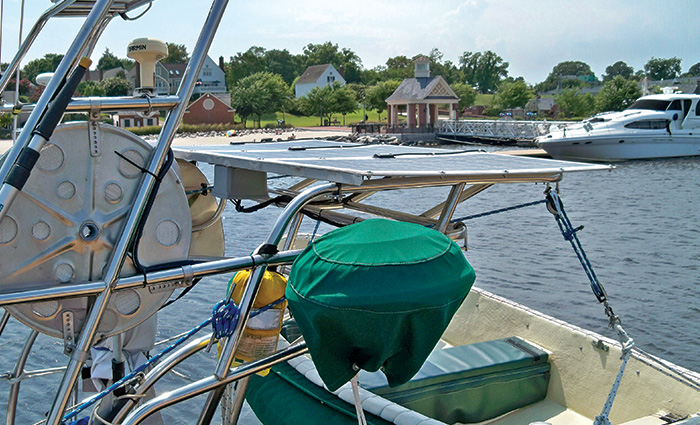

I first embraced the idea of solar power while up a pole (literally) in the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway replacing dead batteries. It was the early 1980s, and I was maintaining buoys, beacons, and other such Aids To Navigation (ATON) for the U.S. Coast Guard, replacing massive, nonrechargeable batteries with rechargeable solar-powered ones. The higher-ups said the solar rechargeables would last six years – twice as long as the one-shot batteries. As the deck-ape in charge of lugging all those batteries up and down the ladders, my back and I immediately appreciated the whole “free power from the sun” thing, a concept I continue to embrace.
The strategy behind s olar energy onboard is simple: A solar panel converts sunlight into electricity, after which wiring conducts it to your batteries for storage until needed. Solar panels are used to keep batteries or banks charged rather than to power equipment directly. This arrangement allows the panels to store generated power whenever produced, while providing a steady source of power to a piece of equipment even when the panel is producing no power.
While they do require an initial outlay, solar panels can easily pay for themselves in money saved and independence gained over their service life. They’re noiseless, have no moving parts, and they provide free electricity for years with minimal maintenance. Solar panels also have the benefit of being modular, letting you start small and add more as your power requirements increase.
The benefits of solar
Almost any boat can benefit from solar power. Whether at a slip, mooring, or on a trailer, boats can keep their batteries topped off without the need for external power. You can also use solar power to supplement or even replace other onboard charging sources, reducing or eliminating the need to run engines or generators to keep batteries topped off (a wasteful practice that burns fuel while wearing down the costliest pieces of equipment onboard).
While underway, it’s a plus to be able to recharge a dead battery in an emergency – say, to operate a VHF radio or navigation gear. While dockside, solar panels keep batteries charged and vital systems (such as bilge pumps) up and running without the need for shore power.

Just about any boat can benefit from solar power, whether it’s to keep batteries topped off or supplement other onboard charging sources.

Mount solar panels where they are exposed to maximum sunlight but do not interfere with operation of the vessel.

Bottom: Something as simple as the shadow of a line or shroud can reduce or halt output.
Types of panels
Solar panels contain photovoltaic cells – small silicon semiconductor devices that convert sunlight into electricity. Each cell generates between 0.45 and 0.5 volts, depending on exposure to direct sunlight. Cell size determines amperage, with a 3-inch cell producing roughly 2 amps, a 4-inch cell a little over 3 amps, and a 5-inch cell around 5 amps.
Construction-wise, the three main types of solar panels are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous (or thin-film) technology.
Monocrystalline panels have been around the longest and remain the most popular. The panels are constructed of thin slices of crystal silicon (each cell is cut from a single crystal) housed in a rigid, aluminum frame and covered with tempered shatterproof glass. The panels have a uniform black, blue, or gray appearance and are generally quite rugged, although they can be cracked or broken if subjected to extreme abuse.
Monocrystalline panels have the longest service life of the three types. With a conversion efficiency of around 17%, they’re also the most efficient and have the highest electrical output per area, but they are also the most expensive.
Polycrystalline cells are sliced from a cast silicon block and have a shattered glass appearance. Built in much the same way as monocrystalline panels, they’re rectangular, giving the panel itself a tiled look. Their life span is similar to monocrystalline panels, and while their conversion efficiency is lower (by 14%), they’re also a bit less expensive.
Amorphous panels are made by placing a thin film of active silicon on a solid or flexible backing (such as stainless or aluminum sheeting) depending on whether the panel is to be rigid-framed and glass-fronted or flexible. Flexible amorphous panels, in which cells are sandwiched between rubber and polymer covers, are light and tough enough that you can walk on them and, in some cases, even roll them up for storage.
This type of solar panel is also better if shade is an issue. With crystalline panels, even the thin shadow of a rope or shroud across one cell can reduce or halt output of an entire module. Amorphous panels have “bypass” diodes that essentially turn off shaded cells and provide a current path around them. Some monocrystalline panels also have bypass diodes, but this feature comes at an increase in cost.
Amorphous panels are the least expensive of the three types, but their efficiency is also lower – around 8%, or roughly half that of a monocrystalline type. This lower output is somewhat mitigated in newer panels, however, which use three-layer construction. Each layer absorbs different colors of the solar spectrum, so the panel will deliver more power longer each day and during lower light conditions than the other two types.

The charge controller should be mounted below decks and as close to the battery as possible.

Follow manufacturer instructions for wire connections.
Planning the system
While factors such as cost, mounting options, and output are important, a successful installation depends on knowing what you want the system to accomplish. Is the goal to float-charge a single battery or supplement an overall vessel energy plan? Answering these questions up front will help determine the type, size, and number of panels required.
To understand the process better, let’s walk through the basic steps to determine power requirements and installation considerations for a single solar panel installation. While the example itself is simple, the steps are the same used to plan more complicated installations.
For our example, the goal is to install a solar panel to provide charging for a single 12-volt, 100-amp-hour wet-cell battery used to power an automatic anchor light on a moored vessel.
The first step is compiling a daily power consumption estimate to determine how much solar power is needed.
The daily self-discharge rate for a wet-cell battery is roughly 1%, meaning our 100-amp-hour battery requires one amp every 24 hours just to maintain the status quo. The anchor light draws 50 milliamps per hour of operation, and we’ll assume it operates 10 hours each night. Multiplying current draw (50 milliamps) by hours of daily operation (10) generates a daily energy expense of 500 milliamps or .5 amps.
This means our solar panel must meet a minimum daily energy tab of 1.5 amps – one amp of battery self-discharge rate plus .5 amps of power draw for the anchor light.
Next up is figuring out panel size and the best mounting location. For our example, let’s assume the panel will be a horizontal, fixed-mount installation. A 10-watt horizontally mounted panel should generate between 3- and 5-amp hours per day.
We’ll need at least 13 volts to fully charge our 12-volt battery. As most solar cells generate at least 0.45 volts, you’ll want a panel with a minimum of 33 cells, which should provide around 14.85 volts.
Keep in mind that’s the minimum needed, which may not be enough once you factor in a few cloudy days. Most panels are designed to generate between 15 and 20 volts to overcome problems like cloudy days or inherent electrical resistance within the panel or installation components. While this higher voltage lets you make up for less electrically productive days, it also means you’ll want to install a solar charge controller (voltage regulator) to avoid battery damage due to overcharging.
Attempts to plan a system that tries to use the output of the panel and capacity of the battery to prevent overcharging (and avoid the installation of a charge controller) is false economy and should not be done. The system will never meet its full output potential and, worst case, can damage the battery due to overcharging.
A word on ‘charge controller confliction’
If your vessel has multiple charging sources, such as solar panels and a wind turbine, a crucial but often overlooked consideration is “charge controller confliction.” In short, this is an issue where the charge controller for your solar panel and the charge controller for your wind turbine are internally adjusted to the same maximum charge voltage set point. This means they are constantly fighting each other to be the dominant power source, which results in diminished overall charging output and performance. An in-depth article on this issue can be found at missioncriticalenergy.com (in the website footer, click “Superwind Turbine Manuals & Technical Bulletins.” Under the header “Charge Controllers,” select the document “Resolving Charge Controller Confliction”).
While this article addresses charge controller confliction at remote, off-grid sites, the information provided is also applicable to vessel installations. — F.L.
Location and mounting
Solar panels should be mounted in a location where they are exposed to the maximum amount of sunlight but do not interfere with operation of the vessel or the movement of passengers and crew. Solar panels will typically be either fixed or mounted on some type of movable bracket that allows you to actively point the panel toward the sun for maximum output. Both methods have their pros and cons. Fixed panels (which are normally mounted horizontally) don’t produce as much power as a panel that can be adjusted to face the sun. The downside is that adjustable panels must be aimed throughout the day to maximize their output.
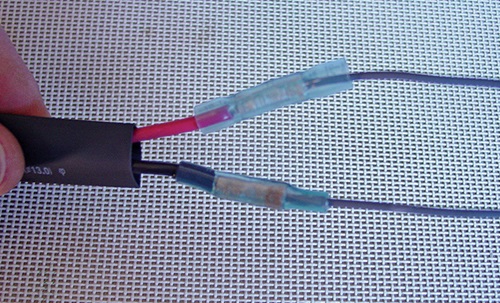
Use good quality, marine-grade heat shrink connectors (top) and liquid electrical tape (right) to create airtight, waterproof seals and reduce corrosion.

