- Add a definition
- User settings


Top 37 Slang For Boat – Meaning & Usage
Boats, whether they’re cruising along the open seas or peacefully floating on a tranquil lake, have their own language. From nautical terms to slang that’s been passed down through generations of sailors, the world of boat lingo is as vast as the ocean itself.
In this listicle, we’ve rounded up the top slang for boat that will have you speaking like a seasoned sailor in no time. So hop aboard and get ready to navigate the waves of boat jargon with confidence!
Click above to generate some slangs
1. Gin Palace
A “gin palace” is a slang term for a luxurious and extravagant boat, typically a large yacht. The term is often used to describe opulent and high-end vessels.
- For example , “He arrived at the party in his gin palace, turning heads with its sleek design and lavish features.”
- In a conversation about boating , someone might say, “I dream of owning a gin palace one day, sailing around the world in style.”
- A boating enthusiast might admire a gin palace and exclaim , “That boat is the epitome of luxury, a true gin palace.”
A “barge” is a type of boat that is flat-bottomed and designed for carrying goods on rivers and canals. The term can also be used to refer to any large and unwieldy boat.
- For instance , “The barge slowly made its way down the river, carrying a heavy load of cargo.”
- In a discussion about transportation , someone might mention, “Barges are often used to transport goods efficiently and cost-effectively.”
- A person describing a boat they saw might say , “It wasn’t the most elegant boat, more like a floating barge.”
3. Ditch crawler
A “ditch crawler” is a slang term for a small boat, typically used for navigating narrow waterways or shallow areas. The term emphasizes the boat’s ability to maneuver in tight spaces.
- For example , “He took his ditch crawler out for a peaceful day of fishing in the narrow canals.”
- In a conversation about boating options , someone might say, “I prefer a ditch crawler for exploring hidden waterways and marshes.”
- A boating enthusiast might recommend a ditch crawler and say , “If you love exploring remote areas, a ditch crawler is the way to go.”
4. Tupperware
A “Tupperware” is a slang term for a boat made of plastic, typically referring to small recreational boats. The term is often used humorously to describe boats that are lightweight and easily transportable.
- For instance , “He took his Tupperware out on the lake for a day of fishing and relaxation.”
- In a discussion about boat materials , someone might say, “Tupperware boats are popular among beginners due to their affordability and durability.”
- A person describing a boat they saw might joke , “It was a classic Tupperware, perfect for a picnic on the water.”
A “plastic” is a slang term for a boat made of fiberglass. The term is commonly used among boating enthusiasts and refers to the material used in the construction of the boat.
- For example , “He proudly showed off his new plastic, a sleek and shiny vessel.”
- In a conversation about boat maintenance , someone might mention, “Plastic boats require regular cleaning and waxing to keep their glossy appearance.”
- A boating enthusiast might discuss the advantages of a plastic and say , “Fiberglass boats are lightweight, durable, and offer excellent performance on the water.”
A scow is a type of boat with a flat-bottomed hull, typically used for transporting goods or dredging. The flat-bottom design allows for easy loading and unloading of cargo.
- For example , “The scow was used to transport lumber down the river.”
- In a discussion about water transportation , someone might ask, “Has anyone ever been on a scow before?”
- A boating enthusiast might say , “Scows are great for shallow waters and navigating through marshes.”
In boating slang, “A1” refers to a boat that is in excellent condition. It indicates that the boat is well-maintained and ready for use.
- For instance , “That yacht is A1, it’s been well taken care of.”
- A boat owner might advertise , “Selling my A1 sailboat, it’s in pristine condition.”
- In a discussion about boat maintenance , someone might say, “Regular cleaning and servicing is important to keep your boat A1.”
8. At Loggerheads
The phrase “at loggerheads” is a nautical term that refers to two boats coming into contact and becoming stuck together. Figuratively, it means to be in a state of disagreement or conflict.
- For example , “The two politicians are at loggerheads over the new policy.”
- In a debate , someone might say, “We’ve been at loggerheads for hours, let’s try to find some common ground.”
- A news headline might read , “Labor and management at loggerheads in contract negotiations.”
9. Barge In
To “barge in” means to interrupt or intrude into a conversation or situation without invitation or permission. The term comes from the image of a barge forcefully entering a space.
- For instance , “He always barge in when we’re trying to have a serious discussion.”
- In a social gathering , someone might say, “Please don’t barge in, wait for your turn.”
- A parent might scold their child , “You can’t just barge in without knocking.”
10. Coasties
In boating slang, “Coasties” refers to members of the Coast Guard. It is a colloquial term used to describe individuals who serve in the maritime branch of a country’s military or law enforcement.
- For example , “The Coasties rescued the stranded boaters during the storm.”
- In a discussion about maritime safety , someone might ask, “Do the Coasties patrol this area regularly?”
- A Coast Guard member might say , “I’m proud to be one of the Coasties, protecting our shores.”
11. Blowboater
This term is often used to refer to someone who is passionate about sailing and owns a sailboat. It can also be used to describe someone who enjoys participating in sailboat races or regattas.
- For example , “He spends every weekend out on the water, he’s a true blowboater.”
- A sailing club might organize an event and invite blowboaters to join and showcase their skills.
- A sailing enthusiast might say , “I love being a blowboater because it allows me to connect with nature and experience the thrill of the wind in my sails.”
12. Snailboater
This term is used to describe a sailboat that is moving at a slow speed, often due to light wind or unfavorable sailing conditions. It can also be used as a playful nickname for someone who prefers a leisurely pace while sailing.
- For instance , “We were stuck behind a snailboater during the race, and it took us longer to reach the finish line.”
- A sailor might say , “I enjoy being a snailboater because it allows me to relax and enjoy the peacefulness of the water.”
- During a sailing trip , someone might jokingly say, “We’re not in a rush, let’s embrace our inner snailboaters and take our time.”
13. Dead in the water
This phrase is used to describe a boat that has come to a complete stop and is not moving. It can also be used metaphorically to describe a situation where there is no progress or forward movement.
- For example , “The engine failed, and we were dead in the water until help arrived.”
- A sailor might say , “We encountered a strong current that left us dead in the water for hours.”
- In a business context , someone might say, “Without a clear plan, the project is dead in the water.”
14. Stinkpot
This term is often used to refer to a motorboat, particularly one with a gasoline-powered engine. It is derived from the strong smell of exhaust fumes emitted by motorboats.
- For instance , “He prefers the speed and convenience of a stinkpot over a sailboat.”
- A boat enthusiast might say , “I enjoy sailing, but sometimes it’s nice to take a break and hop on a stinkpot.”
- During a conversation about different types of boats , someone might ask, “Are you more of a stinkpot person or a blowboater?”
15. Oil burner
This term is used to describe a boat that is powered by a diesel engine. Diesel-powered boats are sometimes referred to as oil burners due to the fuel they use.
- For example , “He owns an oil burner and enjoys the fuel efficiency it provides.”
- A boat mechanic might say , “When maintaining an oil burner, it’s important to regularly check the fuel filters.”
- During a discussion about different types of boat engines , someone might ask, “Do you prefer gas-powered boats or oil burners?”
16. High-tide riders
This term refers to experienced boaters who are skilled at navigating during high tide conditions. It implies that these boaters are familiar with the challenges and nuances of boating in high tide.
- For example , “The high-tide riders know exactly how to navigate through the narrow channels during high tide.”
- A boater might say , “If you want to learn how to handle your boat during high tide, seek advice from the high-tide riders.”
- In a discussion about boating techniques , someone might mention, “The high-tide riders have mastered the art of reading the water and understanding the tides.”
17. As the crow flies
This phrase is often used to describe the shortest distance between two points, without considering any obstacles or detours. It implies a direct and efficient route.
- For instance , “The marina is just two miles away as the crow flies, but it will take longer if we follow the winding river.”
- A boater might say , “Let’s go to that island over there, it’s only a few miles as the crow flies.”
- In a discussion about navigation , someone might mention, “As the crow flies, the distance between two points may seem short, but you have to consider the actual route on the water.”
18. Go Fast
This phrase is used to encourage or describe the act of increasing the speed of a boat. It implies a desire for a thrilling and fast-paced boating experience.
- For example , “Hold on tight, we’re going fast!”
- A boater might say , “I love to go fast and feel the wind in my hair.”
- In a discussion about different boating styles , someone might mention, “Some boaters prefer a leisurely cruise, while others like to go fast and enjoy the adrenaline rush.”
19. Go Fast/Go Loud
This phrase is often used to describe a boating style that involves both high speed and loud engine noise. It implies a preference for a powerful and attention-grabbing boating experience.
- For instance , “When they go fast, they also go loud with their engines revving.”
- A boater might say , “If you want to make a statement on the water, go fast and go loud.”
- In a discussion about different types of boating events , someone might mention, “The go fast/go loud races are always a crowd favorite.”
20. Boating Dollars
This term refers to the expenses associated with owning and operating a boat. It implies that boating can be a costly hobby or lifestyle.
- For example , “He has invested a lot of boating dollars in his yacht.”
- A boater might say , “Before you buy a boat, make sure you’re prepared for the boating dollars that come with it.”
- In a discussion about budgeting for boating , someone might mention, “It’s important to factor in all the boating dollars, including maintenance, fuel, and insurance.”
21. Sailboat
A type of boat that is propelled by wind, using sails to harness the power of the wind. Sailboats come in various sizes and configurations, from small single-handed dinghies to large luxury yachts.
- For example , “Let’s go out for a day of sailing on my sailboat.”
- A sailor might say , “I prefer the freedom and tranquility of sailing on a sailboat.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might mention, “Sailboats are known for their elegance and grace on the water.”
22. Motorboat
A boat that is powered by an engine, typically an internal combustion engine. Motorboats come in various sizes and styles, from small speedboats to large yachts.
- For instance , “Let’s take the motorboat out for some water skiing.”
- A boating enthusiast might say , “I love the thrill and speed of a motorboat.”
- In a conversation about different types of boats , someone might mention, “Motorboats are great for exploring large bodies of water quickly and efficiently.”
A narrow boat that is pointed at both ends and propelled by paddles. Canoes are typically used for recreational purposes, such as leisurely paddling on calm lakes or navigating rivers.
- For example , “Let’s go canoeing down the river and enjoy the peacefulness of nature.”
- A nature enthusiast might say , “Canoeing allows you to explore remote and untouched areas.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might mention, “Canoes are perfect for solo or tandem paddling adventures.”
A small, narrow boat that is propelled by a double-bladed paddle. Kayaks are designed for one or two people and are commonly used for recreational activities such as touring, fishing, and whitewater rafting.
- For instance , “Let’s go kayaking and explore the hidden coves along the coast.”
- An outdoor enthusiast might say , “Kayaking allows you to get up close and personal with nature.”
- In a conversation about different types of boats , someone might mention, “Kayaks are versatile and can be used in various water conditions.”
A small, shallow-draft boat that is typically used for fishing in calm waters. Skiffs are lightweight and easy to maneuver, making them popular among anglers.
- For example , “Let’s take the skiff out for some early morning fishing.”
- A fishing enthusiast might say , “Skiffs allow you to access shallow areas where larger boats can’t go.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might mention, “Skiffs are perfect for fly fishing or casting in tight spaces.”
26. Jon boat
A small, flat-bottomed boat typically used for fishing or hunting in shallow waters. The term “Jon boat” is a colloquialism, derived from the name “John,” and is often used interchangeably with “John boat.”
- For example , “Let’s take the Jon boat out on the lake and do some fishing.”
- A person discussing boating options might say , “A Jon boat is perfect for navigating narrow rivers.”
- In a conversation about different types of boats , someone might ask, “What’s the difference between a Jon boat and a bass boat?”
27. Pontoon boat
A flat-bottomed boat that is buoyant due to pontoons, which are air-filled chambers attached to the bottom of the boat. Pontoon boats are often used for leisure activities such as cruising, fishing, or partying on the water. The term “party barge” is a colloquialism used to emphasize the social and recreational aspects of pontoon boats.
- For instance , “We rented a pontoon boat for a day of fun on the lake. It was like a floating party barge!”
- A person discussing boating options might say , “A pontoon boat is great for a relaxing day on the water with friends.”
- In a conversation about different types of boats , someone might ask, “Can you fish from a pontoon boat?”
28. Houseboat
A boat that has been designed or modified for use as a permanent residence. Houseboats typically have living spaces, bedrooms, kitchens, and bathrooms, providing all the comforts of a traditional home. The term “floating home” is often used to highlight the fact that houseboats serve as both a means of transportation and a place to live.
- For example , “We spent our vacation on a houseboat, and it felt like living in a floating home.”
- A person discussing alternative living arrangements might say , “I’m considering buying a houseboat and living on the water.”
- In a conversation about unique vacation experiences , someone might ask, “Have you ever stayed in a houseboat?”
29. Jet ski
A small, motorized vehicle designed to be ridden on the water. Jet skis are typically used for recreational purposes, such as cruising, racing, or performing tricks. The term “personal watercraft” is a more formal and descriptive term for jet ski.
- For instance , “Let’s go to the beach and rent a jet ski for some fun on the water.”
- A person discussing water sports might say , “I love riding a personal watercraft like a jet ski.”
- In a conversation about different types of watercraft , someone might ask, “What’s the difference between a jet ski and a wave runner?”
30. Catamaran
A boat that has two parallel hulls connected by a deck or framework. Catamarans are known for their stability and speed, making them popular for both recreational and commercial purposes. The term “twin-hull boat” is a more technical description of a catamaran.
- For example , “We went on a catamaran cruise and enjoyed the smooth ride and spacious deck.”