Installation
After choosing and mounting your panel, it’s time to connect it. The first thing you need to determine is the size (gauge) of the wiring to be used. Multiply your panel’s rated amp output by 1.25 (which adds a 25% safety factor). Then measure the length of the entire wiring run, panel to battery, and multiply by 2. Once you have these two numbers, refer to the American Boat and Yacht Council’s (ABYC) 3% voltage-drop table for wire size. Ancor Products offers a handy wire calculator on its website ( ancorproducts.com/resources ).
Always use good quality marine grade connectors and tinned, multi-stranded copper wire with vinyl sheathing. The wire will run from the solar panel to the charge controller first, then to the battery. Try to keep the wire run as short as possible, and if it transits an external deck or cabin house (it likely will), be sure to use an appropriate weatherproof deck fitting.
The charge controller should be mounted below decks and as close to the battery as possible. You’ll always want to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for connections, but in a typical installation you’ll connect the solar panel’s positive (red wire) lead to the charge controller’s positive input wire or terminal and the negative (black wire) lead to the charge controller’s negative input wire or terminal.
Next, connect the charge controller’s negative output to the battery negative terminal and the controller’s positive output to the battery’s positive terminal via an appropriately sized in-line fuse (or circuit breaker). ABYC recommends these be installed within 7 inches of connection to the battery or other point in the DC system. To reiterate, the installation of the charge controller can vary among models, so follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions.
Finally, ensure all connections are waterproof and secure any loose wire runs with wire ties and cable clamps for a neat installation. Then get ready to lean back and soak up some free sun.
Related Articles
The truth about ceramic coatings for boats.
Our editor investigates the marketing claims of consumer-grade ceramic coatings.
Fine-Tune Your Side Scan Fishfinder
Take your side-scanning fishfinder off auto mode, and you’ll be spotting your prey from afar in no time
DIY Boat Foam Decking
Closed-cell foam flooring helps make boating more comfortable. Here’s how to install it on your vessel
Click to explore related articles
Frank Lanier
Contributing Editor, BoatUS Magazine
Capt. Frank Lanier is a SAMS Accredited Marine Surveyor with more than 40 years of experience in the marine and diving industries. He’s also an author, public speaker, and multiple award-winning journalist whose articles on boat maintenance, repair, and seamanship appear regularly in numerous marine publications worldwide. He can be reached via his YouTube channel “Everything Boats with Capt. Frank Lanier” and website captfklanier.com.
BoatUS Magazine Is A Benefit Of BoatUS Membership
Membership Benefits Include:
Subscription to the print version of BoatUS Magazine
4% back on purchases from West Marine stores or online at WestMarine.com
Discounts on fuel, transient slips, repairs and more at over 1,200 businesses
Deals on cruises, charters, car rentals, hotel stays and more…
All for only $25/year!
We use cookies to enhance your visit to our website and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our website, you’re agreeing to our cookie policy.
Captain Curran's sailing blog
~ a collection of sailing adventures from Alaska to Cabo
October 6, 2014
Solar panels for boats: an easy installation guide., marine solar panel installation.
- I am writing the following instructions for boat people or RV campers.
- I describe a basic set up that provides a charge onto your 12 Volt DC battery bank.
- If you want to use this system to power your home, then you'll also need an inverter to switch the 12 Volt DC electricity to 110 Volt AC.
Ok, here's my simple DIY instructions for solar installation on a boat or an RV camper.
How to install solar panels for boats, step by step guide for installing a solar panel boat system, faq: what size panel should i get, faq: which brand of solar panel is best, faq: do i need a controller, faq: how did you mount your panel on your stern rail, faq: how do you wire up the panels/controller/battery, faq: how much will this whole solar panel project cost, solar power for boats price breakdown, okay - good luck with your marine solar panel installation , capt. curran, 60 comments:.
Heany - Don't hesitate, the beauty of this system is that there are no moving parts, which means maintenance is minimal.. turning photons to electrons
Good question - visit your local machine shop They should have barrels of aluminum flat panels You want 12-16 inch long, need to measure panel That's it Then drill holes and strap in on the rail Have fun!
Thanks Douglass - all the best..
Great information, thank you! Where did you purchase the white plastic rail mounts?
Hello Philip Magistro, I bought them at a boating store in Seattle - called Fisheries Supply - they may ship. But I would also check your local west marine - they are standard stern rail mounts - they fit lots of other stuff as well as solar panels. Good luck !
Excellent, glad it was helpful. I'm about to post a couple new photos of the system. Everything is still working great.
Two questions 1. Is a 30w panel large enough to trick charge two 12v batteries? 2. How large an in-line on the positive lead to the battery?
Hello - Yes, a 30watt panel is large enough to trickle charge 2 12 V batteries. That is the set up I have on my boat - it works great - even in mixed sun/cloud conditions. When you ask 'how large' an in-line on the pos. lead - I am assuming you're asking the guage. I can't give the exact guage that is suited for your set-up. But, I know that the reasonable range is between 10-14 awg. Hope that helps.. Cheers
Kevin Thanks. Great info! I was actually trying to ask type and size of fuse on the positive lead to the battery. Fingers! Cheers Bill Pierson
Thanks for a great post! I'll go with the Renogy 200 Watt kit. I know it's not as adventurous, but easier and faster. And time is money :)
Lucas, I hear ya. Time is money - best of luck with that kit. I think you've made a wise decision.... Kevin
Thanks a lot Kavin for your guidance on installing a solar panel on boat. As solar panels are the most effective and the best way of generating electricity these days so everybody wants to install a solar panel of their own. But installing a solar panel in the boat is little challenging. Thanks for sharing the step by step guidelines, it is definitely going to help the readers.
Great article. A few questions: The article explains how to hook it up to one battery. But I have a system with two house banks of two bateries each, as well as a starter battery. How do I ensure that the trickle charge gets to all give batteries? Or do you just hook it up to the starter battery? How does this system interact with my charger?
Mary, I have a similar battery bank - but the two are connected. I connect the leads of the solar panel to my house batteries. However, if they are not connected - then I would connect the leads of your solar panel to the starter battery.
Mary, I would get a MorningStar SunSaver Duo controller which can charge 2 batteries (or banks thereof) and set the 2 house banks in parallel on the controller's Batt1 and the Starter Battery on Batt2. This controller has the option to charge 90/10 or 50/50, 90/10 is best for this setup because the starting battery doesn't need much, just enough to top-it-off.
Hi Kevin, I purchased the Renogy 100w panel with controler. I like your plastic rail mounts. Where can I find those. I plan to mount this on the stern of my 73, 27' Catalina stern rail. Thanks, Chris
Chris, I got mine at a boat store in Seattle called Fishery Supplies. I just looked it up on their website. Here's the page for those rail clamps. https://www.fisheriessupply.com/sea-dog-line-removable-rail-mount-clamps-327199-1 Made by a company called Sea Dog. Good luck - Kevin
I have a 20 volt panel, single marine battery, with a controler working without problem for about 4 years. While motoring out of the marina the controler caught fire. I did not have a fuse installed as you described in your installation guide. Any idea what might have caused this? Barry
Barry Curran, That is an odd and unfortunate situation. I am not an expert on safeguarding circuits, however I can weigh in with my opinion. I do think that the installation of a circuit fuse would help prevent over-charge or over-heating happening within the circuit. I think - assuming the over-charge was happening throughout the circuit - that the fuse would have blown, thereby salvaging your controller. However, there is a chance that a diode or some other internal circuit on the controller was the weak link. In that case, I don't believe a downstream fuse would have helped save your controller. I would install a fuse and get yourself a new controller. Best of luck! Kevin Curran
Just an helpful clarification on the purpose and location of the fuse. The fuse is to protect the wire, and should be placed as close to the origination of the power source as possible which, in this case, is the positive lead near the solar panel. We're all use to hearing about locating the main fuse on a boat as close to the battery as possible; that's because that's where the power comes from. Also, the fuse should be sized based upon the length and gauge of the wire.
Thanks for that additional insight on the location of the fuse! Sorry I didn't see this comment earlier.
Thanks for sharing the helpful guide to install solar panels .
Thanks for sharing article solar installation on boats it is really informative.A Solar panel is typically a panel that absorbs solar energy and uses it as a source of energy to generate electricity. They are basically made up of solar cells or the photovoltaic cells that are arranged as a photovoltaic array making up the photovoltaic system.I know a place one of the best solar installation company provides best solar services and products that are not just economical, but also efficient with customized solutions to offer you the best from our vast range of affordable models...
Greetings, How lucky am I to have happened upon your easily understood blog. Stupid question: can I mount the solar panel flat on the deck of my Nonsuch sailboat? (I know: don’t step on it!). Will it be worthwhile? (It can’t go on the stern rail).
Yes, that can be done. If you have a bimini or any cover in your cockpit, that is probably a better location. But flat on the deck can work, you can create a border around it to prevent falling on it...
Thank you so much for your excellent blog. I am considering a solar system for my 28' Catalina sailboat. Battery question: Any problem using solar systems with AGM batteries? I have two, house and starter battery.
Hmmm, that's a good question. I have never heard of any issue with AGMs on a solar system. Any other readers here have comments?
Selecting the correct charger depends primarily on the design of your deep cycle battery, so the first thing you need to do is determine the construction type of your battery. TrollingBatteryAdvisor.com This is likely to prolong the life of each battery and save you money in the long run.
Great blog! Can I leave my solar panel attached to the battery while I'm drawing from the battery to run my trolling motor?
Anonymous, Yes, you certainly can. There is no issue with drawing from a battery that is being fed energy from a solar panel. Enjoy Captain Curran
Thanks for sharing this article here about the solar panels for boats . Your article is very informative and I will share it with my other friends as the information is really very useful. Keep sharing your excellent work.
Great to hear! Glad the post was helpful..
Thanks a lot, Captain Curran and co-Captain Jessica for a nice and informative article about "Marine solar panel installation". This article will surely help the sailor in the Sea. And using a solar panel in the mid-sea is a very nice idea as an alternative source of power. Best wishes from SolarPandit
Thank you very much, Captain Curran and co-Captain Jessica, for a very interesting and insightful post on "Marine solar panel installation." This article will undoubtedly assist the sailor at sea. Using a solar panel and in the middle of the sea as an alternate source of electricity is also a great idea.
Hello all, Great to see the article has been helpful for those putting panels on their boat. Don't hesitate to reach out with any questions. I changed the notification, so I should be pinged when someone asks a question. Fair winds!
The Renogy 30 Watt Solar Panel is an excellent choice for light energy users, while the 100 Watt Solar Panel is preferred for moderate energy users. And remember to use a suitable quality controller like the Morningstar SunSaver-10 to control the panel's charge and prevent over-charging the battery.
Their step-by-step guide for installing solar panels on boats is incredibly helpful, and I appreciate the personal touch of sharing their own experiences and the success they've had with their solar panel system. The detailed explanations, recommended products, and estimated costs make it easy for someone like me to envision completing this project over a weekend. I'm definitely inspired to take on this DIY installation and enjoy the freedom of generating my own energy while sailing.
I can’t really help but admire your article your topic is so adorable and nice.
Forbidden love in a mesmerizing supernatural universe. Anime like Devils Line
Captain Curran's guide to installing solar panels on boats is a real lifesaver! After following his easy-to-understand steps, I completed my own installation over a weekend, and now my boat's batteries are always topped off during my fishing trips in the Chesapeake Bay. No more worries about a dead battery spoiling the fun!
Hello Captain, Great article, thank you. Our vessel has (6) 6 volt golf cart batteries, a 2000 Watt inverter, plus a generator. I want to limit the generator recharge time by installing a 100 or 200 watt kit that you recommend. My question is can I just connect the pos. and neg. marine grade wires from the controller directly to my battery bank pos. and neg. Thanks, John
This article on installing solar panels for boats brought back memories of my own sailing adventures along the coast of California. I remember the frustration of being stranded due to a dead battery and the relief that came with finding a solution. Capt. Curran's step-by-step guide is not only practical but also reflects his passion for sustainable energy solutions, making it a valuable resource for fellow sailors.
Post a Comment

Top 3 Best Solar Panels For Sailboats

Last Updated by
Daniel Wade
June 15, 2022
Choosing whether or not to install solar panels on your sailboat is a big decision. They are not exactly cheap, though they can start to pay themselves off pretty quickly.
This article is going to cover not only why you might want to use solar panels but all the benefits they provide. You will also find a helpful guide on which solar panels would be best for you and your budget. Hopefully, by the end, you will feel confident in your decision to install solar panels on your sailboat and even have an idea of which ones you might like.
Table of contents
Are solar panels on sailboats necessary?
Whether or not you should be installing solar panels on your boat is a matter of choice, not out of necessity. Sailboats get their power from the wind, by harnassing it in their sail. So if you plan to be sailing for the afternoon you probably don’t need solar panels.
You could charge a battery pack from the marina and that will probably see you through several trips. The problems only really start to arise if you are planning to be on your sailboat for longer periods, or even permanently. If you plan to live on your sailboat year-round, even if you spend 80% of it in a marina, you would be better off with some solar panels. Even if it is just as a backup source of power.
Are solar panels on boats safe?
Solar panels are generally pretty safe. They have no moving parts and typically have a very strong protective cover over them so you never come in contact with the electrics themself. So, as a source of power, they are generally pretty safe. The only time they may become unsafe is if they are badly damaged.
Solar panels are often covered by glass plating that keeps them safe. It also helps them absorb sunlight and warmth. This is great, except when the glass breaks. If the glass protective cover on your solar panels should crack and splinter you are at risk of serious injury from sharp shards of glass. Not only is the glass itself dangerous at this point, so are the electronic components inside. They have powerful currents running through them, and if you come in contact with them you may be in for a shock.
Furthermore, if these electronics get wet they can become deadly. Electricity and water do not mix well at all. Being as you are on a sailboat, at sea, the chances of them getting wet is very high. Luckily, the chances of them breaking in the first place are slim to none. The only real way they would break, besides vandalism, is by debris hitting them during a bad storm. There is not often debris at sea, so this shouldn’t be too much of a problem.
What are the benefits of having solar panels on a sailboat?
There are so many great benefits of having solar panels on a sailboat. They can be a lifesaver if you find yourself at sea for a long time. There benefits range from trivial comforts to being the difference between life and death. Here are some of the benefits you might not have considered about having solar panels installed on your sailboat.
Money-saving
Solar panels are not cheap, it is far cheaper to just run a generator or charge your batteries from the marina the whole time. At least, it is in the short term. Over time, it can start to become very expensive. With solar panels, you are looking at a big initial cost (the solar panels themself) and then it’s smooth sailing. You don’t need to pay for power again. Solar panels last for about 40 years before they start to become too inefficient at producing power. The cost of a few solar panels upfront compared to 40 years of marina fees and gasoline for a generator is the financially savvy move.
Emergency power
If you find yourself at sea, the wind dies down (or becomes too strong), and you find yourself stuck bobbing around waiting for more favorable conditions you may run into trouble. Depending on how long you are out there, you may find yourself with dead electronics. Be it a satellite phone, radio, or secondary engine (depending on the boat). Having a set of solar panels and a power bank can be a genuine lifesaver in these situations.
Comfort amenities
Whether you are day sailing or making a week-long voyage, having access to the comforts in life can make the whole journey so much more enjoyable. The amenities may not be available to you without having a constant source of power at sea. Having access to a kettle, tv, videogame system, radio or microwave oven may be the only thing keeping you going at rougher times. As exciting as sailing can be, when you aren’t sailing and are just bobbing around it can be quite dull. The sea is beautiful, but there is only so much time you can spend looking at the water before you miss the comforts of land. With solar panels, you can bring those comforts with you.
Eco-friendly
There are only two alternatives to solar panels. A gasoline generator, and taking power from the grid. Neither of these is good for the environment. Luckily, solar panels are a great third option. Solar panels are completely eco-friendly and are great for the environment. This is not just great for the earth, and your conscience, but for the journey itself. If you are running a gasoline generator at sea you are going to be listening to it thrumming away and smell the burning gasoline. Wouldnt you prefer silence and nothing but the smell of the sea breeze?
How much do solar panels cost?
How much solar panels cost is almost entirely tied into both their voltage/wattage and whether or not they are portable panels. Portable solar panels are great for people who don’t spend a lot of time on their boat or are happy enough living off the marina’s power grid. Permanent solar panels, the kind that may need to professionally installed, can end up costing far more. They are also likely to be far superior and you can pretty much forget about them once they are installed.
Portable solar panels will cost just a few hundred dollars each. You will need a few to be sustainable, but that’s not going to be much of a problem. These portable solar panels can just be rolled out on the deck of your boat, weighed down, and then hooked up to a battery pack. The battery itself here is going to be the most expensive part of the whole set up. A decent-sized battery could set you back a $1000. But, when charged fully it will last days. Even with constant use.
Permanently installed solar panels can cost one or two thousand dollars in some cases. The advantage here though is once they are installed that’s it, you can forget about them. You don’t have to put them up, take them down, and find somewhere to stow them every time they need using. They too will need to be hooked up to a battery, the battery is still only going to cost you $1000. If you are installing permanent solar panels because you plan to be making long voyages, it is ideal to have two or perhaps even three large batteries hooked up to your boat. One to run off, one or two for emergencies.
How do I maintain my solar panels?
Solar panels, unlike gasoline generators, are generally pretty easy to maintain. They have no moving parts and are thus pretty self-sufficient. They don’t need taking apart and they last as long as 40 years. That being said, if they do break they need repairing as soon as possible. The exposed electrics can be deadly when water is thrown into the mix. Which, on a boat, is almost always. The glass cover will need replacing and the electronics inside may need repairing, though not always. Don’t ever attempt to do this yourself unless you are experienced at making these repairs. The cost of hiring someone to do it for you is preferable to being dead. Solar panels have very powerful electric currents, that when in contact with water and yourself can be fatal. As mentioned above, these panels rarely break so you will likely not ever run into this problem. If you do, hire a contractor.
Do my solar panels need cleaning?
Solar panels work by converting the light and heat of the sun into useable power. The process itself is rather complicated but the results are simple to understand. That being said, there are some reasons that your solar panels will stop working as effectively. They all revolve around a lack of sunlight. It could be because it is night time. It could be because it is very cloudy. Or, it could be because they are dirty. If solar panels become too dusty, dirty, and become too covered in grime they stop operating at maximum efficiency. This is not as much of a problem at sea, the sea spray stops dust settling. The biggest thing you will need to clean off your solar panels is salt build-up and slime. This is easy enough to do with some warm soapy water. Freshwater, not seawater. You want to be removing as much salt as possible. Salt is corrosive to electronics, so removing it is important. Never clean your solar panels using pressure washers as they can crack the glass.
Which are the best solar panels for sailing?
There are so many options on the market at various price points. Here are three very different options that will all make good choices, depending on your needs. It is important to consider not just price but power output. Spending a lot of money on solar panels now might not feel ideal, but it is the most cost-effective decision.
1. Renogy Starter Kit
This starter kit is going to be perfect for installing on almost any sized boat. There are four solar panels, each can be fitted permanently to the boat. They can be mounted (and unmounted) easily, for your convenience. They do require a flat surface, but they are small enough that that likely won’t be too much of a problem. This starter kit is very middle of the pack price-wise but should provide enough power for a small to medium-sized vessel easily. It is also possible to buy extra panels individually should you need them.
Wattage: 400/4 (100 per panel)
2. Nature Power Rigid
The nature power rigid is a large, powerful, single solar panel. If you are looking for the right panels to power your entire boat comfortably, these are the ones for you. They are very large so they will need a large flat surface area. alternatively, they can be hung vertically from rails. This is an inefficient way of using them, so you would need to buy more this way. Nature power makes various solar panels so you could find some smaller ones of the same brand to supplement it. This one is not so easy to install, you might need to hire someone to install it for you.
Wattage: 165
3. Nature Power Monocrystalline
Nature power makes a portable solar panel that fits inside a special briefcase. It is perfect for stowing away easily and only taking it out when it is needed. It is decently powerful considering its portable, but there is the inconvenience factor of having to set it up each time. If you planned to buy the nature power rigid, buying one of these portable panels might be ideal for supplementing your power supply when it is especially sunny. Though, it may be cheaper for you to just fit more of the Nature Power Rigids.
Wattage: 120
Hopefully, you now have a good idea about whether solar panels would be right for you and your sailboat. Sailing is great, but the lack of power at sea can be dreadfully boring. Luckily, there are so many great options available on the market. Not just the ones mentioned above. Buying a solar panel is an investment, the initial cost is minor compared to the steady return from all the savings you will make.
Related Articles
I've personally had thousands of questions about sailing and sailboats over the years. As I learn and experience sailing, and the community, I share the answers that work and make sense to me, here on Life of Sailing.
by this author
Sailboat Upgrades
Most Recent

What Does "Sailing By The Lee" Mean?
October 3, 2023

The Best Sailing Schools And Programs: Reviews & Ratings
September 26, 2023
Important Legal Info
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies.
Similar Posts

How To Choose The Right Sailing Instructor
August 16, 2023

Cost To Sail Around The World
May 16, 2023

Small Sailboat Sizes: A Complete Guide
October 30, 2022
Popular Posts

Best Liveaboard Catamaran Sailboats
December 28, 2023

Can a Novice Sail Around the World?
Elizabeth O'Malley

4 Best Electric Outboard Motors

How Long Did It Take The Vikings To Sail To England?

10 Best Sailboat Brands (And Why)
December 20, 2023

7 Best Places To Liveaboard A Sailboat
Get the best sailing content.
Top Rated Posts
Lifeofsailing.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. This site also participates in other affiliate programs and is compensated for referring traffic and business to these companies. (866) 342-SAIL
© 2024 Life of Sailing Email: [email protected] Address: 11816 Inwood Rd #3024 Dallas, TX 75244 Disclaimer Privacy Policy
- Solar Companies
Solar Energy
The Ultimate Guide to Solar Panels for Boats