- A person discussing sailing might say , “Catamarans are great for long-distance voyages due to their stability.”
- In a conversation about different types of boats , someone might ask, “What are the advantages of a catamaran over a traditional single-hull boat?”
31. Trawler
A trawler is a type of fishing vessel that is designed to tow a trawl net through the water to catch fish. It is often used for commercial fishing purposes.
- For example , “The trawler returned to the harbor with a big catch of cod.”
- A fisherman might say , “I’ve been working on a trawler for over 10 years.”
- In a discussion about sustainable fishing , someone might mention, “Trawlers can have a negative impact on marine ecosystems if not properly regulated.”
32. Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of boat that is designed for leisure and recreational purposes. It is typically larger and more luxurious than other types of boats and is often used for cruising or sailing.
- For instance , “They spent the weekend on their cruiser, exploring the nearby islands.”
- A boating enthusiast might say , “I love taking my cruiser out on the lake for a relaxing day on the water.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might ask, “What’s the difference between a cruiser and a yacht?”
33. Gondola
A gondola is a traditional Venetian boat that is used for transportation in the canals of Venice, Italy. It is typically long and narrow, with a flat bottom and a high prow and stern.
- For example , “They took a romantic gondola ride through the canals of Venice.”
- A traveler might say , “Riding a gondola is a must-do experience when visiting Venice.”
- In a discussion about unique modes of transportation , someone might mention, “Gondolas are an iconic symbol of Venice.”
34. Pontoon
A pontoon is a type of boat that is supported by pontoons, or flotation devices, instead of a traditional hull. It is often used for recreational activities such as fishing or leisurely cruising.
- For instance , “They went fishing on their pontoon and caught several bass.”
- A boating enthusiast might say , “Pontoon boats are great for relaxing and enjoying time on the water.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might ask, “What are the advantages of a pontoon boat over a traditional motorboat?”
35. Speedboat
A speedboat is a type of boat that is designed for high speed and performance. It is typically smaller and more agile than other types of boats and is often used for water sports or racing.
- For example , “They went water skiing behind their speedboat.”
- A boating enthusiast might say , “I love the adrenaline rush of driving a speedboat at top speed.”
- In a discussion about different types of boats , someone might ask, “What’s the fastest speedboat ever recorded?”
36. Canoe-kayak
A canoe-kayak, often referred to as a “paddlecraft,” is a small and narrow boat that is propelled by paddling. It can be used for recreational purposes or for competitive sports such as canoeing and kayaking.
- For example , “Let’s take the canoe-kayak out on the lake for a relaxing afternoon.”
- In a discussion about water sports , someone might say, “I prefer canoe-kayaking over other forms of boating.”
- A person planning a camping trip might ask , “Does anyone know where we can rent a canoe-kayak for our adventure?”
37. Paddleboard
Short for “Stand-Up Paddleboard,” a paddleboard is a long and wide board that is used for standing and paddling on water. It is propelled by a single paddle and can be used for various activities such as surfing, touring, or practicing yoga.
- For instance , “I love taking my paddleboard out to catch some waves.”
- In a conversation about outdoor fitness , someone might say, “I’ve recently started doing SUP yoga on my paddleboard.”
- A person planning a beach vacation might ask , “Are there any good spots for paddleboarding in this area?”
You may also like
- Nautical Sayings: Exploring the Fascinating World of Maritime Language
Ahoy there, fellow adventurers of the sea! Whether you're an experienced sailor or just someone fascinated by the world of nautical adventures, you've probably come across some intriguing and often perplexing maritime sayings. In this comprehensive article, we'll dive deep into the ocean of nautical sayings, yacht word origins, boating sayings, and the rich tapestry of nautical slang that has shaped the language of the high seas.
Setting Sail with Nautical Sayings
Ahoy, matey.
Our journey begins with the iconic greeting, "Ahoy, matey!" This classic nautical saying has been immortalized in countless pirate tales and seafaring adventures. But have you ever wondered about its origins and the fascinating history behind it?
The phrase "Ahoy, matey!" finds its roots in the 17th century when pirates and sailors needed a catchy and distinctive way to greet each other on the high seas. We'll explore how this phrase became a symbol of maritime camaraderie and adventure.
Charting the Course of Nautical Language
Before we delve into specific nautical sayings, let's navigate through the history of maritime language. The sea has always been a source of inspiration for unique expressions, and understanding the evolution of this language is key to appreciating its richness.
Maritime language is a dynamic blend of influences from various cultures, including English, Dutch, and even French. We'll journey through time to uncover how these linguistic influences shaped the nautical lexicon we know today.
Knots and Nautical Expressions
The maritime world is a treasure trove of fascinating expressions related to knots and ropes. From "tying the knot" to "left in the lurch," we'll unravel the meanings behind these captivating sayings.
Let's explore more nautical phrases related to knots, rigging, and seamanship. Each saying carries a unique history, often reflecting the practical challenges and traditions of sailors.
The Call of the Sea
Beyond greetings and practical expressions, sailors had a language of their own to communicate effectively on the vast expanse of the ocean. We'll delve into the lesser-known but equally intriguing nautical phrases that were used for signaling, navigation, and coordination.
Discovering Yacht Word Origins
The yacht: a luxurious icon .
Yachts epitomize elegance and luxury on the water. But have you ever wondered where the term "yacht" itself comes from? Let's set sail on a journey through time to explore its origins.
The word "yacht" has a fascinating history that dates back to the early days of sailing. We'll trace its evolution from humble beginnings to the opulent vessels we associate with yachts today.
Yacht or Jacht: A Linguistic Odyssey
Did you know that "yacht" is closely related to the Dutch word "jacht"? We'll uncover the linguistic connection between these two words and how it has influenced modern yacht culture.
The Dutch influence on yacht design and terminology is profound. We'll delve into how Dutch shipbuilders and explorers played a pivotal role in shaping the yacht industry.
The Golden Age of Yachting
Yachting isn't just about boats; it's a cultural phenomenon with a rich history. During the 19th century, the "Golden Age of Yachting" saw a surge in yacht building and racing. We'll explore this period and its impact on yacht word origins.
Sailing Through Boating Sayings
Smooth sailing ahead.
When it comes to boating, the saying "smooth sailing" is music to a captain's ears. Join us as we explore the origin of this optimistic phrase and how it reflects the sailors' eternal quest for favorable winds.
"Smooth sailing" isn't just a saying; it embodies the aspirations and experiences of mariners throughout history. We'll recount stories of legendary voyages and the calm seas that inspired this expression.
Weathering the Storm
Boating isn't always smooth sailing. Sometimes, sailors must "weather the storm." We'll examine the origin of this phrase and its enduring relevance to the maritime world.
Navigating storms at sea has always been a formidable challenge. We'll share tales of courage and resilience that shed light on the origins of this powerful metaphor.
Deciphering Nautical Slang
Aye, aye, captain .
Nautical slang is a language all its own, and "aye, aye, captain" is one of its most recognizable phrases. But what does it really mean, and why is it used so frequently on ships?
Read our top notch articles on topics such as sailing, sailing tips and destinations in our Magazine .
Check out our latest sailing content:
Swabbing the Deck: Nautical Work Lingo
"Swabbing the deck" might sound like a chore, but it's also a nautical saying with a rich history. We'll uncover its origins and its role in the daily life of sailors.
Navigating Ship Sayings
Shipshape and bristol fashion .
When something is "shipshape and Bristol fashion," it's in excellent condition. Discover the intriguing story behind this phrase, which hails from the bustling port city of Bristol.
Between the Devil and the Deep Blue Sea
Sometimes, sailors find themselves "between the devil and the deep blue sea." Explore the origins of this saying and the predicaments it describes.
Exploring Boat Phrases
In the same boat .
We often say we're "in the same boat" when facing a common challenge. But where does this saying come from, and why do we use it to express solidarity?
Casting Adrift: Origins of "Adrift"
Being "adrift" can have a figurative meaning beyond just being at sea. Discover the roots of this saying and how it found its way into everyday language.
Unraveling Nautical Expressions
By and large: a nautical measurement .
The phrase "by and large" has nautical origins tied to sail trimming. Join us as we explore the history of this saying and its transition to everyday language.
Three Sheets to the Wind: A Nautical Reference to Intoxication
Have you ever heard someone described as being "three sheets to the wind"? Learn about the nautical basis of this humorous expression.
Boating Phrases and Sailor Jargon
"know the ropes": mastering the art of sailing.
To "know the ropes" means to be skilled and knowledgeable. We'll sail through the history of this saying and its significance for sailors.
"The Whole Nine Yards": Nautical or Not?
Is "the whole nine yards" a nautical phrase? We'll unravel this linguistic mystery and see if it has nautical origins or not.
Sailing Expressions and Seafaring Terms
"batten down the hatches": preparing for a storm.
When sailors "batten down the hatches," they're preparing for a storm. Discover the practical origins of this vital nautical saying.
"Between the Devil and the Deep Blue Sea": A Nautical Dilemma
We revisit the phrase "between the devil and the deep blue sea" to explore its deeper connotations in the context of seafaring.
Nautical Words and Phrases: A Sailor's Lexicon
Nautical sayings: the ultimate lexicon .
Summarizing our exploration, we'll compile a comprehensive list of some of the most intriguing nautical words and phrases that have left their mark on the English language.
As we sail back to the shore of this captivating journey through nautical sayings and maritime language, it's clear that the sea has not only inspired adventurers but also enriched our vocabulary with colorful expressions. From "ahoy, matey" to "the whole nine yards," each saying carries a piece of nautical history that continues to resonate with us today.
So what are you waiting for? Take a look at our range of charter boats and head to some of our favourite sailing destinations.
I am ready to help you with booking a boat for your dream vacation. Contact me.

Denisa Nguyenová
Nautical Slang in Common Usage

Many phrases that have been adopted into everyday use originate from seafaring – in particular from the days of sail.
It is an undoubted fact that seafaring is also the source of more false etymology than any other sphere. This can be attributed to the attractiveness of the romantic image of horny-handed sailors singing shanties and living a hearty and rough life at sea. After all, it sounds plausible that ‘cold enough to freeze the balls off a brass monkey’ comes from brass ship’s fittings and that POSH means ‘Port out, starboard home’, but neither of these is correct. CANOE, the Committee to Ascribe a Naval Origin to Everything, doesn’t really exist, but the number of these folk myths makes it seem as though they do…
It is lucky for us, in our endeavours to distinguish truth from falsehood, that activities at sea have been scrupulously recorded over the centuries, in insurance records, newspaper accounts and, not least, in ships’ log books. The term log-book has an interesting derivation in itself. An early form of measuring a ship’s progress was by casting overboard a wooden board (the log) with a string attached. The rate at which the string was paid out as the ship moved away from the stationary log was measured by counting how long it took between knots n the string. These measurements were later transcribed into a book. Hence we get the term ‘log-book’ and also the name ‘knot’ as the unit of speed at sea.