by Federica Rustico 8 months ago 15 min
Reading time 15 min
Boats, irrespective of their size, require a substantial amount of energy for various functions such as maintaining autopilot, illuminating navigation lights, and powering communication systems. Harnessing solar energy for boats is a revolutionary step towards clean, reliable, and cost-effective power. They serve as a dependable power source, ensuring the uninterrupted operation of onboard systems and appliances, from navigation and communication devices to lighting and refrigeration.
They also eliminate the need for carrying additional fuel or relying on marina power hookups, enhancing a boat’s autonomy and reducing operating costs. This way, the journey becomes more enjoyable and less restrictive, whether it’s a leisurely sail or an adventurous long-distance voyage. Adopting solar power for boats also has considerable environmental implications. By leveraging this renewable energy source, we can lower carbon footprints and contribute towards a greener, more sustainable future. Solar panels for boats create no noise pollution, making them the perfect energy solution for maintaining the serene ambiance of marine surroundings. Given these numerous advantages, it’s no surprise that more and more boat owners are equipping their vessels with solar panels. This article provides an in-depth look into the world of marine solar panels and sheds light on why they are an excellent choice for energy generation on your boat.
How Do Solar Panels for Boats Work?
The operating principle of solar panels for boats is largely similar to their application on land-based systems, with some specific adjustments to cater to the marine environment. At their core, solar panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells, which are semiconductors that absorb sunlight. This absorbed sunlight triggers the movement of electrons in the semiconductor material, producing an electric current.
When a solar panel is exposed to sunlight, it produces DC (Direct Current) electricity. However, many boat systems and appliances run on AC (Alternating Current) electricity, which requires the DC electricity to be converted via an inverter. In contrast, some boat-specific equipment, like navigation systems, radios, and certain light fixtures, run directly on DC power. One significant component of a solar power system is the charge controller, or solar regulator, which protects the batteries from overcharging by regulating the voltage and current coming from the solar panels.
Solar panels for boats are often coupled with a battery system for energy storage. The most commonly used batteries are lead-acid and lithium-ion, with the latter becoming increasingly popular due to their longer lifespan, high energy density, and decreasing costs. When sunlight is abundant, the solar panels charge these batteries, storing energy that can be used when the sun isn’t shining or during nighttime operations. In marine applications, solar panels need to be durable to withstand the harsh conditions at sea, including exposure to saltwater, strong winds, and extreme temperatures. Therefore, marine solar panels often come with water-resistant and corrosion-resistant features. They also need to be flexible or semi-flexible to conform to the shape of the vessel and must be installed in a way that does not interfere with the boat’s operations. One significant advantage of solar panels for boats is the potential for an infinite range. When sunlight is available, and the energy system, including battery storage, is well-managed, a solar-powered boat could theoretically operate indefinitely without the need for traditional refueling stops.
Solar Power Suitability for Different Boat Sizes
The application of solar energy transcends the limitations of boat sizes. Regardless of the vessel’s dimensions, incorporating solar power has proven to be an efficient and effective solution. Having enough space on your boat that is unobstructed and exposed to sunlight is crucial for the effective functioning of your solar panels. Shading can drastically reduce energy production. Therefore, it’s essential to identify a suitable spot for permanent installation. For boats with limited space, high-efficiency panels that produce more power per unit area are recommended. To determine the appropriate solar panel setup, you can review the power consumption of your appliances or use a battery monitor to assess your boat’s daily energy consumption. This, in conjunction with the size of your boat’s battery, will guide you in choosing the right solar panels.
Small-sized Boats: For small-sized boats, like dinghies or small sailboats, a limited solar setup can provide ample energy. These boats typically have fewer electronic systems, thus necessitating less power. Small, portable, or flexible solar panels can effectively cater to these energy needs without overwhelming the limited space.
Medium-sized Boats: Medium-sized boats, such as cabin cruisers or larger sailboats, often have more extensive electrical systems, including lighting, refrigeration, navigation equipment, and entertainment systems. They require a more substantial solar setup, often necessitating a combination of portable, flexible, and rigid solar panels to meet their energy demands efficiently.
Large-sized Boats: Large-sized boats like yachts or commercial ships have extensive and varied power needs, including substantial lighting systems, comprehensive navigation and communication equipment, HVAC systems, kitchen appliances, and more. These vessels require a significant investment in solar infrastructure. A combination of high-efficiency rigid solar panels, potentially supplemented with flexible panels to utilize available space, can help meet these higher power demands.
It is important to note that while solar power is a fantastic solution for energy generation on boats of all sizes, the individual needs, space availability, and power requirements should always be considered when designing a boat’s solar energy system.
Do you need a charge controller?
While installing a solar panel system on your boat, consider incorporating a charge controller. This device ensures your battery is neither overloaded nor overcharged, thereby prolonging its lifespan. Even though it’s not strictly necessary, a charge controller helps your boat use just the right amount of energy and is generally a good idea to install.
Different Types of Solar Panels for Boats
Boating enthusiasts have a wide range of solar panel options to choose from, each with unique benefits and drawbacks. It’s crucial to choose the right one for your boat, taking into account your specific needs, the vessel’s size, and the available space. Here’s a closer look at the three main types:
Portable Solar Panels
Portable solar panels are growing in popularity among boat owners due to their mobility and easy installation. Their compact design allows for straightforward transportation and setup, making them an excellent option for those seeking a reliable energy source onboard. These solar solutions are not only cost-effective, as they negate the need for fuel, but they’re also maintenance-free and eco-friendly. They produce zero emissions and don’t contribute to noise pollution. When considering portable panels, factors like size, power output rating, and panel quality are critical. It’s equally important to ensure they are waterproof and weather-resistant — panels with an IP68 rating are ideal. Portable panels are an exemplary choice for boaters wanting to keep their ecological footprint minimal while maintaining a steady power supply.
Rigid Solar Panels
Rigid solar panels provide a long-term solution for those wanting a steady power supply for their boat. These are permanently affixed to the boat’s surface and usually composed of robust materials such as tempered glass or aluminum, making them durable. Rigid panels are prized for their efficiency, generating a higher power yield per square inch than portable alternatives. This makes them well-suited for larger vessels or boats with substantial energy needs. Their durability is another significant benefit. These panels can withstand harsh marine conditions, including constant saltwater exposure and extreme weather. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the selected panels are waterproof, with an IP68 rating being optimal. Installation can be complex due to the permanent nature of these panels. Proper mounting is vital to prevent potential damage or loss. Despite this complexity, rigid panels offer room for customization and expansion, as you can form larger arrays by connecting several panels.
Flexible Solar Panels
Flexible solar panels, a recent innovation in solar technology , offer a more adaptable alternative to rigid panels. These consist of lightweight and bendable materials, such as thin-film photovoltaic cells, allowing them to conform to curved or uneven surfaces. The primary advantage of flexible panels is their adaptability. They can fit onto a variety of surfaces, making them an ideal choice for boats, recreational vehicles, and other outdoor applications. Their lightweight design is beneficial where weight restrictions apply.
Flexible panels are also quite durable, capable of enduring severe weather conditions such as hail, rain, and high winds. As with other types, an IP68 waterproof rating is crucial. However, flexible panels do have their drawbacks. They typically generate less power than rigid panels, which can limit their ability to meet high energy demands. They also tend to have shorter lifespans and may need replacing more frequently. In conclusion, flexible panels are best suited for enhancing a rigid solar panel system, allowing you to utilize all available space for solar power generation. They are not intended to be the sole solar solution.
Choosing the Appropriate Solar Panel for Your Boat
The process of choosing the right solar panel for your boat entails several considerations, each essential in ensuring an optimal and efficient solar energy system. Here are the key factors to take into account:
Power Output: First, it’s essential to identify the total energy required by all electrical equipment aboard your boat. This can be achieved by estimating each device’s wattage and operational duration. Following this, calculate the minimum panel output needed to cater to this energy demand by dividing the total watt-hours required by the average number of sunlight hours per day. The power output also influences the choice of your solar battery and system balance since the overall solar power system must be compatible with your photovoltaic (PV) panels. Note that you cannot feed electricity directly from the panels into your boat appliances; a portable power station or a similar solution is needed to store and distribute the energy.
Durability and Weather Resistance: It’s crucial to ensure your chosen solar panels are resistant to impact and adverse weather conditions. An IP68 waterproof rating is highly recommended to protect your panels from wave splashes and rainfall.
Size and Weight: The dimensions and weight of the panels should correspond to your energy needs and the available space on your boat. Aim to choose panels that can meet your energy demands without occupying too much space or adding significant weight.
Installation and Maintenance: Consider the time and cost required for installation and maintenance. Depending on the complexity, you might need professional assistance for installation. Note that not all panels require mounting brackets; portable panels allow for flexibility and cost-saving, bypassing the need for permanent installation.
Brand Reputation: It’s advisable to invest in solar panels from a trusted brand with a proven track record of quality and reliability. Seeking reviews and insights from other boat owners can be beneficial when making your decision.
Cost: Solar panel costs can vary based on size, efficiency, and brand. Keep your budget in mind and aim to select panels that offer the best return on investment.

Top Picks for Solar Panels for Boats
When choosing the perfect solar panel for your boat, several factors should be considered, such as efficiency, cost, ease of installation, and durability. Here, we delve into five top-notch solar panels for boats based on EcoWatch :
1. SunPower 170W Solar Panel
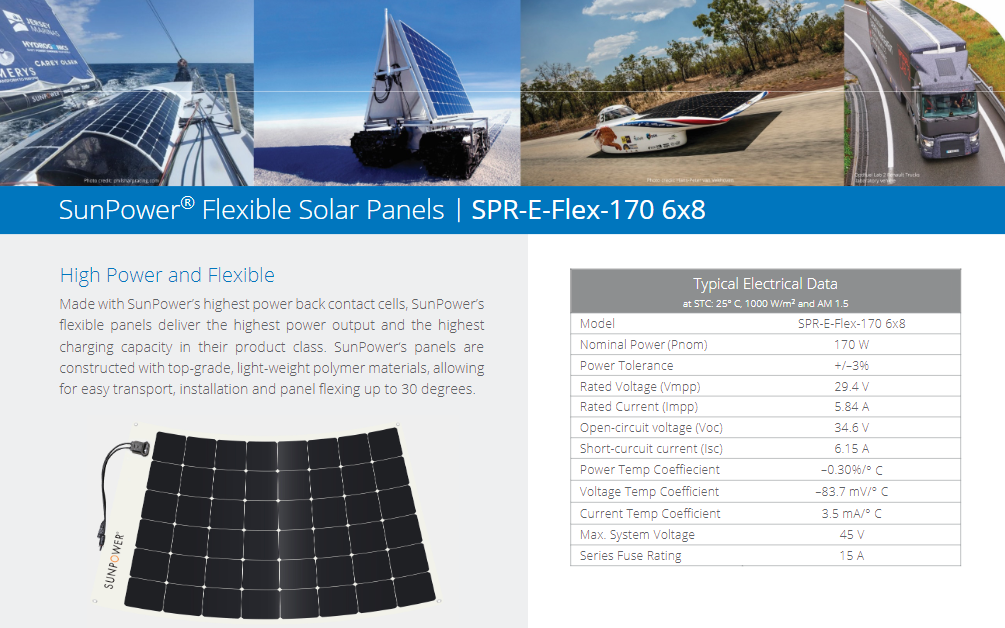
Known for their excellent residential solar panels, SunPower extends their reputation into marine applications with their high-performance 170W solar panel. This unit comes at a higher cost, but its robust power output justifies the price. With this panel, you can comfortably power your boat’s primary battery, emergency backups, and various appliances. Unfortunately, this package doesn’t include a solar charge controller or an inverter, necessitating extra expenses. Nevertheless, the power efficiency makes the investment worthwhile. The panel carries an IP67 waterproof rating, enabling it to survive water immersion up to three feet for about half an hour.
- High-quality materials with optimal power output
- Reliable brand reputation
- Waterproof to a depth of about one meter for 30 minutes
- High cost and no extra equipment included
2. Renogy 100W Flexible Marine Solar Panel
For a reasonable cost, the Renogy Flexible solar panel offers respectable power output and waterproofing. With a capacity of 100W, it’s an excellent choice for moderate power needs, charging various electronic devices. It also includes a controller and wiring, only requiring an inverter and battery to complete the setup.
- Good power output with an IP67 waterproof rating
- Comes with a controller and wiring
- Renowned brand
- It costs more than some other options and doesn’t include a battery or inverter
3. EcoWorthy 25W Solar Panel Kit
For those new to solar energy, the EcoWorthy solar panel kit makes a great entry point. The kit includes MC4 connectors, making installation quick and hassle-free. However, its smaller power output restricts its use to backup power or charging smaller electronics. With an IP65 rating, it can endure water submersion up to five feet for half an hour.
- IP65 waterproof rating
- Highly affordable
- No included battery or inverter
- Lower power output compared to top picks
4. NewPowa 30W Solar Panel Kit
The NewPowa solar panel kit is a cost-effective option that includes a panel, a controller, and wiring. With a 30W output, it’s well-suited for light-duty use. Its IP67-rated panels and controller make it a safe choice for various boat types.
- Affordable with an IP67 waterproof rating
- Easy installation
- Low power output
- Battery and inverter not included
5. TopSolar Monocrystalline Solar Panel Kit
If you’re a beginner seeking a backup energy source, the TopSolar kit is an excellent choice. While its 20W output limits its use to emergency power, it’s easy to install and comes at a lower price. Though no specific IP rating is provided, the manufacturer claims it is waterproof.
- Affordable and easy to install
- Includes a controller and wiring
- Suitable for backup power
- Doesn’t include a battery or inverter
- No specific IP rating
- Limited power output
The Benefits of Installing Solar Panels for Boats
Opting to install solar panels on your boat opens a gateway into the realm of clean energy, significantly improving your boating experience in multiple ways. There are a few key use cases that help illustrate the value of adopting a solar panel system on your boat. These scenarios do not only help determine the necessity of solar panels for your vessel, but they also aid in identifying the most suitable and cost-efficient system for your needs. Below, we delve into the different motivations for embracing solar power on your boat.
Emergency Equipment Charging
The unpredictable nature of sea adventures underscores the importance of having reliable emergency equipment on board. Whether you find yourself in a situation where you’ve run out of fuel, encountered a mechanical issue, or faced with other unforeseen complications preventing a safe return to shore, having a dependable communication device can be a lifesaver. Many boats are equipped with emergency systems such as radio systems, satellite phones, or regular phones. However, these devices are reliant on power. By integrating a solar system into your boat, you can ensure a continuous power supply for these devices, providing peace of mind during your sea excursions.
Recreational Equipment Charging
Beyond emergencies, the utility of solar panels extends to everyday recreational needs. Having the ability to charge devices like smartphones, e-readers, speakers, and other entertainment equipment can enhance your sea experience. This aspect gains significance, especially if you plan on spending multiple days at sea and don’t want to deplete your boat’s batteries. By allowing your solar system to handle the power needs of your recreational equipment, you ensure that your boat’s batteries remain sufficiently charged for critical functions such as lighting, navigation tools, and starting your boat’s engine.
Low Maintenance
Solar systems for boats are generally hassle-free once installed, requiring only periodic maintenance to ensure safety and optimal energy production. Approximately every six months, it’s advisable to clean your solar panels by rinsing them with water to remove any accumulation of dirt or salt. This simple routine helps maintain the panels’ efficiency by maximizing energy generation. During these semiannual checks, it’s also crucial to inspect the system’s wires and connectors for signs of corrosion, especially if your boat operates in saltwater environments. Checking for intact connections after major storms is a prudent practice to avoid battery charging issues, which could pose a problem if backup power is ever needed. Solar systems on boats are generally considered safe. There is a minimal risk of fire, but regular maintenance and system checks can effectively mitigate such risks. Therefore, while the maintenance required is not extensive, its impact on safety and efficiency is significant.
Wrapping Up
Installing solar panels on your boat presents an array of benefits that enhance your boating experience while also contributing to the preservation of our planet. From powering emergency and recreational equipment, improving your quality of life at sea, offering a low-maintenance energy solution, to providing silent operation, the advantages of solar power on the water are undeniable. Choosing the right solar panels for your boat might require some careful consideration and calculations, but the payoff in terms of cost savings, environmental impact, and overall comfort is certainly worth the investment. With the advancements in solar technology and growing awareness of sustainable practices, it’s an opportune time to harness the power of the sun and sail towards a greener future.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Do i need a charge controller for my boat’s solar panel system.
While not strictly necessary, a charge controller helps regulate the voltage and current coming from the solar panels, protecting the batteries from overcharging and prolonging their lifespan.
Do solar panels require regular maintenance on boats?
Solar panels on boats require minimal maintenance. Periodic cleaning to remove dirt, salt, or debris and checking connections for any signs of damage or corrosion are recommended to ensure optimal performance.
You might also like
Stay a while and read more posts like this