Above board - Anything on or above the open deck. If something is open and in plain view, it is above board. All at sea - This dates to the time when accurate navigational aids weren’t available. Any ship that was out of sight of land was in an uncertain position and in danger of becoming lost. Aloof - Now means to stand apart or be indifferent, but it came from the Old Dutch word loef which meant “windward” and was used to describe a ship within a fleet which sailed higher to the wind and was thus drawn apart from the rest of the fleet. At loggerheads - An iron ball attached to a long handle was a loggerhead. When heated it was used to seal the pitch in deck seams. It was sometimes a handy weapon for quarrelling crewmen. Chock-a-block - A block and tackle is a pulley system used on sailing ships to hoist the sails. The phrase describes what occurs the system is raised to its fullest extent – when there is no more rope free and the blocks jam tightly together. Predictably this lead to its current meaning, “crammed so tightly together as to prevent movement”. Clean bill of health - A certificate signed by a port authority attesting that no contagious disease existed in the port of departure and none of the crew was infected with a disease at the time of sailing. Shore-side, it means in good shape. Clear the deck - One of the things done in preparation for battle. Current usage similar to batten down the hatches. Close quarters - In the 17th century, the barriers that sailors laid across a ship’s deck in order to provide a safe haven from the enemy were called close-fights. By the mid 18th century that confined defensive space became called ‘close quarters’, i.e. close dwellings. This eventually came to mean ‘near enough to to be able to fight hand to hand’. Copper-bottomed - described ships that were fitted with copper plating on the underside of their hulls. The process was first used on ships of the British Navy in 1761 to defend their wooden planking against attack by Teredo worms a.k.a. Shipworms and to reduce infestations by barnacles. The method was successful in protecting ships’ timbers and in increasing speed and manoeuvrability and soon became widely used. Before long, ‘copper-bottomed’ began to be used figuratively to refer to anything that was certain and trustworthy. Cut and run - most often thought to mean the cutting of an anchor line in an effort to make a quick getaway. Hard to imagine that many ship’s masters enjoyed routinely losing an anchor or two, so it is probably more likely referring to the practice of securing the sails of a square-rigged ship with rope yarns that could easily be cut away when a quick departure was necessary. Cut of one’s jib - warships many times had their foresails or jib sails cut thinly so that they could maintain point and not be blown off course. Upon sighting thin foresails on a distant ship a captain might not like the cut of his jib and would then have an opportunity to escape. Deliver a broadside - the simultaneous firing of the guns and/or canons on one side of a warship. Quite a blow, as can be imagined. Today it means much the same type of all-out attack, though done (usually) with words. Devil to pay - Originally, this expression described one of the unpleasant tasks aboard a wooden ship. The devil was the ship’s longest seam in the hull. Caulking was done with pay or pitch (a kind of tar). The task of ‘paying the devil’ (caulking the longest seam) by squatting in the bilges was one of the worst and most difficult jobs onboard. The term has come to mean a difficult, seemingly impossible task. ‘The devil to pay and no pitch hot’. Landlubbers, having no seafaring knowledge, assumed it referred to satan and gave the term a moral interpretation. Dressing down - Thin and worn sails were often treated with oil or wax to renew their effectiveness. This was called “dressing down”. An officer or sailor who was reprimanded or scolded received a dressing down. Dutch courage - Dates to the 1600s Anglo-Dutch wars and was likely British propaganda claiming that the Dutch troops were so cowardly they wouldn’t fight unless fortified with copious amounts of schnapps. The term has come to mean false courage induced by drink, or the drink itself. Edging forward - This phrase describes inch-by-inch progress and was first used in the 17th century, typically in nautical contexts and referring to slow advance by means of repeated small tacking movements. Even keel - A vessel that floats upright without list is said to be on an even keel and this term has come to mean calm and steady. A keel is like the backbone of the vessel, the lowest and principal centerline structural member running fore and aft. Keeled over (upside down) was a sailor’s term for death. Fall foul of/foul up - Foul is an often used nautical term generally meaning entangled or impeded. An anchor tangled in line or cable is said to be a foul anchor. A foul berth is caused by another vessel anchoring too close wherein the risk of collision exists. A foul bottom offers poor holding for anchors. A screw up! Fathom - A nautical measure equal to six feet, used to measure the depth of water at sea. The word was also used to describe taking the measure or “to fathom” something. Today when one is trying to figure something out, they are trying to fathom it or get to the bottom of it. Figurehead - An ornamental figure placed on the front of a ship, under the. Originally a religious and/or protective emblem. The custom continued but for purely decorative purposes. Hence the term figurehead – a leader with no real power or function except to ‘look good’ or appeal to a certain group. Filibuster - Buccaneers were sometimes known in England as filibusters. From the Dutch for vrybuiter (freebooter) translated into French as flibustier. It is now used as a political term meaning to delay or obstruct the passage of legislation (as opposed to sailing vessels) by non-stop speech making. First rate - Implies excellence. From the 16th century on until steam powered ships took over, British naval ships were rated as to the number of heavy cannon they carried. A ship of 100 or more guns was a First Rate line-of-battle ship. Second rates carried 90 to 98 guns; Third Rates, 64 to 89 guns; Fourth Rates, 50 to 60 guns. Frigates carrying 20 to 48 guns were fifth and sixth rated. Fits the bill - A Bill of Lading was signed by the ship’s master acknowledging receipt of specified goods and the promise to deliver them to their destination in the same condition. Upon delivery, the goods were checked against the bill to see if all was in order. If so, they fit the bill. Flotsam and jetsam - These are legal terms in maritime law. Flotsam is any part of the wreckage of a ship or her cargo that is lost by accident and found floating on the surface of the water. Jetsam are goods or equipment deliberately thrown overboard (jettisoned) to make the ship more stable in high winds or heavy seas. (Lagan are goods cast overboard with a rope attached so that they may be retrieved and sometimes refers to goods remaining inside a sunken ship or lying on the bottom.) The term flotsam and jetsam shore-side means odds and ends of no great value. Footloose - The bottom portion of a sail is called the foot. If it is not secured, it is footloose and it dances randomly in the wind. From stem to stern - From the front of a ship to the back. Now describes something in its entirety. Flying colours - To come through a battle with flying colours means a ship has come through relatively unscathed and with her colours (flag) flying. Get underway - ‘Way’ here doesn’t mean road or route but has the specifically nautical meaning of ‘the forward progress of a ship though the water’, or the wake that the ship leaves behind. Way has been used like that since at least the 17th century. Give a wide berth - To anchor a ship far enough away from another ship so that they did not hit each other when they swung with the wind or tide. Go overboard - The nautical origin of this one should be fairly self-evident. Gripe - A sailing vessel gripes when, by poor design or imbalance of sail, it tends to end up with its bow into the wind when sailing close-hauled. The sails flap around, forward progress is halted and she is very hard to steer. On land, the term means to complain, complain, complain. Groggy - In 1740, British Admiral Vernon (whose nickname was “Old Grogram” for the cloak of grogram which he wore) ordered that the sailors’ daily ration of rum be diluted with water. The men called the mixture “grog”. A sailor who drank too much grog was “groggy”. Groundswell - A sudden rise of water along the shore. It often happens when the weather is fine and the sea behind it appears calm. Said to occur when undulating water from a far away storm reaches the shoreline where friction causes the swell. In common use, the term groundswell means a growing change in public opinion. Hand over fist - Hand over hand was a British term for the act of moving quickly up a rope or hoisting a sail, which was a matter of pride and competition among sailors. It is thought that American sailors changed this term to ‘hand over fist’, and the term now means to advance or accumulate rapidly. Hard and fast - A ship that was hard and fast was simply one that was firmly beached on land. Has come to mean ‘rigidly adhered to – without doubt or debate’. Hard-up - Hard is another often used nautical term. To put the helm hard over is to put it as far as it will go in that direction. Hard and fast describes a vessel firmly aground and unable to make progress and has come ashore to mean rigid. ‘Hard up in a clinch and no knife to cut the seizing’, the term from which hard up derives, was a sailor’s way of saying he had been overtaken by misfortune and saw no way of getting clear of it. Shore-side, the term means in need. Haze - Long before fraternal organisations, hazing was the practice of keeping the crew working all hours of the day or night, whether necessary or not, in order to deprive them of sleep and to make them generally miserable. In the 19th century, many captains used this practice to assert their authority. Hazing has come to mean the initiation of a newcomer to a group by humiliating and harassing him or her, thereby asserting the authority of the group. High and dry - This term originally referred to ships that were beached. The ‘dry’ implies that not only were they out of the water, but had been for some time and could be expected to remain so. Hot chase - A principle of naval warfare, though without basis in law, that allowed a fleeing enemy to be followed into neutral waters and captured there if the chase had begun in international waters. The term hot pursuit derives from this ‘principle’. Hulk/hulking - A large and unwieldy ship of simple construction and dubious seaworthiness. On shore, it means big and clumsy. In the offing - This phrase is quite simple to understand once you know that ‘the offing’ is the part of the sea that can be seen from land, excluding those parts that are near the shore. Early texts also refer to it as ‘offen’ or ‘offin’. A ship that was about to arrive was “in the offing”, therefore imminent, which is how the phrase is used today. Idle/idler - Idler was the name for those members of a ship’s crew that did not stand night watch because of their work. Carpenters, sailmakers, cooks, etc. worked during the day and were excused from watch duty at night. They were called idlers, but not because they had nothing to do, simply because they were off duty at night. Junk - Old rope no longer able to take a load, it was cut into shorter lengths and used to make mops and mats. Land-side, junk is all that stuff in your garage you know you’ll need right after you throw it away. Jury rig - A temporary repair to keep a disabled ship sailing until it could make port, such as a jury sail erected when the mast was lost or a jury rudder as an emergency means of steering when the ship’s rudder was damaged. Keel hauling - A severe naval punishment during the 15th and 16th centuries. The victim, presumably a delinquent sailor, was dragged from one side of the boat to the other, under the bottom of the boat (keel). Tossed over one side and pulled up on the other, he was usually allowed to catch his breath before suddenly being tossed overboard again. Keel hauling lost favour at the beginning of the 18th century, to be replaced by the cat-o-nine-tails. The term still means a rough reprimand. Know the ropes - This is pretty obvious if you’ve ever seen a tall ship. It was such an important skill on sailing vessels that an honourable discharge from service was marked, at one time, with the term ‘knows the ropes’. Land-side it still means a person with experience and skill. Also, learn the ropes and show them the ropes. Leeway - The weather side of a ship is the side from which the wind is blowing. The Lee side is the side of the ship sheltered from the wind. A lee shore is a shore that is downwind of a ship. If a ship does not have enough “leeway” it is in danger of being driven onto the shore. Listless - When a ship was listless, she was sitting still and upright in the water, with no wind to make her lean over (list) and drive ahead. Long hau l - Operation on ship requiring the hauling of a lot of line. Also seen in short haul, an operation requiring little line. Long shot - In old warships, the muzzle-loading cannon were charged with black powder of uncertain potency that would propel the iron shot an equally uncertain distance with doubtful accuracy. A 24-pounder long gun, for instance, was considered to have a maximum effective range of 1200 yards, even though, under the right conditions, a ball might travel some 3000 yards. Similarly, a short, stubby 32-pounder carronade’s lethality faded fast beyond 400 yards. Thus, the odds were against a hit when one fired a long shot. Loose cannon - A cannon having come loose on the deck of a pitching, rolling, and yawing deck could cause severe injury and damage. Has come to mean an unpredictable or uncontrolled person who is likely to cause unintentional damage. Mainstay - A stay that extends from the maintop to the foot of the foremast of a sailing ship. Currently, a thing upon which something is based or depends. No room to swing a cat - The entire ship’s company was required to witness flogging at close hand. The crew might crowd around so that the Bosun’s Mate might not have enough room to swing his cat o’ nine tails. On your ends - The beams here are the horizontal transverse timbers of ships. This phrase came about with the allusion to the danger of imminent capsize if the ends were touching the water. Currently, means ‘to be in a bad situation’. Over the barrel - The most common method of punishment aboard ship was flogging. The unfortunate sailor was tied to a grating, mast or over the barrel of a deck cannon. Overbearing - To sail downwind directly at another ship thus “stealing” or diverting the wind from his sails. Overhaul - To prevent the buntline ropes from chaffing the sails, crew were sent aloft to haul them over the sails. This was called overhauling. Overreach - If a ship holds a tack course too long, it has overreached its turning point and the distance it must travel to reach its next tack point is increased. Overwhelm - Old English for capsize or founder. Pipe down - A boatswain’s call denoting the completion of an all hands evolution, and that you can go below. It was the last signal from the Bosun’s pipe each day which meant “lights out” and “silence”. Pooped - The rearmost, highest deck of a sailing ship was called the poop deck. If a ship were unlucky enough to be overtaken by a massive, breaking sea which drenched her from astern, she was said to have been “pooped.” When you think about it, the sea and shore uses of the word aren’t that different: in both cases, you’re washed out. Press into service - The British navy filled their ships’ crew quotas by kidnapping men off the streets and forcing them into service. This was called Impressment and was done by Press Gangs. Scuttlebutt - A butt was a barrel. Scuttle meant to chop a hole in something. The scuttlebutt was a water barrel with a hole cut into it so that sailors could reach in and dip out drinking water. The scuttlebutt was the place where the ship’s gossip was exchanged. Ship-shape and Bristol fashion - A reference to the precise nature of shipbuilding (and maintenance) as well as the exemplary work that came from Bristol shipyards. Shiver me timbers - one meaning of shiver, which is now largely forgotten, is ‘to break into pieces’. That meaning originated at least as early as the 14th century and is recorded in several Old English texts. So, the sailor’s oath shiver my timbers, is synonymous with (if so and so happens then…) let my boat break into pieces. Skyscraper - A small triangular sail set above the skysail in order to maximise effect in a light wind. Slush fund - A slushy slurry of fat was obtained by boiling or scraping the empty salted meat storage barrels. This stuff called “slush” was often sold ashore by the ship’s cook for the benefit of himself or the crew. The money so derived became known as a slush fund. Son of a gun - When in port, and with the crew restricted to the ship for any extended period of time, wives and ladies of easy virtue often were allowed to live aboard along with the crew. Infrequently, but not uncommonly, children were born aboard, and a convenient place for this was between guns on the gun deck. If the child’s father was unknown, they were entered in the ship’s log as “son of a gun”. Probably a sanitised version of “son of a bitch”, despite the various folk etymologies. A square meal - In good weather, crews’ mess was a warm meal served on square wooden platters. Squared away - On square-rigged vessels, the state of the sails when properly trimmed. Currently, arranged or dealt with in a satisfactory manner. Taken aback - A dangerous situation where the wind is on the wrong side of the sails pressing them back against the mast and forcing the ship astern. Most often this was caused by an inattentive helmsman who had allowed the ship to head up into the wind. Taking the wind out of his sails - Sailing in a manner so as to steal or divert wind from another ship’s sails. Taking turns - Changing watches with the turn of the hour glass. Three sheets to the wind - A sheet is a rope line which controls the tension on the downwind side of a square sail. If, on a three masted fully rigged ship, the sheets of the three lower course sails are loose, the sails will flap and flutter and are said to be “in the wind”. A ship in this condition would stagger and wander aimlessly downwind. Tide over - At first glance, this would seem to be an obviously nautical term. Today it means to make a small bit of something, usually money, last until a supply comes in, as in borrowing some money to tide you over till payday. However, the meaning has changed over the years. Once upon a time, ships could move under sail power, or in the absence of wind, float along with the tide called a tide over. One could say the floating would tide the ship over until wind came again to move it along. Toe the line - When called to line up at attention, the ship’s crew would form up with their toes touching a seam in the deck planking. True colours - The current meaning, ‘to reveal yourself as you really are’, actually came about because of the opposite phrase “false colours” – from the 17th century referring to a vessel which sailed under a flag not her own. This tactic was used by almost everyone as a ruse de guerre, but the rules of gentlemanly behaviour (and possibly actual legal rules) required one to raise one’s true colours before opening fire on another ship. Try a different tack - The direction in which a ship moves as determined by the position of its sails and regarded in terms of the direction of the wind (starboard tack). If one tack didn’t bring the ship up properly, one could always attempt another. Turn a blind eye - From Admiral Lord Nelson’s awesome display of badassery at the Battle of Copenhagen. When the signal was given to stop fighting, Nelson held his spyglass to his blind eye and insisted he didn’t see the signal. He then proceeded to kick butt, of course. Under the weather - Keeping watch onboard sailing ships was a boring and tedious job, but the worst watch station was on the “weather” (windward) side of the bow. The sailor who was assigned to this station was subject to the constant pitching and rolling of the ship. By the end of his watch, he would be soaked from the waves crashing over the bow. A sailor who was assigned to this unpleasant duty was said to be “under the weather.” Sometimes, these men fell ill and died as a result of the assignment, which is why today “under the weather” is used to refer to someone suffering from an illness. A related theory claims that ill sailors were sent below deck (or “under the weather”) if they were feeling sick. Warning shot across the bow - From the literal practice of firing a warning shot across another ship’s bow to encourage the captain to strike without engaging. Windfall - A sudden unexpected rush of wind from a mountainous shore which allowed a ship more leeway.