Renewable Energy , Solar Energy , Solar Energy Basics
Top 10 solar panel suppliers to try out in 2024
Kristina 1 month ago
As the world continues to move towards renewable energy sources, solar power is becoming increasingly popular. Solar panels are a great way to reduce your energy costs...

Solar Energy , Solar Financing
Top 15 Solar Panel Companies in Australia
Bisera Apostolova 6 months ago
Australia’s sun-drenched landscape is more than just picturesque – it’s a powerful catalyst for an impressive solar revolution. Rising as a leading...

Energy Efficiency , Solar Energy , Solar Energy Basics , Solar Financing
How Many Solar Panels Does Your Home Need?
Bisera Apostolova 7 months ago
Many people find themselves wondering, “How many solar panels do I need to power my house?”. In this era of increasing environmental awareness and...
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
The Boat Galley
making boat life better

Installing Solar Panels – Our Choices
Published on January 26, 2022 ; last updated on May 1, 2023 by Carolyn Shearlock

Our second solar panel arrived and we installed it! When I posted about it on Instagram , I got several questions about what we’d gone with and the parts we needed.
When we started the project, we planned to use a 225-watt rigid panel. As we started to build the mount for it, we discovered that with the curve to our hard dodger area, we’d have to raise the panel to the point where it would be in the way of our boom. Back to the drawing board.
After evaluating our options, we decided on a flexible 145-watt panel. It turned out to be out of stock but the company offered us a semi-rigid 150-watt panel that was exactly the same size. It’s made of A+ SunPower cells by Custom Marine Products . Although we don’t intend to, this panel could be walked on and it will flex to follow a 5-degree curve – exactly what we needed for our location. And the semi-rigid is actually better for placing on a deck, as it’s designed with proper insulation.
SunPower makes great solar panels and also sells cells to other manufacturers. But not all SunPower cells are created equal! They have several different grades, with A+ being the best. This translates into more power per square inch AND more power at low sun angles and on cloudy days. Since we are very limited on space for solar, we need the highest efficiency we can get.
To stay out of the way of the boom, we taped the panel to the deck using 3M VHB (very high bond) tape – it should be able to withstand a hurricane as it’s used to attach trim to cars. We bought the tape on Amazon – see it here . Had we used a flexible panel, we planned to put insulation under the panel; this was impossible using the semi-rigid panel as the panel was too stiff to allow the tape to make good contact with the deck with the insulation there. Custom Marine Products said that the lack of insulation won’t cause a problem with the panel output; it’s designed to be placed directly on deck.
The biggest problem in putting it on deck was that our gelcoat is oxidized and the tape would not bond well if we didn’t get down to good gelcoat. That meant that Dave had to wetsand the area where the tape would sit.
We have a Victron battery monitor ( read about it here ) and Victron solar controllers are extremely good. The current “best practice” for solar installations is to put each panel on its own charge controller. We knew we were going to put the new panel on a Victron SmartSolar controller; we decided to replace our existing (non-Victron) controller for the other panel with a Victron SmartSolar as well so they would all talk to each other via Bluetooth and work more efficiently. We bought the controllers from Amazon – see them here and here .
And finally, we needed wire. We bought pre-made ones – 10 gauge AWG – with solar-standard MC4 connectors on one end from Solar Marine Supply – the only marine-grade tinned wire I could find, although I’m sure other suppliers exist. No connectors are needed where the wire goes to the controller. We also bought 5 feet of 10 gauge wire to go from the controller to the batteries, and used a few ring terminals from our onboard supply to make the connections at the battery end.
As boat projects go, it went remarkably well. We tackled different phases on different days and got the charge controllers installed and the wires pulled before the panel even got here. Prepping the panel and deck, and actually taping the panel down, took about 2-1/2 hours with most of that being wetsanding the deck.
The result? We now have more than enough solar power for my energy-hog computer, a refrigerator, freezer and everything else on board. Instead of running a deficit every day, the total 495 watts from the old and new panels have our batteries floating every day.
Be sure to subscribe to The Boat Galley newsletter to keep up with what we’re up to and get helpful tips and encouragement from the water.

And check out our other courses and products

Find this helpful? Share and save:
- Facebook 105
- Pinterest 22
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Each week you’ll get:
• Tips from Carolyn • New articles & podcasts • Popular articles you may have missed • Totally FREE – one email a week
SUBSCRIBE NOW
- Questions? Click to Email Me
- Visit Our Store

- Solar accessories
- Solar panels for boats: What..
Solar panels for boats: What you need to know
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to Facebook
- Kerry Thoubboron
As subject matter experts, we provide only objective information. We design every article to provide you with deeply-researched, factual, useful information so that you can make informed home electrification and financial decisions. We have:
Sourced the majority of our data from hundreds of thousands of quotes through our own marketplace.
Incorporated third-party data and information from primary sources, government agencies, educational institutions, peer-reviewed research, or well-researched nonprofit organizations.
Built our own database and rating system for solar equipment, including solar panels, inverters, and batteries.
We won't charge you anything to get quotes through our marketplace. Instead, installers and other service providers pay us a small fee to participate after we vet them for reliability and suitability. To learn more, read about how we make money and our Editorial Guidelines .
)
Owning a boat can be expensive; you have to pay an upfront cost to purchase it, and you'll also have to spend money on maintenance and fuel charges. Solar panels may be the answer if you're looking for a reliable, cost-effective way to power your boat.
- 100% free to use, 100% online
- Access the lowest prices from installers near you
- Unbiased Energy Advisors ready to help
How do solar panels work on boats?
Solar energy systems on boats work similarly to other portable , off-grid systems. There are four important components to a marine solar panel system:
Solar panels
Charge controller
Most marine solar panel systems require charge controllers to prevent the batteries from receiving more voltage than they can handle. Without charge controllers, you risk overcharging and damaging your battery.
Depending on your boat's electrical setup and the appliances you need to power, you may also need an inverter to convert direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Some boat electronics use DC and don't need an inverter. However, if you use everyday household appliances on your boat (i.e., TVs, microwaves, or hairdryers), they likely run on AC electricity, and you'll need an inverter.
You can buy all of these components separately, but you can find solar panel kits that include some or all of the necessary parts. Some marine solar panel kits include the wires, cables, and mounting equipment required to get your boat's solar panel system up and running.
Best solar panel kits for boats
Below are a few products tailored to off-grid marine solar power systems.
Boat solar panel options
If your solar panel kit does not include an inverter or charge controller, you must buy those components separately. Battery storage products occasionally have built-in inverters and/or charge controllers.
Should you install solar panels on your boat?
There are numerous benefits to powering your boat with solar energy. One of the most attractive benefits of marine solar power systems is the monetary savings. You'll need to invest money upfront to purchase solar equipment; however, once it's up and running, you'll generate free electricity for your boat. Alternatives to electrifying your boat, like gasoline-powered generators, require purchasing fuel on an ongoing basis. Switching to solar power can reduce these purchases while protecting you against rising fuel costs.
Another benefit of marine solar panel systems is the quietness of operation. Running a generator can be a noisy disturbance for those going out on the open water to experience nature. Powering your boat with solar allows you to enjoy peace and quiet without losing power.
Furthermore, you can also safely generate electricity and charge your battery with solar power while you're away from your boat. This isn't feasible with generators - running a generator requires manual operation and monitoring. With solar panels, you can produce usable electricity during the day and then use it for weekend boating adventures.
However, there can be obstacles to installing solar on a boat, perhaps the largest of which is available space. Ideally, your solar panels can be installed in an area with uninterrupted sunshine. Depending on your boat type, this space may be easy or difficult to come by. While you likely get a lot of sun out on the water, the area may be too small or have too many obstacles that make fitting the number of solar panels necessary to generate your electricity needs difficult.
Consider your boat's deck or canvas when you're looking for spots to install a marine solar panel system. Remember that the positioning of your solar panels will also impact the type of equipment you should purchase – you may be able to use traditional monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels if you're installing on a fixed, rigid section of your boat. However, if your only open space available isn't suitable for fixed mounting, installing lower-efficiency flexible solar panels may be a better option. Some flexible solar options have an adhesive backing, so you won't need to worry about the constraints of traditional mounting and racking materials.
How many solar panels do you need for your boat?
Unsurprisingly, a yacht has very different power requirements than a sailboat. The number of solar panels you'll need for your boat not only depends on the type and size of your boat, but also the quality of the equipment you choose, how many sun-hours the boat sees, and the amount of electricity you require. Some boats can get by with one 100-watt solar panel (or even smaller), while others need a multi-panel setup.
Calculating your electricity load is the first step in determining how many solar panels you need. Below are some common appliances you may use on your boat and what they draw for power.
How many solar panels do you need for common appliances?
The last column of the above table is the amount of energy you'll consume in watt-hours running each appliance for the number of hours identified in column three. One 100-watt solar panel that receives direct sunlight for 5 hours will produce approximately 500 Wh of electricity (5 hours x 100 W = 500 Wh). Not considering conversion losses, that's enough electricity to power a mini-fridge for 24 hours or power a boat's GPS display for 10 hours. Running all of the appliances above for everyday use will require multiple 100-watt solar panels or fewer higher-wattage panels.
Install solar to save on electric bills
You can save money by installing a marine solar panel system, but you'll save even more by installing solar on your home or business. If you want to evaluate your solar options, check out the EnergySage Solar Marketplace . You can receive up to seven custom solar quotes from local installers to compare. You can also try our solar calculator for a quick estimate of solar costs and savings on your property.
Create your own clean energy with solar panels.
Enjoy the benefits of solar without rooftop panels.
Explore heat pumps, the latest in clean heating & cooling technology.
See solar prices near you.
Enter your zip code to find out what typical solar installations cost in your neighborhood.
- Our offerings
- Community solar
- Heating & cooling
- Backup power
- EV charging
- For your business
- Other energy options
- Solar calculator
- Solar rebates
- Help center
- Home solar guide
- Market intel
- Refer a friend
- Mission & values
- How it works
- Editorial guidelines
- Work with us
- Solar & HVAC installers
- Corporate partnerships
- Community programs
- Utility programs
ENERGYSAGE is a registered trademark and the EnergySage logo is a trademark of EnergySage, Inc. Other trademarks are the property of either EnergySage, Inc. or our licensors and are used with permission.
© Copyright 2009-2024 EnergySage, Inc. All rights reserved.
Learn more about our success working with the U.S. Department of Energy.