- Like this, share it
- Email a friend
Featured sailing opportunities

The Inside Passage (southern portion)
Boat type: Catalina 36
Location: Prince Rupert, BC, Canada

SW PACIFIC - Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Australia
Boat type: Sail Yacht Beneteau Cyclades 39.3 2006
Location: Vanuatu

Racing crew for club racing - Hamilton, Ontario
Boat type: Racing
Location: Hamilton, Ontario Canada
we love sailing as much as you do
Crewseekers is run by experienced, professional sailors offering a friendly and helpful service to yacht crew and owners. We are the original yacht crew introduction agency – established for over 25 years, offering amateur and professional sailing opportunities throughout the world.
“Yachting” is about more than being paid to party, it’s Hollywood’s murkiest open secret
Yachting 101: Fundamental Terms (+Slang and Jargon) Every Sailor Should Know

Here’s a list of fundamental yachting terms and slang words that are essential for efficient communication and secure navigation in the world of yachting and sailing:
- Aft – Toward the rear (stern) of the boat.
- Ahoy – A call used to greet someone or draw attention.
- Aloft – Up in the rigging.
- Anchor – A device used to hold a vessel in place.
- Astern – Behind the boat, or towards the back.
- Beam Reach – Sailing with the wind coming from the side.
- Beam – The width of the boat at its widest point.
- Bear Away – To steer away from the wind.
- Beating – Sailing upwind in a zigzag pattern.
- Bilge – The lowest part of the boat where water collects.
- Boom – A horizontal pole that extends from the bottom of the mast.
- Bow – The front of the boat.
- Bowline – A type of knot creating a fixed loop at the end of a rope.
- Broach – When a boat is knocked over by the wind.
- Burdened Vessel – The boat required to give way to another.
- Capsize – To overturn the boat in the water.
- Cat’s Paw – A light breeze that ruffles the water surface.
- Catamaran – A boat with two hulls.
- Chine – The intersection of the bottom and sides of a flat or v-bottomed boat.
- Cleat – A device for securing a rope.
- Close Reach – Sailing with the wind coming from the front quarter.
- Close-Hauled – Sailing as directly into the wind as possible.
- Cockpit – The area where the steering and navigation are done.
- Come About – To change direction by turning the bow through the wind.
- Companionway – The entrance from the deck to the cabin below.
- Course – The direction the boat is sailing.
- Cunningham – A line used to adjust the tension in the luff of the mainsail.
- Dead Ahead – Directly in front of the boat.
- Deck – The flat surface on top of the boat’s hull.
- Draft – The depth of water a boat needs to float.
- Draft – The vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull.
- Ease – To let out a sail or a line.
- Fairlead – A device to guide a line in a desired direction.
- Fender – A cushion used to protect the boat from rubbing against the dock.
- Forepeak – The front-most part of the interior of a boat.
- Foul – Tangled or obstructed.
- Galley – The kitchen area on a boat.
- Genoa – A large foresail that overlaps the mainsail.
- Gimbals – A device that allows an object to stay level despite the boat’s motion.
- Gybe – To change direction by turning the stern through the wind.
- Halyard – A rope used for hoisting sails.
- Hard Alee – Command to push the tiller all the way to leeward.
- Hatch – An opening in the deck for access below.
- Head – The bathroom on a boat.
- Heave To – A way to stop the boat by adjusting the sails and rudder.
- Helm – The wheel or tiller used to steer the boat.
- Hull – The main body of the boat.
- Jackline – A safety line running the length of the boat for attaching a safety harness.
- Jib – A triangular foresail.
- Jibe – Another term for gybe.
- Keel – The central structural basis of the hull, extending along the bottom.
- Ketch – A two-masted sailboat with the mizzen mast shorter and aft of the mainmast.
- Knot – A measure of speed; one knot equals one nautical mile per hour.
- Lazarette – A storage space in the stern.
- Lee Helm – A tendency for the boat to turn away from the wind.
- Leeward – The direction away from the wind.
- Lines – Ropes used on a boat.
- List – When the boat tilts to one side.
- Log – A record of a boat’s journey and operations.
- Mainsail – The primary and largest sail on a sailboat.
- Mast – A vertical pole that supports the sails.
- Mooring – Securing the boat to a fixed object.
- Navigation – The process of planning and following a course.
- Painter – A line attached to the bow of a small boat for towing or securing.
- Painter – A rope attached to the bow of a small boat.
- Port – The left side of the boat when facing forward.
- Porthole – A window in the side of the boat.
- Quarter – The sides of a boat near the stern.
- Reef – To reduce the area of a sail.
- Reefing – Reducing the sail area.
- Rigging – The system of ropes, wires, and chains used to support and control the sails.
- Rudder – A flat piece, usually at the stern, used to steer the boat.
- Running Rigging – The ropes used to control sails and other movable equipment.
- Saloon – The main living or dining area below deck.
- Scuppers – Drains on the deck that allow water to flow off.
- Seacock – A valve on a hull fitting.
- Sheet – A rope used to control the angle of a sail.
- Shroud – A rope or wire that supports the mast laterally.
- Slip – A docking space for a boat.
- Spinnaker – A large, balloon-like sail used when sailing downwind.
- Spreaders – Horizontal struts attached to the mast to support the shrouds.
- Starboard – The right side of the boat when facing forward.
- Stays – Wires or ropes that support the mast fore and aft.
- Staysail – A sail attached to the stay, running from the mast to the bow.
- Stern – The rear part of the boat.
- Stow – To put away or secure gear.
- Tack – The lower forward corner of a sail; also, to change direction by turning the bow through the wind.
- Telltale – Indicators attached to a sail to show the airflow over the sail.
- Telltales – Small pieces of material on the sails that show the direction of airflow.
- Transom – The flat surface forming the stern of the boat.
- Trim – To adjust the sails for optimal performance.
- True Wind – The actual wind speed and direction, as opposed to apparent wind.
- Underway – When the boat is moving through the water.
- Vang – A rope or tackle used to control the angle of the boom.
- Waypoint – A reference point on a navigation route.
- Weather Helm – A tendency for the boat to turn into the wind.
- Winch – A mechanical device used to haul in or let out ropes.
- Windward – The direction from which the wind is coming.
- Yacht – A large recreational boat.
- Yaw – When the boat swings off course.
These terms cover a broad range of yachting and sailing vocabulary, from basic components to specific maneuvers and navigational practices. We hope they will help you get into safe yachting more easily and quickly!
If you have any ideas on how to improve this list, or perhaps any other suggestions, please let us know in the comments below. Happy yachting! ⛵
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Yacht Sales
- Destinations
- Monaco Grand Prix
- About Ahoy Club
- Meet The Team
21 Common Yachting Terms Explained
Does it ever feel like yacht enthusiasts speak a whole other language? We get it. Everyone was new to yachting once and we all had to learn what different terms mean. Luckily, you have Ahoy Club to show you the ropes. Brush up on your sea vocabulary with some common definitions in our glossary below.

Essentially, parking your yacht so that you can hop over to shore and explore. It also refers to the literal anchor which holds your yacht in place.
APA (Advanced Provisioning Allowance)
A deposit paid by charterers to cover expenses during their trip. Expenses may include taxes, harbour fees, food and alcohol.
Base charter rate
The rate that you pay for the hire of your yacht and its crew. This does not include on board expenses and taxes which are covered by your APA (see above).
The total width of the yacht at its widest point.
The bedrooms on your yacht.
A type of yacht with two hulls. It was designed this way for increased stability on the water.
Explorer yacht
A yacht that is built to go to the farthest corners of the globe and into rough terrains. See examples in our past blog .
The territory under which a yacht is registered. The yacht’s flag state will govern the laws and regulations which it must follow.
A traditional motorised sailing yacht typically found in Turkey.
The main body of the yacht floating in the water; covers the front, sides, back and underside.
A boat or yacht’s speed measured in nautical miles per hour (see below).
A large luxury yacht typically measuring over 70m.
A boat with a single hull. May be a sailing yacht, motor yacht, luxury super- or megayacht. See Catamaran above for comparison.
Motor yacht (or M/Y)
A yacht which is powered with engines.
Nautical mile
A measure of distance on the water. One nautical mile is equal to 1852 metres or 1-minute of latitude on a navigational chart.
Preference sheet
The questionnaire that guests fill out before beginning their charter. It is meant to provide as much information as possible to the captain, crew and chef so that they may meet your preferences for an excellent trip.
Sailing yacht (or S/Y)
A yacht which is primarily powered with wind sails. Most also have motors as a backup.
The main living or lounge area on your yacht. Pronounced ‘sal-on’ not ‘sal-oon’.
A luxury yacht measuring between 24-69m.
A smaller boat housed on your yacht which can be used for transfers to shore, with your watertoys or on short day trips.
VAT (Value Added Tax)
A compulsory consumption tax set out by the countries you are visiting. See our blogs on the recent changes in Italy and France to learn more.
Yachting from A to Z with Ahoy Club
With Ahoy Club, you can expect everything about yacht chartering to be simpler. From our digital platform allowing you to browse thousands of yachts to our concierge team here to help with any questions. Check out our yachts for charter and test out your new yachting lingo ASAP.
Make an Enquiry

- Frank Magazine
- Denison History
- Virtual Tours
- Alaskan Yachts
- Azimut Yachts
- Back Cove Yachts
- Beneteau Yachts
- Benetti Superyachts
- Bertram Yachts
- Boston Whaler
- Broward Yachts
- Buddy Davis Sportfish
- Burger Yachts
- Cabo Yachts
- Carver Motoryachts
- Center Console
- Chris-Craft Yachts
- Cruisers Yachts
- DeFever Trawlers
- Dufour Sailboats
- Fairline Yachts
- Feadship Yachts
- Ferretti Yachts
- Formula Yachts
- Fountaine Pajot Cats
- Grady-White
- Grand Banks Trawlers
- Hargrave Yachts
- Hatteras Yachts
- Hinckley Picnic Boats
- Horizon Yachts
- Hydra-Sports
- Intrepid Boats
- Jarrett Bay Sportfish
- Jeanneau Yachts
- Kadey-Krogen Trawlers
- Lazzara Yachts
- Lekker Boats
- Luhrs Sportfish
- Marlow Yachts
- Maritimo Yachts
- Marquis Yachts
- McKinna Motoryachts
- Meridian Yachts
- Midnight Express
- Mochi Craft
- Neptunus Motoryachts
- Nordhavn Trawlers
- Nordic Tugs
- Ocean Alexander Yachts
- Offshore Yachts
- Oyster Sailing Yachts
- Pacific Mariner Yachts
- Palmer Johnson Yachts
- Pershing Yachts
- Prestige Yachts
- Princess Yachts
- Pursuit Yachts
- Riva Yachts
- Riviera Yachts
- Sabre Downeast
- San Lorenzo Yachts
- Sea Ray Boats
- SeaVee Central Consoles
- Selene Trawlers
- Scout Yachts
- Sunseeker Yachts
- Tiara Yachts
- Trinity Superyachts
- Viking Yachts
- Westport Yachts
Nautical + Sailing Terms You Should Know [578 Phrases]
![yacht slang definition Nautical + Sailing Terms You Should Know [578 Phrases]](https://cdn.denisonyachtsales.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/nautical-terms-you-should-know.jpg)

June 5, 2019 2:05 pm
A seaman’s jargon is among the most challenging to memorize. With over 500 terms used to communicate with a captain, crew, and sailors regarding navigation and more, there’s a word for nearly everything. No need to jump ship, this comprehensive list will have you speaking the lingo in no time.
Abaft the beam: A relative bearing of greater than 90 degrees from the bow. e.g. “two points abaft the port beam.”
Abaft: Toward the stern, relative to some object (“abaft the fore hatch”).
Abandon Ship: An imperative to leave the vessel immediately, usually in the face of some imminent danger.
Abeam: “On the beam”, a relative bearing at right angles to the centerline of the ship’s keel.
Aboard: On or in a vessel. Close aboard means near a ship.
Above board: On or above the deck, in plain view, not hiding anything.
Accommodation ladder: A portable flight of steps down a ship’s side.
Admiral: Senior naval officer of Flag rank. In ascending order of seniority, Rear Admiral, Vice Admiral, Admiral and Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy). Derivation reputedly Arabic, from “Emir al Bath” (“Ruler of the waters”).
Admiralty law: Body of law that deals with maritime cases. In the UK administered by the Probate, Divorce and Admiralty Division of the High Court of Justice.
Adrift: Afloat and unattached in any way to the shore or seabed. It may also imply that a vessel is not anchored and not under control, therefore goes where the wind and current take her, (loose from moorings, or out of place). Also refers to any gear not fastened down or put away properly. It can also be used to mean “absent without leave”.