Installing Solar Panels on a Boat
Installing solar panels on a boat can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to power your boats appliances whilst on the water. With the right equipment and knowledge, it is possible to install solar panels on your boat yourself, without the need for professional help.
In this blog post, we will provide a step-by-step guide for installing solar panels on your boat, including information on what equipment you will need, how to prepare your boat, and how to test and maintain your solar panel system.

Choosing the Right Solar Panels and Equipment for Your Boat
Before you begin installing solar panels on your boat, you will need to choose the right equipment .
Power Required
The first step is to determine how much power you will need to generate. This will depend on the size of your boat and the type of and number of appliances you will be running. You will also need to consider the amount of sunlight you will be exposed to and the amount of space you have available on your boat.
Once you have determined your power needs, you can choose the right solar panels and equipment.
Solar Panels
When it comes to solar panels, you will have a choice between polycrystalline and monocrystalline panels.
Polycrystalline panels are generally less expensive, but they are also less efficient.
Monocrystalline panels are more expensive, but they are more efficient and will generate more power per square foot.
You will also need to consider whether you want to install a solar panel that is Rigid to allow circulation behind the panels, or Flexible or Semi-Flexible panels to follow the contours of your boat.
Charge Controller, Inverter and Battery
In addition to solar panels, you will need to purchase an Inverter, charge controller , wiring, and a Lithium-ion battery bank . The charge controller will help regulate the power flowing into the batteries, while the wiring will connect the solar panels to the charge controller and the battery bank. The battery bank will store the power generated by the solar panels.
Preparing Your Boat for Solar Panel Installation
Preparing your boat for solar panel installation is an important step in the process, as it will ensure that the installation is done correctly and that the solar panels will be able to function efficiently.
There are several things to consider when preparing your boat for solar panel installation, including the location of the panels, the amount of sunlight the boat will receive and the amount of space available on the boat.
Determining the location for the solar panels is one of the first steps in preparing your boat for installation. The solar panels should be mounted on a surface that receives the most sunlight, such as the roof of the boat.
It’s also important to consider the location of other equipment and structures on your boat, such as antennas or vents, to ensure that the panels will not be in the way or obstructed.
The location of the panel should be such that the panel is not in the way of any other equipment or structures on your boat.
The amount of sunlight that the boat will receive is also an important consideration when preparing your boat for solar panel installation. The solar panels will generate more power when they receive more sunlight.
Therefore, it’s important to install the panels in a location that will receive maximum sunlight exposure. This will allow the solar panels to generate more power and reduce the need for external power sources.
The amount of space available on the boat is also an important consideration when preparing your boat for solar panel installation. The solar panels need to be installed in an area that is free from debris and that is large enough to accommodate the panels.
Additionally, the area should be free from potential shading, such as from overhead lines or nearby buildings when moored. This will ensure that the solar panels receive maximum sunlight exposure and that they are able to function efficiently.
By following these guidelines for preparing your boat for solar panel installation, you will be able to ensure that the installation is done correctly and that the solar panels will be able to function efficiently. This will allow you to enjoy the benefits of solar power on your boat for a long time to come.
Step-by-Step Guide for Mounting Solar Panels on Your Boat
Mounting the solar panels on your boat is an important step in the installation process. The panels need to be securely mounted and angled in the direction that receives the most sunlight in order to be effective. Here is a step-by-step guide for mounting solar panels on your boat:
Step 1: Determine the location for the solar panels.
The first step is to determine where on your boat the solar panels will be installed. Ideally, the panels should be mounted on the roof or on a surface that receives the most sunlight. You should also consider the location of other equipment and structures on your boat, such as antennas or vents, to ensure that the panels will not be in the way or obstructed.
Step 2: Measure and mark the mounting points.
Once you have determined the location for the solar panels, measure and mark the mounting points. This will ensure that the panels are installed in the correct position and at the correct angle.
Step 3: Install the brackets.
The next step is to install the brackets that will hold the solar panels in place. The brackets can be mounted using screws, bolts, or adhesive. It is important to ensure that the brackets are securely attached to the boat and that they are level.
Step 4: Install the solar panels.
With the brackets in place, you can now install the solar panels. The panels will typically come with pre-drilled holes that align with the brackets. Use the screws or bolts provided to attach the panels to the brackets.
Step 5: Adjust the angle of the panels.
Finally, adjust the angle of the panels to ensure that they are pointing in the direction that receives the most sunlight. This can typically be done by adjusting the angle of the brackets or by using an adjustable mount.
It is important to note that the solar panels should be installed in a way that allows for easy maintenance and cleaning. Additionally, it’s important to make sure that the panels are not in the way of any other equipment or structures on your boat. By following this step-by-step guide, you will be able to mount the solar panels on your boat securely, and at the right angle to ensure maximum efficiency.
Wiring and Connecting the Solar Panels to Your Boat’s Power System
Wiring and connecting the solar panels to your boat’s power system is an important step in the installation process.
This involves running the wiring from the panels to the charge controller and then from the charge controller to the battery bank. This will ensure that the power generated by the solar panels is properly regulated and stored.
Here are some important things to keep in mind when wiring and connecting your solar panels to your boat’s power system:
It is important to use marine-grade wiring, as it is designed to withstand the harsh conditions of a marine environment. This includes exposure to saltwater and UV rays. The wiring should be properly rated for the current and voltage of your system.
When running the wiring from the solar panels to the charge controller, it is important to use appropriate conduit or protective covering to protect the wiring from the elements. This can include PVC conduit, flexible conduit, or wire loom.
When connecting the solar panels to the charge controller, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and to make sure that the polarity is correct. The charge controller will regulate the power flowing into the batteries, so it is important to ensure that it is properly connected.
When running the wiring from the charge controller to the battery bank, it is important to use the correct size and type of wire . The wire should be properly rated for the current and voltage of your system. It is also important to use appropriate conduit or protective covering to protect the wiring from the elements.
Finally, it is important to properly ground the system to prevent electrical shock and damage to the equipment. This can typically be done by connecting the negative terminal of the battery bank to the boat’s ground.
By following these guidelines, you will be able to wire and connect your solar panels to your boat’s power system safely and effectively, ensuring that the power generated by the solar panels is properly regulated and stored.
Testing and Maintaining Your Solar Panel System
Testing and maintaining your solar array is an important step in ensuring that it continues to function at optimal levels. Proper testing and maintenance will ensure that the system is working properly, and that any issues are identified and resolved quickly.
Here are some important things to keep in mind when testing and maintaining your solar panel system:
Testing the system includes checking the voltage and current flowing through the system, as well as checking the battery charge level. These readings can be taken using a multimeter or other test equipment. If the readings are not within the expected range, it may indicate a problem with the system and further troubleshooting may be needed.
Regular cleaning of the solar panels is important to ensure that they are able to generate power efficiently. The panels should be cleaned of dirt, dust and bird droppings, which can reduce their effectiveness. A mild detergent and water can be used to clean the panels, and they should be wiped dry to prevent water spots.
Checking the wiring and connections is important to ensure that they are secure and not corroded. Loose connections or corroded terminals can cause the system to malfunction, and should be addressed immediately.
Checking the battery charge level is important to ensure that the battery bank is properly charged and that the batteries are not overcharged or undercharged. This can help prevent damage to the batteries and prolong their lifespan.
By following these guidelines for testing and maintaining your solar panel system, you can ensure that it is working properly, and that any issues are identified and resolved quickly. This will allow you to enjoy the benefits of solar power on your boat for a long time to come.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with DIY Solar Panel Installations on Boats
Troubleshooting common issues with DIY solar panel installations on boats is an important step in ensuring that the system is working correctly.
Despite your best efforts, you may encounter issues with your solar panel system that need to be addressed. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Low voltage or current: This can be caused by loose connections or damaged wiring. Check the wiring and connections to ensure that they are secure and not corroded. Additionally, check the charge controller to ensure that it is functioning correctly.
- Low battery charge level: This can be caused by a malfunctioning charge controller or a problem with the battery bank. Check the charge controller to ensure that it is functioning correctly and check the battery bank to ensure that the batteries are properly charged.
- Shading on the solar panels: This can occur if nearby buildings or other structures cast shadows on the panels, reducing their effectiveness. To resolve this issue, you may need to adjust the angle of the panels or move them to a different location on the boat.
- Faulty equipment: If the issue persists after checking the connections, wiring and charge controller, it may be necessary to replace faulty equipment.
It is important to note that these are common issues and there could be other issues specific to your solar panel system. It is always a good idea to consult the manufacturer’s manual, or an expert in the field, if you are unsure of how to troubleshoot the issue.
In conclusion, a DIY installation on a boat can be a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to power your vessel while on the water. By choosing the right equipment and following a step-by-step guide, you can install solar panels on your boat yourself, without the need for professional help.
One of the main benefits of a DIY solar panel installation is cost savings. Installing solar panels on your boat can be a significant investment, but by doing it yourself, you can save money on labor costs. Additionally, a DIY installation can help you to better understand and maintain your solar panel system, which can save you money on future repairs and maintenance.
Another benefit of a DIY solar panel installation is independence from external power sources. By generating your own power, you will no longer have to rely on shore power or generators to power your boat. This can be especially beneficial for boaters who spend a lot of time on the water and want to be self-sufficient.
Finally, a DIY solar panel installation can have a reduced environmental impact. Solar energy is a clean, renewable energy source that does not produce any greenhouse gases or pollutants. By generating your own power, you can reduce your carbon footprint and do your part to help the environment.
Similar Posts

Solar Charge Controllers: Maximizing Solar Power Efficiency
MPPT and PWM solar charge controllers: They might sound like a handful of technical jargon, but trust me, they are the unsung heroes of solar power efficiency. Want to know why? Because they help you get the most out of your solar panels, save you money, and save the planet – allegedly. Keep reading to…

10 Best Solar Powered Security Cameras 2024
Solar powered security cameras are becoming increasingly popular due to the many benefits they offer. They are environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and easy to install. Solar powered security cameras are the perfect way to keep an eye on your home or business while helping to protect the environment. Used in conjunction with sets of solar security…

Renewable Energy: The Green Options
Renewable energy is defined as an energy that is generated from natural energy sources that are continually replenished. It includes renewable sources such as solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and biomass. Renewable energy is important because it provides a clean energy source of power that does not contribute to climate change or global warming. Additionally, it…

12 Ways Solar Power Can Be Used in 2023
Solar Power is becoming more and more popular, accessible and affordable. Advance in renewable technology, especially Solar Power, has created a suitable alternative energy source that can be harnessed to power many different everyday applications, thereby decreasing energy costs, creating a means to live a different lifestyle and of course, reducing your carbon footprint. Technology…

MPPT vs PWM Solar Charge Controllers: Understanding the Differences
As solar technology continues to improve, creating new ways to convert photovoltaic energy into electricity, the importance of understanding the differences between MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) solar charge controllers becomes increasingly critical. There are many similarities but also some fundamental distinctions between these two very important components when it…

11 Best MPPT Solar Charge Controllers 2023
MPPT Solar Charge Controllers – the unsung heroes of the solar power world. These devices might not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think about harnessing the power of the sun, but trust me, they are important. In short, a MPPT solar charge controller regulates the amount of energy that flows…
One Comment
- Pingback: 7 Best Solar Panels for Boats 2023 - Mark Green World
Comments are closed.