Affreightment: Hiring of a vessel
Aft: Towards the stern (of the vessel).
Afterdeck: Deck behind a ship’s bridge
Afterguard: Men who work the aft sails on the quarterdeck and poop deck
Aground: Resting on or touching the ground or bottom.
Ahead: Forward of the bow.
Ahoy: A cry to draw attention. A term used to hail a boat or a ship, as “Boat ahoy!”.
Ahull: With sails furled and helm lashed to the lee-side.
Aid to Navigation: ( ATON) Any device external to a vessel or aircraft specifically intended to assist navigators in determining their position or safe course, or to warn them of dangers or obstructions to navigation.
All hands: Entire ship’s company, both officers and enlisted personnel.
All-Round White Light: On power-driven vessels less than 39.4 feet in length, this light may be used to combine a masthead light and sternlight into a single white light that can be seen by other vessels from any direction. This light serves as an anchor light when sidelights are extinguished.
Aloft: Above the ship’s uppermost solid structure; overhead or high above.
Alongside: By the side of a ship or pier.
Amidships (or midships): In the middle portion of the ship, along the line of the keel.
Anchor ball: Black shape hoisted in the forepart of a ship to show that ship is anchored in a fairway.
Anchor buoy: A small buoy secured by a light line to anchor to indicate the position of the anchor on the bottom.
Anchor chain or cable: Chain connecting the ship to the anchor.
Anchor detail: Group of men who handle ground tackle when the ship is anchoring or getting underway.
Anchor light: White light displayed by a ship at anchor. Two such lights are displayed by a ship over 150 feet (46 m) in length.
Anchor watch: Making sure that the anchor is holding and the vessel is not drifting. Important during rough weather and at night. Most marine GPS units have an Anchor Watch alarm capability.
Anchor: An object designed to prevent or slow the drift of a ship, attached to the ship by a line or chain; typically a metal, hook-like object, designed to grip the bottom under the body of water.
Anchorage: A suitable place for a ship to anchor. Area of a port or harbor.
Anchor’s aweigh: Said of an anchor when just clear of the bottom.
As the crow flies: A direct line between two points (which might cross land) which is the way crows travel rather than ships which must go around land.
Ashore: On the beach, shore or land.
Astern: Toward the stern; an object or vessel that is abaft another vessel or object.
ASW: Anti-submarine warfare.
Asylum Harbor: A harbor used to provide shelter from a storm.
Athwart, athwartships: At right angles to the fore and aft or centerline of a ship.
Avast: Stop! Cease or desist from whatever is being done.
Awash: So low in the water that the water is constantly washing across the surface.
Aweigh: Position of an anchor just clear of the bottom.
Aye, aye: Reply to an order or command to indicate that it, firstly, is heard; and, secondly, is understood and will be carried out. (“Aye, aye, sir” to officers).
Azimuth circle: Instrument used to take bearings of celestial objects.
Azimuth compass: An instrument employed for ascertaining the position of the sun with respect to magnetic north. The azimuth of an object is its bearing from the observer measured as an angle clockwise from true north.
Back and fill: To use the advantage of the tide being with you when the wind is not.
Backstays: Long lines or cables, reaching from the rear of the vessel to the mast heads, used to support the mast.
Baggywrinkle: A soft covering for cables (or any other obstructions) that prevents sail chafing from occurring.
Bale Cube (or Bale Capacity): The space available for cargo measured in cubic feet to the inside of the cargo battens, on the frames, and to the underside of the beams.
Ballaster: One who supplies ships with ballast.
Bank (sea floor): A large area of elevated sea floor.
Banyan: Traditional Royal Navy term for a day or shorter period of rest and relaxation.
Bar pilot: A bar pilot guides ships over the dangerous sandbars at the mouth of rivers and bays.
Bar: Large mass of sand or earth, formed by the surge of the sea. They are mostly found at the entrances of great rivers or havens, and often render navigation extremely dangerous, but confer tranquility once inside. See also: Touch and go, grounding. Alfred Lord Tennyson’s poem ‘Crossing the bar’ an allegory for death.
Bargemaster: Owner of a barge.
Barrelman: A sailor that was stationed in the crow’s nest.
Beacon: A lighted or unlighted fixed aid to navigation attached directly to the earth’s surface. (Lights and daybeacons both constitute beacons).
Beam ends: The sides of a ship. “On her beam ends” may mean the vessel is literally on her side and possibly about to capsize; more often, the phrase means the vessel is listing 45 degrees or more.
Beam: The beam of a ship is its width at the widest point or a point alongside the ship at the mid-point of its length.
Bear away: Turn away from the wind, often with reference to a transit.
Bear down: Turn away from the wind, often with reference to a transit.
Bearing: The horizontal direction of a line of sight between two objects on the surface of the earth.
Bee: Hardwood on either side of bowsprit through which forestays are reeved
Before the mast: Literally, the area of a ship before the foremast (the forecastle). Most often used to describe men whose living quarters are located here, officers being housed behind (abaft) the mast and enlisted men before the mast. This was because the midships area where the officers were berthed is more stable, being closer to the center of gravity, and thus more comfortable. It is less subject to the up and down movement resulting from the ship’s pitching.
Belay: To secure a rope by winding on a pin or cleat
Belaying pins: Bars of iron or hardwood to which running rigging may be secured, or belayed.
Berth: A bed on a boat, or a space in a port or harbor where a vessel can be tied up.
Best bower (anchor): The larger of two anchors carried in the bow; so named as it was the last, best hope.
Bilge: The bilge is the compartment at the bottom of the hull of a ship or boat where water collects so that it may be pumped out of the vessel at a later time.
Bilged on her anchor: A ship that has run upon her own anchor.
Bimini: Weather-resistant fabric stretched over a stainless steel frame, fastened above the cockpit of a sailboat or flybridge of a power yacht which serves as a rain or sun shade.
Bimmy: A punitive instrument.
Binnacle list: A ship’s sick list. The list of men unable to report for duty was given to the officer or mate of the watch by the ship’s surgeon. The list was kept at the binnacle.
Binnacle: The stand on which the ship’s compass is mounted.
Bitter end: The anchor cable is tied to the bitts when the cable is fully paid out, the bitter end has been reached. The last part of a rope or cable.
Bitts: Posts mounted on a ship for fastening ropes
Bloody: An intensive derived from the substantive ‘blood’, a name applied to the Bucks, Scrowers, and Mohocks of the seventeenth centuries.
Blue Peter: A blue and white flag hoisted at the foretrucks of ships about to sail.
Boat: A craft or vessel designed to float on, and provide transport over, water.
Boatswain or bosun: A non-commissioned officer responsible for the sails, ropes, and boats on a ship who issues “piped” commands to seamen.
Bobstay: Rope used on ships to steady the bowsprit
Bollard: From “bol” or “bole”, the round trunk of a tree. A substantial vertical pillar to which lines may be made fast. Generally on the quayside rather than the ship.
Boltrope: Strong rope stitched to edges of a sail
Booby hatch: A sliding hatch or cover.
Booby: A type of bird that has little fear and therefore is particularly easy to catch, hence booby prize.
Boom vang: A sail control that lets one apply downward tension on the boom, countering the upward tension provided by the mainsail. The boom vang adds an element of control to mainsail shape when the mainsheet is let out enough that it no longer pulls the boom down. Boom vang tension helps control leech twist, a primary component of sail power.
Boom: A spar used to extend the foot of a fore-and-aft sail.
Booms: Masts or yards, lying on board in reserve.
Bosun: Boatswain
Bottomry: Pledging a ship as security in a financial transaction.
Bow: The front of a ship.
Bower: Anchor carried at bow of a ship
Bowline: A type of knot, producing a strong loop of a fixed size, topologically similar to a sheet bend. Also, a rope attached to the side of a sail to pull it towards the bow (for keeping the windward edge of the sail steady).
Bowse: To pull or hoist.
Bowsprit: A spar projecting from the bow used as an anchor for the forestay and other rigging.
Brail: To furl or truss a sail by pulling it in towards the mast, or the ropes used to do so.
Bream: To clean a ship’s bottom by burning off seaweed.
Bridge: A structure above the weather deck, extending the full width of the vessel, which houses a command center, itself called by association, the bridge.
Bring to: Cause a ship to be stationary by arranging the sails.
Broaching-to: A sudden movement in navigation, when the ship, while scudding before the wind, accidentally turns her leeward side to windward, also use to describe the point when water starts to come over the gunwale due to this turn.
Buffer: The chief bosun’s mate, responsible for discipline.
Bulkhead: An upright wall within the hull of a ship. Particularly a load bearing wall.
Bulwark: The extension of the ship’s side above the level of the weather deck.
Bumboat: A private boat selling goods.
Bumpkin: An iron bar (projecting outboard from a ship’s side) to which the lower and topsail brace blocks are sometimes hooked. Chains supporting/stabilizing the bowsprit.
Bunt: Middle of sail, fish-net or cloth when slack.
Buntline: One of the lines tied to the bottom of a square sail and used to haul it up to the yard when furling.
Buoy: A floating object of defined shape and color, which is anchored at a given position and serves as an aid to navigation.
Buoyed Up: Lifted by a buoy, especially a cable that has been lifted to prevent it from trailing on the bottom.
Burgee: Small ship’s flag used for identification or signaling.
By and Large: By means into the wind, while large means with the wind. By and large, is used to indicate all possible situations “the ship handles well both by and large”.
By the board: Anything that has gone overboard.
Cabin boy: attendant on passengers and crew.
Cabin: an enclosed room on a deck or flat.
Cable: A large rope; also a measure of length or distance. Equivalent to (UK) 1/10 nautical mile, approx. 600 feet; (USA) 120 fathoms, 720 feet (219 m); other countries use different values.
Cabotage: Shipping and sailing between points in the same country.
Camber: Slight arch or convexity to a beam or deck of a ship.
Canister: A type of anti-personnel cannon load in which lead balls or other loose metallic items were enclosed in a tin or iron shell. On firing the shell would disintegrate releasing the smaller metal objects.
Cape Horn fever: The name of the fake illness a malingerer is pretending to suffer from.
Capsize: When a ship or boat lists too far and rolls over, exposing the keel. On large vessels, this often results in the sinking of the ship.
Capstan: A huge rotating hub (wheel) mounted vertically and provided with horizontal holes to take up the capstan bars (when manually rotated), used to wind in anchors or other heavy objects; and sometimes to administer flogging over.
Captain’s daughter: The cat o’ nine tails, which in principle is only used on board on the captain’s (or a court martial’s) personal orders.
Careening: Cause the ship to tilt on its side, usually to clean or repair the hull below the water line.
Cargo Deadweight Tons: The weight remaining after deducting fuel, water, stores, dunnage and such other items necessary for use on a voyage from the deadweight of the vessel.
Carlin: Similar to a beam, except running in a fore and aft direction.
Cat Head: A beam extending out from the hull used to support an anchor when raised in order to secure or “fish” it.
Cat: To prepare an anchor, after raising it by lifting it with a tackle to the Cat Head, prior to securing (fishing) it alongside for sea. (An anchor raised to the Cat Head is said to be catted).
Catamaran: A vessel with two hulls.
Catboat: A cat-rigged vessel with only one sail, usually on a gaff.
Centreboard: A removable keel used to resist leeway.
Chafing Gear: Material applied to a line or spar to prevent or reduce chafing. See Baggywrinkle.
Chafing: Wear on the line or sail caused by constant rubbing against another surface.
Chain-wale or channel: A broad, thick plank that projects horizontally from each of a ship’s sides abreast a mast, distinguished as the fore, main, or mizzen channel accordingly, serving to extend the base for the shrouds, which supports the mast.
Chine: A relatively sharp angle in the hull, as compared to the rounded bottoms of most traditional boat hulls.
Chock: Metal casting with curved arms for passing ropes for mooring ship.
Chock-a-block: Rigging blocks that are so tight against one another that they cannot be further tightened.
Clean bill of health: A certificate issued by a port indicating that the ship carries no infectious diseases.
Clean slate: At the helm, the watch keeper would record details of speed, distances, headings, etc. on a slate. At the beginning of a new watch the slate would be wiped clean.
Cleat: A stationary device used to secure a rope aboard a vessel.
Clew: Corner of sail with a hole to attach ropes.
Clew-lines: Used to truss up the clews, the lower corners of square sails.
Club: hauling the ship drops one of its anchors at high speed to turn abruptly. This was sometimes used as a means to get a good firing angle on a pursuing vessel.
Coaming: The raised edge of a hatchway used to help keep out water.
Cocket: Official shipping seal; customs clearance form.
Cofferdam: Narrow vacant space between two bulkheads of a ship.
Cog: Single-masted, square-sailed ship with a raised stern.
Companionway: A raised and windowed hatchway in the ship’s deck, with a ladder leading below and the hooded entrance-hatch to the main cabins.
Compass: Navigational instrument that revolutionized travel.
Complement: The full number of people required to operate a ship. Includes officers and crewmembers; does not include passengers.
Cordage: Ropes in the rigging of a ship.
Corrector: a device to correct the ship’s compass.
Courses: The mainsail, foresail, and mizzen.
Coxswain or cockswain: The helmsman or crew member in command of a boat.
Cringle: Loop at the corner of a sail to which a line is attached.
Crosstrees: Horizontal crosspieces at a masthead used to support ship’s mast.
Crow’s nest: Specifically a masthead constructed with sides and sometimes a roof to shelter the lookouts from the weather, generally by whaling vessels, this term has become a generic term for what is properly called masthead. See masthead.
Cube: The cargo carrying capacity of a ship, measured in cubic feet.
Cuddy: A small cabin in a boat.
Cunningham: A line invented by Briggs Cunningham, used to control the shape of a sail.
Cut and run: When wanting to make a quick escape, a ship might cut lashings to sails or cables for anchors, causing damage to the rigging, or losing an anchor, but shortening the time needed to make ready by bypassing the proper procedures.
Cut of his jib: The “cut” of a sail refers to its shape. Since this would vary between ships, it could be used both to identify a familiar vessel at a distance and to judge the possible sailing qualities of an unknown one.
Cut splice: A join between two lines, similar to an eye-splice, where each rope end is joined to the other a short distance along, making an opening which closes under tension.
Cutline: The “valley” between the strands of a rope or cable. Before serving a section of laid rope e.g. to protect it from chafing, it may be “wormed” by laying yarns in the cuntlines, giving that section an even cylindrical shape.
Daggerboard: A type of centerboard that is removed vertically.
Davit: Device for hoisting and lowering a boat.
Davy Jones (Locker): An idiom for the bottom of the sea.
Daybeacon: An unlighted fixed structure which is equipped with a dayboard for daytime identification.
Dayboard: The daytime identifier of an aid to navigation presenting one of several standard shapes (square, triangle, rectangle) and colors (red, green, white, orange, yellow, or black).
Deadeye: A round wooden plank which serves a similar purpose to a block in the standing rigging of large sailing vessels.
Deadrise: The design angle between the keel (q.v.) and horizontal.
Deadweight Tons (DWT): The difference between displacement, light and displacement, and loaded. A measure of the ship’s total carrying capacity.
Deadwood: Timbers built into ends of a ship when too narrow to permit framing.
Deckhand: A person whose job involves aiding the deck supervisor in (un)mooring, anchoring, maintenance, and general evolutions on deck.
Deck supervisor: The person in charge of all evolutions and maintenance on deck; sometimes split into two groups: forward deck supervisor, aft deck supervisor.
Deckhead: The under-side of the deck above. Sometimes paneled over to hide the pipework. This paneling, like that lining the bottom and sides of the holds, is the ceiling.
Decks: the structures forming the approximately horizontal surfaces in the ship’s general structure. Unlike flats, they are a structural part of the ship.
Demurrage: Delay of the vessel’s departure or loading with cargo.
Derrick: A lifting device composed of one mast or pole and a boom or jib which is hinged freely at the bottom.
Directional light: A light illuminating a sector or very narrow-angle and intended to mark a direction to be followed.
Displacement, Light: The weight of the ship excluding cargo, fuel, ballast, stores, passengers, and crew, but with water in the boilers to steaming level.
Displacement, Loaded: The weight of the ship including cargo, passengers, fuel, water, stores, dunnage and such other items necessary for use on a voyage, which brings the vessel down to her load draft.
Displacement: A measurement of the weight of the vessel, usually used for warships. Displacement is expressed either in long tons of 2,240 pounds or metric tons of 1,000 kg.
Disrate: To reduce in rank or rating; demote.
Dodger: Shield against rain or spray on a ship’s bridge.
Dog watch: A short watch period, generally half the usual time (e.g. a two-hour watch between two four hour ones). Such a watch might be included in order to slowly rotate the system over several days for fairness or to allow both watches to eat their meals at approximately normal times.
Dolphin: A structure consisting of a number of piles driven into the seabed or riverbed in a circular pattern and drawn together with wire rope.
Downhaul: A line used to control either a mobile spar or the shape of a sail.
Draft, Air: Air Draft is the distance from the water line to the highest point on a ship (including antennas) while it is loaded.
Draft: The distance between the waterline and the keel of a boat; the minimum depth of water in which a boat will float.
Dressing down: Treating old sails with oil or wax to renew them, or a verbal reprimand.
Driver: The large sail flown from the mizzen gaff.
Driver-mast: The fifth mast of a six-masted barquentine or gaff schooner. It is preceded by the jigger mast and followed by the spanker mast. The sixth mast of the only seven-masted vessel, the gaff schooner Thomas W. Lawson, was normally called the pusher-mast.
Dromond: Large single-sailed ship powered by rowers.
Dunnage: Loose packing material used to protect a ship’s cargo from damage during transport. Personal baggage.
Dyogram: Ship’s chart indicating compass deflection due to ship’s iron.
Earrings: Small lines, by which the uppermost corners of the largest sails are secured to the yardarms.
Embayed: The condition where a sailing vessel is confined between two capes or headlands, typically where the wind is blowing directly onshore.
Ensign: Large naval flag.
Escutcheon: Part of ship’s stern where name is displayed.
Extremis (also known as “in extremis”): The point under International Rules of the Road (Navigation Rules) at which the privileged (or stand-on) vessel on a collision course with a burdened (or give-way) vessel determines it must maneuver to avoid a collision. Prior to extremes, the privileged vessel must maintain course and speed and the burdened vessel must maneuver to avoid a collision.
Fairlead: Ring through which rope is led to change its direction without friction.
Fardage: Wood placed in the bottom of the ship to keep cargo dry.
Fathom: A unit of length equal to 6 feet (1.8 m), roughly measured as the distance between a man’s outstretched hands.
Fender: An air or foam filled bumper used in boating to keep boats from banging into docks or each other.
Fiddley: Iron framework around hatchway opening.
Figurehead: Symbolic image at the head of a traditional sailing ship or early steamer.
Fireship: A ship loaded with flammable materials and explosives and sailed into an enemy port or fleet either already burning or ready to be set alight by its crew (who would then abandon it) in order to collide with and set fire to enemy ships.
First Lieutenant: In the Royal Navy, the senior lieutenant on board; responsible to the Commander for the domestic affairs of the ship’s company. Also known as ‘Jimmy the One’ or ‘Number One’. Removes his cap when visiting the mess decks as a token of respect for the privacy of the crew in those quarters. Officer i/c cables on the forecastle. In the U.S. Navy the senior person in charge of all Deckhands.
First Mate: The Second in command of a ship.
Fish: To repair a mast or spar with a fillet of wood. To secure an anchor on the side of the ship for sea,otherwise known as “catting”.
Flag hoist: A number of signal flags strung together to convey a message, e.g. “England expects…”.
Flagstaff: Flag pole at the stern of a ship.
Flank: The maximum speed of a ship. Faster than “full speed”.
Flatback: A Great Lakes slang term for a vessel without any self-unloading equipment.
Flemish Coil: A line coiled around itself to neaten the decks or dock.
Flog: To beat, to punish.
Fluke: The wedge-shaped part of an anchor’s arms that digs into the bottom.
Fly by night: A large sail used only for sailing downwind, requiring little attention.
Following sea: Wave or tidal movement going in the same direction as a ship.
Foot: The bottom of a sail.
Footloose: If the foot of a sail is not secured properly, it is footloose, blowing around in the wind.
Footrope: Each yard on a square-rigged sailing ship is equipped with a footrope for sailors to stand on while setting or stowing the sails.
Fore: Towards the bow (of the vessel).
Forebitt: Post for fastening cables at a ship’s foremast.
Forecabin: Cabin in the fore part of a ship.
Forecastle: A partial deck, above the upper deck and at the head of the vessel; traditionally the sailors living quarters. Pronounced “foc-sle”. The name is derived from the castle fitted to bear archers in time of war.
Forefoot: The lower part of the stem of a ship.
Foremast: Mast nearest the bow of a ship
Foresail: The lowest sail set on the foremast of a square-rigged ship.
Forestays: Long lines or cables, reaching from the front of the vessel to the mast heads, used to support the mast.
Forward: The area towards the bow.
Founder: To fill with water and sink → Wiktionary.
Frap: To draw a sail tight with ropes or cables.
Freeboard: The height of a ship’s hull (excluding superstructure) above the waterline. The vertical distance from the current waterline to the lowest point on the highest continuous watertight deck. This usually varies from one part to another.
Full and by: Sailing into the wind (by), but not as close-hauled as might be possible, so as to make sure the sails are kept full. This provides a margin for error to avoid being taken aback (a serious risk for square-rigged vessels) in a tricky sea. Figuratively it implies getting on with the job but in a steady, relaxed way, without undue urgency or strain.
Furl: To roll or wrap a sail around the mast or spar to which it is attached.
Futtock: Rib of a ship.
Gaff: The spar that holds the upper edge of a fore-and-aft or gaff sail. Also, a long hook with a sharp point to haul fish in.
Gaff-topsail: Triangular topsail with its foot extended upon the gaff.
Galley: The kitchen of the ship.
Gangplank: A movable bridge used in boarding or leaving a ship at a pier; also known as a “brow”.
Gangway: Either of the sides of the upper deck of a ship
Garbled: Garbling was the (illegal) practice of mixing cargo with garbage.
Garboard: The strake closest to the keel (from Dutch gaarboard).
Genoa: Large jib that overlaps the mainsail
Global Positioning System (GPS): A satellite-based radio navigation system providing continuous worldwide coverage. It provides navigation, position, and timing information to air, marine, and land users.
Grain Cube (or Grain Capacity): The maximum space available for cargo measured in cubic feet, the measurement being taken to the inside of the shell plating of the ship or to the outside of the frames and to the top of the beam or underside of the deck plating.
Grapnel: Small anchor used for dragging or grappling.
Gross Tons: The entire internal cubic capacity of the ship expressed in tons of 100 cubic feet to the ton, except certain spaces which are exempted such as: peak and other tanks for water ballast, open forecastle bridge and poop, access of hatchways, certain light and air spaces, domes of skylights, condenser, anchor gear, steering gear, wheelhouse, galley and cabin for passengers.
Groundage: A charge on a ship in port.
Gudgeon: Metal socket into which the pintle of a boat’s rudder fits.
Gunnage: Number of guns carried on a warship.
Gunwhale: Upper edge of the hull.
Gybe: To swing a sail from one side to another.
Halyard or Halliard: Originally, ropes used for hoisting a spar with a sail attached; today, a line used to raise the head of any sail.
Hammock: Canvas sheets, slung from the deckhead in mess decks, in which seamen slept. “Lash up and stow” a piped command to tie up hammocks and stow them (typically) in racks inboard of the ship’s side to protect the crew from splinters from shot and provide a ready means of preventing flooding caused by damage.
Hand Bomber: A ship using coal-fired boilers shoveled in by hand.
Handsomely: With a slow even motion, as when hauling on a line “handsomely.”
Hank: A fastener attached to the luff of the headsail that attaches the headsail to the forestay. Typical designs include a bronze or plastic hook with a spring-operated gate or a strip of cloth webbing with a snap fastener.
Harbor: A harbor or haven is a place where ships may shelter from the weather or are stored. Harbors can be man-made or natural.
Haul wind: To point the ship so as to be heading in the same direction as the wind, generally not the fastest point of travel on a sailing vessel.
Hawse: Distance between ship’s bow and its anchor.
Hawse-hole: A hole in a ship’s bow for a cable or chain, such as for an anchor, to pass through.
Hawsepiper: An informal maritime industry term used to refer to a merchant ship’s officer who began his or her career as an unlicensed merchant seaman and did not attend a traditional maritime college/academy to earn the officer license.
Hawser: Large rope for mooring or towing a ship.
Head of navigation: A term used to describe the farthest point above the mouth of a river that can be navigated by ships.
Head: The toilet or latrine of a vessel, which for sailing ships projected from the bows.
Headsail: Any sail flown in front of the most forward mast.
Heave down: Turn a ship on its side (for cleaning).
Heave: A vessel’s transient up-and-down motion.
Heaving to: To stop a sailing vessel by lashing the helm in opposition to the sails. The vessel will gradually drift to leeward, the speed of the drift depending on the vessel’s design.
Heeling: The lean caused by the wind’s force on the sails of a sailing vessel.
Helm: Ship’s steering wheel.
Helmsman: A person who steers a ship.
Hogging or hog: The distortion of the hull where the ends of the keel are lower than the center.
Hold: In earlier use, below the orlop deck, the lower part of the interior of a ship’s hull, especially when considered as storage space, as for cargo. In later merchant vessels, it extended up through the decks to the underside of the weather deck.
Holiday: A gap in the coverage of newly applied paint, slush, tar, or other preservatives.
Holystone: Sandstone material used to scrape ships’ decks
Horn: A sound signal which uses electricity or compressed air to vibrate a disc diaphragm.
Horse: Attachment of sheets to the deck of the vessel (Main-sheet horse).
Hounds: Attachments of stays to masts.
Hull: The shell and framework of the basic flotation-oriented part of a ship.
Hydrofoil: A boat with wing-like foils mounted on struts below the hull.
Icing: A serious hazard where cold temperatures (below about -10°C) combined with high wind speed (typically force 8 or above on the Beaufort scale) result in spray blown off the sea freezing immediately on contact with the ship.
Idlers: Members of a ship’s company not required to serve watches. These were in general specialist tradesmen such as the carpenter and the sailmaker.
In Irons: When the bow of a sailboat is headed into the wind and the boat has stalled and is unable to maneuver.
In the offing: In the water visible from on board a ship, now used to mean something imminent.
Inboard: Inside the line of a ship’s bulwarks or hull.
Inboard-Outboard drive system: A larger Power Boating alternative drive system to transom mounted outboard motors.
Jack: Ship’s flag flown from jack-staff at the bow of a vessel.
Jack-block: Pulley system for raising topgallant masts.
Jack-cross-tree: Single iron cross-tree at the head of a topgallant mast.