INSTALLING SOLAR PANELS ON A BOAT

Solar panel technology has improved tremendously in the past few years. The panels are highly efficient, flexible, walkable and comes with very low weight. They can be attached to the deck or canvas with fasteners such as Tenax/Loxx, using velcro or glue. Some panels are suitable for boom/mast assembly as well. The latest technology allows also putting panels onto sails .
Oceanvolt uses solar panels from Sunbeam . The panels have proven to be reliable and efficient with good value for money.
The panels can charge either 12/24 VDC house battery or the 48 VDC propulsion battery bank. Charging the house battery bank is no different than in normal installation: a charge controller must be added compatible with the panel power. Charging a 48VDC lithium ion propulsion battery bank is however a little more challenging.
Lithium Ion batteries require careful balancing to remain fully operational. The balancing is a slow process and thus can be completed only with shore power charger or with solar power: a generator or regeneration under sails can never reach the 100% level as the process is designed to cut off the charge at 80-90%. In applications where shore power is not available some solar power is a requirement – Oceanvolt recommends minimum 200 W of solar panels in this case.
Using solar panels with Oceanvolt propulsion system requires either Victron MPPT series charge controller or Genasun Li-Ion Boost controller. The former is used where the amount of panel voltage is 60-150 VDC/70 amps, the latter if the panel voltage is less than 60 VDC (max 8 amp). The advantage of the Victron MPPT is that it does not require an external balancing relay (the Genasun requires this) & it is fully compatible with the Victron GX which allows remote monitoring of the solar yield.
Panels on the same side of the sun should be connected into the same group if connected in series. Otherwise shading will have significant effect on the power. However, two panels on the opposite sides of the boat can be connected in parallel: one is likely to be on the sun when the other is not.
There is no upper limit for the amount of panels. The number of MPPTs depend on the amount of panels. Oceanvolt has done boats with up to 5 kW (50x 100 W) panels.
SOLAR MOTORING
It is possible to do solar motoring with the Oceanvolt system. The system shows the current yield from the panels and the motor speed can easily be adjusted to match the solar power to get independency. Typically 1 kW of solar gets about 3 knots for a boat suitable for Oceanvolt motors.

Written by admin
View all posts by: admin
Comments are closed.
- Sponsorships
- Hydrogenerator

- Forums New posts Unanswered threads Register Top Posts Email
- What's new New posts New Posts (legacy) Latest activity New media
- Media New media New comments
- Boat Info Downloads Weekly Quiz Topic FAQ 10000boatnames.com
- Classifieds Sell Your Boat Used Gear for Sale
- Parts General Marine Parts Hunter Beneteau Catalina MacGregor Oday
- Help Terms of Use Monday Mail Subscribe Monday Mail Unsubscribe
Flexible Solar Panel on Bimini - Backing?
- Thread starter Monterey385
- Start date Apr 3, 2021
- Forums for All Owners
- Ask All Sailors
Monterey385
I am planning to install two Renogy 175 watt flexible solar panels on my bimini this summer. After numerous detailed conversations with several local canvas professionals and marine electronic professionals, the consensus is that I should keep it simple for the first few months if not the first entire season. By simple, they are suggesting that I stick with bungee cords to make it simple to remove the panels for various reasons (high wind events, extended periods at dock, etc.). My question, what are the group's recommendations to mitigate chafe under the panels? I have seen references to a variety of fabrics and liners but am uncertain right now about the best options ... thoughts?
Sailrite has a decent how - to video on attaching a flexible solar panel. Backing matl. for chafe ,matl. list and details. I am planning on the install myself in the near future.
Joe23455 said: Sailrite has a decent how - to video on attaching a flexible solar panel. Backing matl. for chafe ,matl. list and details. I am planning on the install myself in the near future. Click to expand
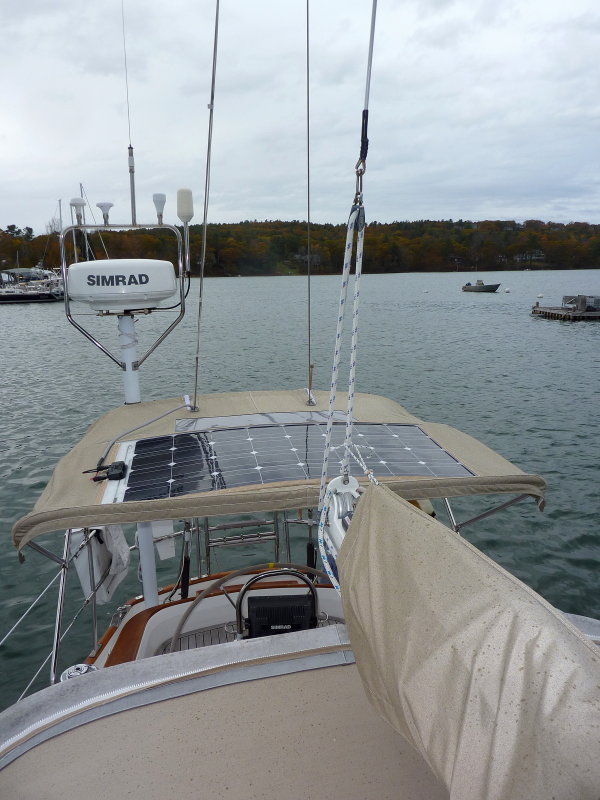

Installing Semi-Flexible Solar Panels - Marine How To
dlochner, thank you for posting the Solbian how to. I saw that a while back and could not locate where I had seen it ! I like the velco details. Sailrite does not use that detail and I am a little leary of snaps only. Adhesive I think.. would cause heat buildup and ruin the bimini surface forever if the adhesive was also used on that. Just my thoughts in researching the install. Doing the same homework.... The bungee would work for a while but not UV tolerant, might last a season ?.
dlochner said: Here's another option. Installing Semi-Flexible Solar Panels - Marine How To Panel Layout In this article we used a Solbian panel that is no longer in production. Solbian solar panels are a unique product that fill a great niche for the marine market. They are really the absolute top tier semi-flexible panel marinehowto.com Click to expand
Joe23455 said: The bungee would work for a while but not UV tolerant, might last a season ?. Click to expand
McMaster-Carr
We used 3M dual lock on our panels the last couple of years. My wife sewed the non stick dual lock to the bimini fabric and we used the self adhesive type on the panels. It worked well. We're having all new canvas installed on the boat this year, and our canvas guy is using zippers for the new canvas (like was pictured a few posts above).
THECUSCUS said: [URL="https://forums.sailboatowners.com/media/northernstarsolar1.26195/"] [/URL] Have had a Solbian panel held on to my bimini with zippers for the past 4 years with no problems. It doesn't go over any of the framework. Zippers on two long sides only, allows air to flow in on the short sides. Super easy to install and remove when needed. Have never felt excessive heat underneath. Click to expand
DArcy said: How is the zipper attached to the panel? Click to expand
I attach1/4" thick clear twin-wall polycarbonate panels to the back of the flexible panels. You can get these at Home Depot. These are used for green house windows. They are extremely light and are almost invisible under the panel. I attached the panel to the polycarbonate using 1" bits of 3M VHB tape. The polycarbonate is flexible enough to follow the curve of the bimini but stiff enough to protect the flexible panel from flexing too much. This also insulates the bimini fabric from the hot panel. With the polycarbonate you can also run the panels across the bimini bows. I sewed little sunbrella loops to the bimini and then simply tie the panel to the loops with thin dyneema cord. I've had no problem with the panels lifting in the wind. They just lie there even in 40knot winds. Also no visible chafe in three years on the sunbrella - which makes sense as the polycarbonate is very smooth (I did wrap chafe tape along the edges). If I need to take the bimini off for a storm, I just cut the cord, store the panels, and then retie with new cord after the storm (BTW, install some form of wire connector so you can put your panels below during a storm). Be extremely careful handing the flexible panels. Don't let them "flop" around when installing. Bending one just a little too much will break a solder joint inside rendering it useless. Also, be sure you have a good warranty for your panels (Renogy does well) and that you have an easy way to take a panel off to send back for a warranty replacement. About half of these panels fail in two years - especially in Florida and southern areas.
Attachments

- This site uses cookies to help personalise content, tailor your experience and to keep you logged in if you register. By continuing to use this site, you are consenting to our use of cookies. Accept Learn more…

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

Join NASA in Celebrating Earth Day 2024 by Sharing a #GlobalSelfie

NASA Selects New Aircraft-Driven Studies of Earth and Climate Change

The Ocean Touches Everything: Celebrate Earth Day with NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Astronauts Home
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Work Underway on Large Cargo Landers for NASA’s Artemis Moon Missions

Mars Science Laboratory: Curiosity Rover

NASA Open Science Initiative Expands OpenET Across Amazon Basin

NASA Motion Sickness Study Volunteers Needed!

Students Celebrate Rockets, Environment at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center

AI for Earth: How NASA’s Artificial Intelligence and Open Science Efforts Combat Climate Change

Sols 4159-4160: A Fully Loaded First Sol

NASA’s Juno Gives Aerial Views of Mountain, Lava Lake on Io

Hubble Captures a Bright Galactic and Stellar Duo

NASA’s TESS Returns to Science Operations

Astronauts To Patch Up NASA’s NICER Telescope

Hubble Goes Hunting for Small Main Belt Asteroids

NASA’s Near Space Network Enables PACE Climate Mission to ‘Phone Home’

NASA Photographer Honored for Thrilling Inverted In-Flight Image

NASA Langley Team to Study Weather During Eclipse Using Uncrewed Vehicles

ARMD Solicitations

Amendment 10: B.9 Heliophysics Low-Cost Access to Space Final Text and Proposal Due Date.

Tech Today: Taking Earth’s Pulse with NASA Satellites
Earth Day 2024: Posters and Virtual Backgrounds

NASA Names Finalists of the Power to Explore Challenge

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos

Resultados científicos revolucionarios en la estación espacial de 2023
Nasa next-generation solar sail boom technology ready for launch.

Tara Friesen
Nasa’s new lightweight sailor , enabling future solar sails.
Sailing through space might sound like something out of science fiction, but the concept is no longer limited to books or the big screen. In April, a next-generation solar sail technology – known as the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System – will launch aboard Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand. The technology could advance future space travel and expand our understanding of our Sun and solar system.
Solar sails use the pressure of sunlight for propulsion, angling toward or away from the Sun so that photons bounce off the reflective sail to push a spacecraft. This eliminates heavy propulsion systems and could enable longer duration and lower-cost missions. Although mass is reduced, solar sails have been limited by the material and structure of the booms, which act much like a sailboat’s mast. But NASA is about to change the sailing game for the future.
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System demonstration uses a twelve-unit (12U) CubeSat built by NanoAvionics to test a new composite boom made from flexible polymer and carbon fiber materials that are stiffer and lighter than previous boom designs. The mission’s primary objective is to successfully demonstrate new boom deployment, but once deployed, the team also hopes to prove the sail’s performance.
Like a sailboat turning to capture the wind, the solar sail can adjust its orbit by angling its sail. After evaluating the boom deployment, the mission will test a series of maneuvers to change the spacecraft’s orbit and gather data for potential future missions with even larger sails.
“Booms have tended to be either heavy and metallic or made of lightweight composite with a bulky design – neither of which work well for today’s small spacecraft. Solar sails need very large, stable, and lightweight booms that can fold down compactly,” said Keats Wilkie, the mission’s principal investigator at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. “This sail’s booms are tube-shaped and can be squashed flat and rolled like a tape measure into a small package while offering all the advantages of composite materials, like less bending and flexing during temperature changes.”