Jacklines or Jack Stays: Lines, often steel wire with a plastic jacket, from the bow to the stern on both port and starboard. The Jack Lines are used to clip on the safety harness to secure the crew to the vessel while giving them the freedom to walk on the deck.
Jackstaff: Short staff at ship’s bow from which the jack is hoisted.
Jackyard: Spar used to spread the foot of a gaff-topsail
Jib: A triangular staysail at the front of a ship.
Jibboom: Spar forming an extension of the bowsprit.
Jibe: To change a ship’s course to make the boom shift sides.
Jigger-mast: The fourth mast, although ships with four or more masts were uncommon, or the aft-most mast where it is smallest on vessels of less than four masts.
Junk: Old cordage past its useful service life as lines aboard ship. The strands of old junk were teased apart in the process called picking oakum.
Jurymast: Mast erected on a ship in place of one lost.
Kedge: Small anchor to keep a ship steady.
Keel: A boat’s backbone; the lowest point of the boat’s hull, the keel provides strength, stability and prevents sideways drift of the boat in the water.
Keel: The central structural basis of the hull.
Keelson: Lengthwise wooden or steel beam in ship for bearing stress.
Kentledge: Pig-iron used as ballast in ship’s hold.
Killick: A small anchor. A fouled killick is the substantive badge of non-commissioned officers in the RN. Seamen promoted to the first step in the promotion ladder are called “Killick”. The badge signifies that here is an Able Seaman skilled to cope with the awkward job of dealing with a fouled anchor.
Ladder: On board a ship, all “stairs” are called ladders, except for literal staircases aboard passenger ships. Most “stairs” on a ship are narrow and nearly vertical, hence the name. Believed to be from the Anglo-Saxon word “hiaeder”, meaning ladder.
Lagan: Cargo jettisoned from the ship but marked by buoys for recovery.
Laker: Great Lakes slang for a vessel who spends all its time on the 5 Great Lakes.
Landlubber: A person unfamiliar with being on the sea.
Lanyard: Rope or line for fastening something in a ship.
Larboard: The left side of the ship.Derived from the old ‘lay-board’ providing access between a ship and a quay.
Lastage: Room for stowing goods in a ship.
Lateen: Triangular sail rigged on ship’s spar.
Lateral System: A system of aids to navigation in which characteristics of buoys and beacons indicate the sides of the channel or route relative to a conventional direction of buoyage (usually upstream).
Laveer: To sail against the wind.
Lay down: To lay a ship down is to begin construction in a shipyard.
Lay: To come and go, used in giving orders to the crew, such as “lay forward” or “lay aloft”. To direct the course of the vessel. Also, to twist the strands of a rope together.
Lazaret: Space in ship between decks used for storage.
League: A unit of length, normally equal to three nautical miles.
Lee shore: A shore downwind of a ship. A ship which cannot sail well to windward risks being blown onto a lee shore and grounded.
Lee side: The side of a ship sheltered from the wind (opposite the weather side or windward side).
Leeboard: Wood or metal planes attached to the hull to prevent leeway.
Leech: The aft or trailing edge of a fore-and-aft sail; the leeward edge of a spinnaker; a vertical edge of a square sail. The leech is susceptible to twist, which is controlled by the boom vang and mainsheet.
Lee helm: If the helm was centered, the boat would turn away from the wind (to the lee). Consequently, the tiller must be pushed to the lee side of the boat in order to make the boat sail in a straight line.
Leeward: In the direction that the wind is blowing towards.
Leeway: The angle that a ship is blown leeward by the wind. See also “weatherly”.
Length at Waterline (LWL): The ship’s length measured at the waterline.
Length Overall (LOA): The maximum length of the ship.
Length: The distance between the forwardmost and aftermost parts of the ship.
Let go and haul: An order indicating that the ship is in line with the wind.
Lifeboat: A small steel or wood boat located near the stern of a vessel. Used to get the crew to safety if something happens to the mothership.
Line: The correct nautical term for the majority of the cordage or “ropes” used on a vessel. A line will always have a more specific name, such as mizzen topsail halyard, which describes its use.
Liner: Ship of The Line: a major warship capable of taking its place in the main (battle) line of fighting ships. Hence the modern term for most prestigious passenger vessel: Liner.
List: The vessel’s angle of lean or tilt to one side, in the direction called the roll.
Loggerhead: An iron ball attached to a long handle, used for driving caulking into seams and (occasionally) in a fight. Hence: “at loggerheads”.
Loxodograph: Device used to record the ship’s travels.
Lubber’s line: A vertical line inside a compass case indicating the direction of the ship’s head.
Luff: The forward edge of a sail. To head a sailing vessel more towards the direction of the wind.
Luffing: When a sailing vessel is steered far enough to windward that the sail is no longer completely filled with wind. The flapping of the sail(s) which results from having no wind in the sail at all.
Lugsail: Four-sided sail bent to an obliquely hanging yard.
Lutchet: Fitting on ship’s deck to allow the mast to pivot to pass under bridges.
Lying ahull: Waiting out a storm by dousing all sails and simply letting the boat drift.
Mainbrace: The brace attached to the mainmast.
Mainmast (or Main): The tallest mast on a ship.
Mainsail: Principal sail on a ship’s mainmast.
Mainsheet: Sail control line that allows the most obvious effect on mainsail trim. Primarily used to control the angle of the boom, and thereby the mainsail, this control can also increase or decrease downward tension on the boom while sailing upwind, significantly affecting sail shape. For more control over downward tension on the boom, use a boom vang.
Mainstay: Stay that extends from the main-top to the foot of the foremast.
Man overboard: A cry let out when a seaman has gone overboard.
Manrope: Rope used as a handrail on a ship.
Marina: A docking facility for small ships and yachts.
Martingale: Lower stay of rope used to sustain the strain of the forestays.
Mast: A vertical pole on a ship which supports sails or rigging.
Master: Either the commander of a commercial vessel, or a senior officer of a naval sailing ship in charge of routine seamanship and navigation but not in command during combat.
Masthead Light: This white light shines forward and to both sides and is required on all power-driven vessels.
Masthead: A small platform partway up the mast, just above the height of the mast’s main yard. A lookout is stationed here, and men who are working on the main yard will embark from here. See also Crow’s Nest.
Matelot: A traditional Royal Navy term for an ordinary sailor.
Mess: An eating place aboard ship. A group of the crew who live and feed together.
Midshipman: A non-commissioned officer below the rank of Lieutenant. Usually regarded as being “in training” to some degree.
Mizzen staysail: Sail on a ketch or yawl, usually lightweight, set from, and forward of, the mizzen mast while reaching in light to moderate air.
Mizzen: Three-masted vessel; aft sail of such a vessel.
Monkey fist: A ball woven out of line used to provide heft to heave the line to another location. The monkey fist and other heaving-line knots were sometimes weighted with lead (easily available in the form of foil used to seal e.g. tea chests from dampness) although Clifford W. Ashley notes that there was a “definite sporting limit” to the weight thus added.
Moonraker: Topmost sail of a ship, above the skyscraper.
Moor: To attach a boat to a mooring buoy or post. Also, to a dock a ship.
Navigation rules: Rules of the road that provide guidance on how to avoid collision and also used to assign blame when a collision does occur.
Net Tons: Obtained from the gross tonnage by deducting crew and navigating spaces and allowances for propulsion machinery.
Nipper: Short rope used to bind a cable to the “messenger” (a moving line propelled by the capstan) so that the cable is dragged along too (Used because the cable is too large to be wrapped around the capstan itself). During the raising of an anchor, the nippers were attached and detached from the (endless) messenger by the ship’s boys. Hence the term for small boys: “nippers”.
Oakum: Old ropes untwisted for caulking the seams of ships.
Oreboat: Great Lakes Term for a vessel primarily used in the transport of iron ore.
Orlop deck: The lowest deck of a ship of the line. The deck covering in the hold.
Outhaul: A line used to control the shape of a sail.
Outrigger: Spar extended from the side of the ship to help secure mast.
Outward bound: To leave the safety of the port, heading for the open ocean.
Overbear: To sail downwind directly at another ship, stealing the wind from its sails.
Overfall: Dangerously steep and breaking seas due to opposing currents and wind in a shallow area.
Overhaul: Hauling the buntline ropes over the sails to prevent them from chaffing.
Overhead: The “ceiling,” or, essentially, the bottom of the deck above you.
Overreach: When tacking, to hold a course too long.
Overwhelmed: Capsized or foundered.
Owner: Traditional Royal Navy term for the Captain, a survival from the days when privately-owned ships were often hired for naval service.
Ox-Eye: A cloud or other weather phenomenon that may be indicative of an upcoming storm.
Painter: Rope attached to the bow of a boat to attach it to a ship or a post.
Pallograph: Instrument measuring ship’s vibration.
Parrel: A movable loop, used to fasten the yard to its respective mast.
Patroon: Captain of a ship; coxswain of a longboat.
Pay: Fill a seam (with caulking or pitch), or to lubricate the running rigging; pay with slush (q.v.), or protect from the weather by covering with slush. See also: The Devil to pay. (French from paix, pitch).
Paymaster: The officer responsible for all money matters in RN ships including the paying and provisioning of the crew, all stores, tools, and spare parts. See also: purser.
Pilot: Navigator. A specially knowledgeable person qualified to navigate a vessel through difficult waters, e.g. harbor pilot, etc.
Pipe (Bos’n’s), or a Bos’n’s Call: A whistle used by Boatswains (bosuns or bos’ns) to issue commands. Consisting of a metal tube which directs the breath over an aperture on the top of a hollow ball to produce high pitched notes. The pitch of the notes can be changed by partly covering the aperture with the finger of the hand in which the pipe is held. The shape of the instrument is similar to that of a smoking pipe.
Pipe down: A signal on the bosun’s pipe to signal the end of the day, requiring lights (and smoking pipes) to be extinguished and silence from the crew.
Piping the side: A salute on the bos’n’s pipe(s) performed in the company of the deck watch on the starboard side of the quarterdeck or at the head of the gangway, to welcome or bid farewell to the ship’s Captain, senior officers and honored visitors.
Pitch: A vessel’s motion, rotating about the beam axis, so the bow pitches up and down.
Pitchpole: To capsize a boat end over end, rather than by rolling over.
Pontoon: A flat-bottomed vessel used as a ferry or a barge or float moored alongside a jetty or a ship to facilitate boarding.
Poop deck: A high deck on the aft superstructure of a ship.
Port: Towards the left-hand side of the ship facing forward (formerly Larboard). Denoted with a red light at night.
Preventer (Gybe preventer, Jibe preventer): A sail control line originating at some point on the boom leading to a fixed point on the boat’s deck or rail (usually a cleat or pad eye) used to prevent or moderate the effects of an accidental jibe.
Primage: Fee paid to loaders for loading ship.
Privateer: A privately-owned ship authorized by a national power (by means of a Letter of Marque) to conduct hostilities against an enemy. Also called a private man of war.
Propeller walk or prop walk: Tendency for a propeller to push the stern sideways. In theory, a right-hand propeller in reverse will walk the stern to port.
Prow: A poetical alternative term for bows.
Purser: Ship’s officer in charge of finances and passengers.
Quarterdeck: The aftermost deck of a warship. In the age of sail, the quarterdeck was the preserve of the ship’s officers.
Quartering: Sailing nearly before the wind.
Quayside: Refers to the dock or platform used to fasten a vessel to.
Radar reflector: A special fixture fitted to a vessel or incorporated into the design of certain aids to navigation to enhance their ability to reflect radar energy. In general, these fixtures will materially improve the visibility for use by vessels with radar.
Radar: Acronym for Radio Detection And Ranging. An electronic system designed to transmit radio signals and receive reflected images of those signals from a “target” in order to determine the bearing and distance to the “target”.
Rake: The inclination of a mast or another part of a ship.
Range lights: Two lights associated to form a range (a line formed by the extension of a line connecting two charted points) which often, but not necessarily, indicates the channel centerline. The front range light is the lower of the two, and nearer to the mariner using the range. The rear light is higher and further from the mariner.
Ratlines: Rope ladders permanently rigged from bulwarks and tops to the mast to enable access to topmasts and yards. Also, serve to provide lateral stability to the masts.
Reach: A point of sail from about 60° to about 160° off the wind. Reaching consists of “close reaching” (about 60° to 80°), “beam reaching” (about 90°) and “broad reaching” (about 120° to 160°).
Reef points: Small lengths of cord attached to a sail, used to secure the excess fabric after reefing.
Reef: To temporarily reduce the area of a sail exposed to the wind, usually to guard against adverse effects of strong wind or to slow the vessel.
Reef-bands: Long pieces of rough canvas sewed across the sails to give them additional strength.
Reef-tackles: Ropes employed in the operation of reefing.
Reeve: To pass a rope through a ring.
Rigging: the system of ropes, cables, or chains employed to support a ship’s masts and to control or set the yards and sails.
Righting couple: The force which tends to restore a ship to equilibrium once a heel has altered the relationship between her center of buoyancy and her center of gravity.
Rigol: The rim or ‘eyebrow’ above a port-hole or scuttle.
Roach: Curved cut in the edge of sail for preventing chafing.
Roband: Piece of yarn used to fasten a sail to a spar.
Roll: A vessel’s motion rotating from side to side, about the fore-aft axis. List (qv) is a lasting tilt in the roll direction.
Rolling-tackle: A number of pulleys, engaged to confine the yard to the weather side of the mast; this tackle is much used in a rough sea.
Rostrum: Spike on the prow of warship for ramming.
Rowlock: Contrivance serving as a fulcrum for an oar.
Royal: Small sail on the royal mast just above topgallant sail.