After reaching its Sun-synchronous orbit, about 600 miles (1,000 kilometers) above Earth, the spacecraft will begin unrolling its composite booms, which span the diagonals of the polymer sail. After approximately 25 minutes the solar sail will fully deploy, measuring about 860 square feet (80 square meters) – about the size of six parking spots. Spacecraft-mounted cameras will capture the sail’s big moment, monitoring its shape and symmetry during deployment.
With its large sail, the spacecraft may be visible from Earth if the lighting conditions are just right. Once fully expanded and at the proper orientation, the sail’s reflective material will be as bright as Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky.
“Seven meters of the deployable booms can roll up into a shape that fits in your hand,” said Alan Rhodes, the mission’s lead systems engineer at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley. “The hope is that the new technologies verified on this spacecraft will inspire others to use them in ways we haven’t even considered.”

Through NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology program , successful deployment and operation of the solar sail’s lightweight composite booms will prove the capability and open the door to larger scale missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
This boom design could potentially support future solar sails as large as 5,400 square feet (500 square meters), about the size of a basketball court, and technology resulting from the mission’s success could support sails of up to 21,500 square feet (2,000 square meters) – about half a soccer field.
“The Sun will continue burning for billions of years, so we have a limitless source of propulsion. Instead of launching massive fuel tanks for future missions, we can launch larger sails that use “fuel” already available,” said Rhodes. “We will demonstrate a system that uses this abundant resource to take those next giant steps in exploration and science.”
Because the sails use the power of the Sun, they can provide constant thrust to support missions that require unique vantage points, such as those that seek to understand our Sun and its impact on Earth. Solar sails have long been a desired capability for missions that could carry early warning systems for monitoring solar weather. Solar storms and coronal mass ejections can cause considerable damage on Earth, overloading power grids, disrupting radio communications, and affecting aircraft and spacecraft.
Composite booms might also have a future beyond solar sailing: the lightweight design and compact packing system could make them the perfect material for constructing habitats on the Moon and Mars, acting as framing structures for buildings or compact antenna poles to create a communications relay for astronauts exploring the lunar surface.
“This technology sparks the imagination, reimagining the whole idea of sailing and applying it to space travel,” said Rudy Aquilina, project manager of the solar sail mission at NASA Ames. “Demonstrating the abilities of solar sails and lightweight, composite booms is the next step in using this technology to inspire future missions.”
NASA Ames manages the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System project and designed and built the onboard camera diagnostic system. NASA Langley designed and built the deployable composite booms and solar sail system. NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology (SST) program office based at NASA Ames and led by the agency’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD), funds and manages the mission. NASA STMD’s Game Changing Development program developed the deployable composite boom technology. Rocket Lab USA, Inc of Long Beach, California is providing launch services. NanoAvionics is providing the spacecraft bus.
Related Terms
Ames Research Center
- Langley Research Center
- Small Spacecraft Technology Program
Space Technology Mission Directorate
Explore More

NASA Data Helps Beavers Build Back Streams

Climate Change Research
Discover more topics from nasa.

STMD Small Spacecraft Technology

Game Changing Development

This next-generation solar sail unfurls in space thanks to new composite booms
NASA has developed a new generation of deployable structures capable of supporting a solar sail for future space missions. The idea is for the sail to harness the sun's energy, propelling it forward and enabling it to adjust its orbit as required. A first mission is due to be launched shortly to test its effectiveness.
This artist's view shows the ACS3 spacecraft navigating through space using the sun's energy for propulsion.
(Copyright: Courtesy of NASA / Aero Animation / Ben Schweighart)
By the end of April 2024, a new technology developed to support a solar sail will be launched into orbit by Rocket Lab's Electron launcher from New Zealand.
After reaching its sun-synchronous orbit, some 1,000 kilometers above the Earth, the probe will begin unfurling its composite booms, which span the diagonals of the polymer sail, acting much like the mast of a sailboat. It will take almost half an hour for the solar sail to fully unfurl, measuring some 80 square meters in total.
The system consists of booms made from flexible polymer and carbon fiber materials. All seven meters of deployable booms can be coiled into a form that wold fit in your hand, NASA says. Cameras mounted on the space module will film this deployment and ensure that everything operates properly. In addition to supporting a solar sail, this type of composite boom could one day be deployed in the construction of habitats on the Moon or on Mars, as building framing structures that could be easily transported and installed.
The aim of this first mission is to deploy the entire system correctly, so as to assess the sail's performance. The solar sail can adjust its orbit at any time by tilting. A whole series of maneuvers designed to modify the spacecraft's orbit will be tested with a view to future missions with even larger sails. According to its designers, once the sail is deployed and correctly oriented, its reflective material will be as bright as a star like Sirius.
For propulsion, this solar sail uses the pressure of sunlight. The sail positions itself towards or away from the sun, allowing photons to bounce off the reflective sail to push the spacecraft along. This technology eliminates the need for heavy, polluting propulsion systems. Alan Rhodes, the mission’s lead systems engineer, said ina statement: "The Sun will continue burning for billions of years, so we have a limitless source of propulsion. Instead of launching massive fuel tanks for future missions, we can launch larger sails that use 'fuel' already available."
The program is designed to prove the sail's suitability for future missions to the Moon, Mars and possibly even beyond. This new kind of boom technology could potentially support much larger solar sails in the future -- of up to 2,000 m2, in theory -- paving the way for even larger spacecraft.
© Copyright 2024 ETX Studio

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solar on a sailboat goes together like hands and gloves, but sailboat solar systems can be installed in a variety of ways. The solar components themselves create an infinite combination of possibilities for off-grid sailing. Victron Energy chargers, Renogy Panels, Sunpower Yachts, BlueSea Systems, and many more brands have entered the ...
A solar-power installation on a sailboat is made up of two independent systems: one system to charge the batteries, and another system to provide 120-volt AC power for household appliances. In the charging system, the solar panels convert sunlight into electrical current and deliver it to the batteries via a solar charge controller. Similar to ...
Another factor you'll need to consider is the size of your boat battery bank. In general, a 100Ah deep cycle battery will need 180 watts of solar to fully charge, assuming you have at least four hours of sunlight a day. Thus, if you have a 200Ah battery bank, you'll need at least 360 watts of solar. In this case, two 200-watt panels would ...
THE AVAILABLE SPACE. In practical terms, a modern 40ft monohull would have the space for around 1,200W of PV panels (cockpit arch, sprayhood top, deck), maybe 1,500W with the addition of a few portable panels for use at anchor. The 1,200W of fixed position solar array could produce around 360Ah on a sunny summer's day (zero shading) or more ...
The benefits of solar Almost any boat can benefit from solar power. Whether at a slip, mooring, or on a trailer, boats can keep their batteries topped off without the need for external power. ... For our example, the goal is to install a solar panel to provide charging for a single 12-volt, 100-amp-hour wet-cell battery used to power an ...
Researching solar panels for the first time in 13 years, we discovered that much had changed. Panels produced higher output for their size, but larger panels were being manufactured to meet the ever-growing demands of boaters. Our usage had actually decreased over time as our three children grew up and moved off the boat, and the space allotted ...
Output Discrepancies. There's often confusion as to how much power you can harvest from a solar installation. A PV panel is nearly always advertised stating its theoretical peak output power (Pw), but in reality, on a sailboat where there are limited areas in which to mount them, they will more likely produce a maximum of 60 percent of their peak output if mounted horizontally and 80 percent ...
Cruising World Editor at Large Tim Murphy visits West Marine to grab all of the supplies he needs to install a new set of solar panels on a Passport 40 in Po...
How to install solar panels on your sailboat! This is an in-depth video on how I installed my 300W solar system. I'm not advocating any particular vendor, ju...
A few viewers have asked about my two solar panels in the cockpit of my sailboat. In this episode, I explain how I set up my solar system. It's super easy. E...
Step by step guide for installing a solar panel boat system. First I list a quick summary on how to put this together. Details will follow after these instructions. 1. Mount your panel on your stern rail (see photos/details below). 2. Attach marine grade copper wires to the panel.
Solar panels, or photovoltaic (PV) cells as they are known in the industry, have evolved in the past decade. Like cell phone technology, the size of solar panels has reduced over the years, while their efficiency has risen. Recent innovations have made solar panels easier to install in non-traditional places, not to mention that the overall ...
Nature Power Rigid. The nature power rigid is a large, powerful, single solar panel. If you are looking for the right panels to power your entire boat comfortably, these are the ones for you. They are very large so they will need a large flat surface area. alternatively, they can be hung vertically from rails.
Lower power output compared to top picks. 4. NewPowa 30W Solar Panel Kit. The NewPowa solar panel kit is a cost-effective option that includes a panel, a controller, and wiring. With a 30W output, it's well-suited for light-duty use. Its IP67-rated panels and controller make it a safe choice for various boat types.
It's made of A+ SunPower cells by Custom Marine Products. Although we don't intend to, this panel could be walked on and it will flex to follow a 5-degree curve - exactly what we needed for our location. And the semi-rigid is actually better for placing on a deck, as it's designed with proper insulation. SunPower makes great solar ...
Do you want to install solar panels on your tiny sailboat, but don't know how? Watch this video to learn how to easily and affordably set up a solar system that can power your boat's electronics ...
With solar panels, you can produce usable electricity during the day and then use it for weekend boating adventures. However, there can be obstacles to installing solar on a boat, perhaps the largest of which is available space. Ideally, your solar panels can be installed in an area with uninterrupted sunshine.
Step 1: Determine the location for the solar panels. Step 2: Measure and mark the mounting points. Step 3: Install the brackets. Step 4: Install the solar panels. Step 5: Adjust the angle of the panels. Wiring and Connecting the Solar Panels to Your Boat's Power System. Testing and Maintaining Your Solar Panel System.
INSTALLING SOLAR PANELS ON A BOAT. Solar panel technology has improved tremendously in the past few years. The panels are highly efficient, flexible, walkable and comes with very low weight. They can be attached to the deck or canvas with fasteners such as Tenax/Loxx, using velcro or glue. Some panels are suitable for boom/mast assembly as well.
May 28, 2015. 275. Catalina 385 Long Branch, NJ. Apr 3, 2021. #1. I am planning to install two Renogy 175 watt flexible solar panels on my bimini this summer. After numerous detailed conversations with several local canvas professionals and marine electronic professionals, the consensus is that I should keep it simple for the first few months ...
For our sailboat solar power installation, we had three 325 Panasonic Solar Panels, a 316 Stainless Steel frame made to weld over our davits and a Midnight S...
Sailing through space might sound like something out of science fiction, but the concept is no longer limited to books or the big screen. In April, a next-generation solar sail technology - known as the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System - will launch aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rocket from the company's Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
This video shows you our DIY boat solar panel installation - without welding, pipe bending or using any expensive tools! 🔔 SUBSCRIBE http://bit.ly/SBYouTu...
The solar sail can adjust its orbit at any time by tilting. A whole series of maneuvers designed to modify the spacecraft's orbit will be tested with a view to future missions with even larger sails.
A Complete guide on how we installed our Renogy Lithium Smart Batteries, Renogy Solar panels, Renogy Solar charge controllers, 3000w Renogy Inverter / Charge...