Running rigging: Rigging used to manipulate sails, spars, etc. in order to control the movement of the ship. Cf. standing rigging.
Sailing Certification : An acknowledgment of a sailing competence from an established sailing educational body (like NauticEd).
Sail-plan: A set of drawings showing various sail combinations recommended for use in various situations.
Saltie: Great Lakes term for a vessel that sails the oceans.
Sampson post: A strong vertical post used to support a ship’s windlass and the heel of a ship’s bowsprit.
Scandalize: To reduce the area of a sail by expedient means (slacking the peak and tricing up the tack) without properly reefing it.
Scud: To sail swiftly before a gale.
Scudding: A term applied to a vessel when carried furiously along by a tempest.
Scuppers: An opening on the side rail that allows water to run off the deck.
Scuttle: A small opening, or lid thereof, in a ship’s deck or hull. To cut a hole in, or sink something.
Scuttlebutt: Cask of drinking water aboard a ship; rumour, idle gossip.
Scuttles: Portholes on a ship.
Sea anchor: A stabilizer deployed in the water for heaving to in heavy weather. It acts as a brake and keeps the hull in line with the wind and perpendicular to waves.
Sea chest: A valve on the hull of the ship to allow water in for ballast purposes.
Seaman: Generic term for a sailor.
Seaworthy: Certified for, and capable of, safely sailing at sea.
Self-Unloader: Great Lakes slang term for a vessel with a conveyor or some other method of unloading the cargo without shoreside equipment.
Shaft Horsepower (SHP): The amount of mechanical power delivered by the engine to a propeller shaft. One horsepower is equivalent to 746 watts in the SI system of units.
Shakes: Pieces of barrels or casks broken down to save space. They are worth very little, leading to the phrase “no great shakes”.
Sheer: The upward curve of a vessel’s longitudinal lines as viewed from the side.
Sheet: A rope used to control the setting of a sail in relation to the direction of the wind.
Ship: Strictly, a three-masted vessel square-rigged on all three masts, though generally used to describe most medium or large vessels. Derived from the Anglo-Saxon word “scip”.
Ship’s bell: Striking the ship’s bell is the traditional method of marking time and regulating the crew’s watches.
Ship’s company: The crew of a ship.
Shoal: Shallow water that is a hazard to navigation.
Shrouds: Standing rigging running from a mast to the sides of ships.
Sickbay: The compartment reserved for medical purposes.
Sidelights: These red and green lights are called sidelights (also called combination lights) because they are visible to another vessel approaching from the side or head-on. The red light indicates a vessel’s port (left) side; the green indicates a vessel’s starboard (right) side.
Siren: A sound signal which uses electricity or compressed air to actuate either a disc or a cup-shaped rotor.
Skeg: Part of ship connecting the keel with the bottom of the rudderpost.
Skipper: The captain of a ship.
Skysail: A sail set very high, above the royals. Only carried by a few ships.
Skyscraper: A small, triangular sail, above the skysail. Used in light winds on a few ships.
Slipway: Ramp sloping into the water for supporting a ship.
Slop chest: A ship’s store of merchandise, such as clothing, tobacco, etc., maintained aboard merchant ships for sale to the crew.
Small bower (anchor): The smaller of two anchors carried in the bow.
Snotty: Naval midshipman.
Sonar: A sound-based device used to detect and range underwater targets and obstacles. Formerly known as ASDIC.
Spanker: Sail on the mast nearest the stern of a square-rigged ship.
Spanker-mast: The aft-most mast of a fore-and-aft or gaff-rigged vessel such as schooners, barquentines, and barques. A full-rigged ship has a spanker sail but not a spanker-mast (see Jigger-mast).
Spar: A wooden, in later years also iron or steel pole used to support various pieces of rigging and sails. The big five-masted full-rigged tall ship Preussen (German spelling: Preußen) had crossed 30 steel yards, but only one wooden spar—the little gaffe of its spanker sail.
Spindrift: Finely-divided water swept from the crest of waves by strong winds.
Spinnaker pole: A spar used to help control a spinnaker or other headsail.
Spinnaker: A large sail flown in front of the vessel while heading downwind.
Spirketing: Inside planking between ports and waterways of a ship.
Splice: To join lines (ropes, cables, etc.) by unraveling their ends and intertwining them to form a continuous line. To form an eye or a knot by splicing.
Sponson: Platform jutting from ship’s deck for gun or wheel.
Sprit: Spar crossing a fore-and-aft sail diagonally.
Spritsail: Sail extended by a sprit.
Squared away: Yards held rigidly perpendicular to their masts and parallel to the deck. This was rarely the best trim of the yards for efficiency but made a pretty sight for inspections and in the harbor. The term is applied to situations and to people figuratively to mean that all difficulties have been resolved or that the person is performing well and is mentally and physically prepared.
Squat effect: Is the phenomenon by which a vessel moving quickly through shallow water creates an area of lowered pressure under its keel that reduces the ship’s buoyancy, particularly at the bow. The reduced buoyancy causes the ship to “squat” lower in the water than would ordinarily be expected.
Standing rigging: Rigging which is used to support masts and spars, and is not normally manipulated during normal operations. Cf. running rigging.
Starboard: Towards the right-hand side of a vessel facing forward. Denoted with a green light at night. Derived from the old steering oar or ‘steerboard’ which preceded the invention of the rudder.
Starbolins: Sailors of the starboard watch.
Starter: A rope used as a punitive device.
Stay: Rigging running fore (forestay) and aft (backstay) from a mast to the hull.
Staysail: A sail whose luff is attached to a forestay.
Steering oar or steering board: A long, flat board or oar that went from the stern to well underwater, used to control the vessel in the absence of a rudder.
Steeve: To set a ship’s bowsprit at an upward inclination.
Stem: The extension of the keel at the forward of a ship.
Stemson: Supporting timber of a ship.
Stern tube: The tube under the hull to bear the tail shaft for propulsion (usually at the stern).
Stern: The rear part of a ship, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter to the taffrail.
Sternlight: This white light is seen only from behind or nearly behind the vessel.
Sternpost: Main member at the stern of a ship extending from keel to deck.
Sternway: Movement of a ship backward.
Stevedore: Dock worker who loads and unloads ships.
Stokehold: Ship’s furnace chamber.
Strake: One of the overlapping boards in a clinker-built hull.
Studding-sails (pronounced “stunsail”): Long and narrow sails, used only in fine weather, on the outside of the large square sails.
Stunsail: Light auxiliary sail to the side of principal sails.
Supercargo: Ship’s official in charge of business affairs.
Surge: A vessel’s transient motion in a fore and aft direction.
Sway: A vessel’s motion from side to side. Also used as a verb meaning to hoist. “Sway up my dunnage.”
Swigging: To take up the last bit of slack on a line such as a halyard, anchor line or dock line by taking a single turn round a cleat and alternately heaving on the rope above and below the cleat while keeping the tension on the tail.
Swinging the compass: Measuring the accuracy in a ship’s magnetic compass so its readings can be adjusted – often by turning the ship and taking bearings on reference points.
Swinging the lamp: Telling sea stories. Referring to lamps slung from the deckhead which swing while at sea. Often used to indicate that the storyteller is exaggerating.
Swinging the lead: Measuring the depth of water beneath a ship using a lead-weighted sounding line.
Taffrail: Rail around the stern of a ship.
Tail shaft: A kind of metallic shafting (a rod of metal) to hold the propeller and connected to the power-engine. When the tail shaft is moved, the propeller may also be moved for propulsion.
Taken aback: An inattentive helmsmen might allow the dangerous situation to arise where the wind is blowing into the sails “backward”, causing a sudden (and possibly dangerous) shift in the position of the sails.
Tally: The operation of hauling aft the sheets, or drawing them in the direction of the ship’s stern.
The Ropes: Refers to the lines in the rigging.
Thole: Pin in the side of a boat to keep an oar in place.
Three sheets to the wind: On a three-masted ship, having the sheets of the three lower courses loose will result in the ship meandering aimlessly downwind.
Tiller: Handle or lever for turning a ship’s rudder.
Timberhead: Top end of ship’s timber used above the gunwale.
Timenoguy: Rope stretched from place to place in a ship.
Timoneer: From the French, “timonnier”, is a name given on particular occasions to the steersman of a ship.
Ton: The unit of measure often used in specifying the size of a ship. There are three completely unrelated definitions for the word. One of them refers to weight, while others refer to volume.
Tonnage: A measurement of the cargo-carrying capacity of merchant’s vessels. It depends not on weight, but on the volume available for carrying cargo. The basic units of measure are the Register Ton, equivalent to 100 cubic feet, and the Measurement Ton, equivalent to 40 cubic feet. The calculation of tonnage is complicated by many technical factors.
Topgallant: Mast or sail above the topmast and below the royal mast.
Topmast: The second section of the mast above the deck; formerly the upper mast, later surmounted by the topgallant mast; carrying the topsails.
Topsail: The second sail (counting from the bottom) up to a mast. These may be either square sails or fore-and-aft ones, in which case they often “fill in” between the mast and the gaff of the sail below.
Topsides: The part of the hull between the waterline and the deck. Also, Above-water hull.
Touch and go: The bottom of the ship touching the bottom, but not grounding.
Towing: The operation of drawing a vessel forward by means of long lines.
Traffic Separation Scheme: Shipping corridors marked by buoys which separate incoming from outgoing vessels. Improperly called Sea Lanes.
Tranship: To transfer from one ship to another.
Transire: Ship’s customs warrant for clearing goods.
Transom: A more or less flat surface across the stern of a vessel.
Travellers: Small fittings that slide on a rod or line. The most common use is for the inboard end of the mainsheet; a more esoteric form of traveler consists of “slight iron rings, encircling the backstays, which are used for hoisting the top-gallant yards, and confining them to the backstays”.
Treenail: Long wooden pin used to fix planks of the ship to the timbers.
Trice: To haul in and lash secure a sail with a small rope.
Trick: A period of time spent at the wheel (“my trick’s over”).
Trim: Relationship of ship’s hull to the waterline.
Trunnel: Wooden shipbuilding peg used for fastening timbers.
Trysail: Ship’s sail bent to a gaff and hoisted on a lower mast.
Tuck: Part of the ship where ends of lower planks meet under the stern.
Turtleback: Structure over ship’s bows or stern.
Turtling: When a sailboat (in particular a dinghy) capsizes to a point where the mast is pointed straight down and the hull is on the surface resembling a turtle shell.
Under the weather: Serving a watch on the weather side of the ship, exposed to wind and spray.
Underway: A vessel that is not at anchor, or made fast to the shore, or aground.
Underwater hull or underwater ship: The underwater section of a vessel beneath the waterline, normally not visible except when in drydock.
Unreeve: To withdraw a rope from an opening.
Vanishing angle: The maximum degree of heel after which a vessel becomes unable to return to an upright position.
Wake: Turbulence behind a ship.
Wales: A number of strong and thick planks running length-wise along the ship, covering the lower part of the ship’s side.
Walty: Inclined to tip over or lean.
Wardroom: Quarters for ship’s officers.
Washboard: Broad thin plank along ship’s gunwale to keep out sea water.
Watch: A period of time during which a part of the crew is on duty. Changes of watch are marked by strokes on the ship’s bell.
Watching: Fully afloat.
Watercraft: Water transport vessels. Ships, boats, personal watercraft.
Waterline: The intersection of a boat’s hull and the water’s surface, or where the boat sits in the water.
Waveson: Goods floating on the sea after a shipwreck.
Wear: To turn a ship’s stern to windward to alter its course
Weather deck: Whichever deck is exposed to the weather—usually either the main deck or, in larger vessels, the upper deck.
Weather gage: Favorable position over another sailing vessel to with respect to the wind.
Weather side: The weather side of a ship is the side exposed to the wind.
Weatherboard: Weather side of a ship.
: If the helm was centered, the boat would turn towards the wind (weather). Consequently, the tiller must be pulled to the windward side of the boat in order to make the boat sail in a straight line. See lee helm.
Weatherly: A ship that is easily sailed and maneuvered; makes little leeway when sailing to windward.
Weatherly: Able to sail close to the wind with little leeway.
Weigh anchor: To heave up (an anchor) preparatory to sailing.
Wells: Places in the ship’s hold for the pumps.
Wheelhouse: Location on a ship where the steering wheel is located, often interchanged with pilothouse and bridge.
Whipstaff: Vertical lever controlling ship’s rudder.
White Horses: Waves in wind strong enough to produce foam or spray on the wave tops.
Wide berth: To leave room between two ships moored (berthed) to allow space for a maneuver.
Windage: Wind resistance of the boat.
Windbound: A condition wherein the ship is detained in one particular station by contrary winds.
Windlass: A winch mechanism, usually with a horizontal axis. Used where mechanical advantage greater than that obtainable by block and tackle was needed (such as raising the anchor on small ships). Modern sailboats use an electric “Windlass” to raise the anchor.
Windward: In the direction that the wind is coming from.
Xebec: Small three-masted pirate ship.
Yard: Tapering spar attached to ship’s mast to spread the head of a square sail.
Yardarm: The very end of a yard. Often mistaken for a “yard”, which refers to the entire spar. As in to hang “from the yardarm” and the sun being “over the yardarm” (late enough to have a drink).
Yarr: Acknowledgement of an order, or agreement.
Yaw: A vessel’s motion rotating about the vertical axis, so the bow yaws from side to side.
Yawl: Ship’s small boat; sailboat carrying mainsail and one or more jibs.
Zabra: Small Spanish sailing vessel.
Latest News

NEWS | August 23, 2024
Cocktails & canapés at 37th america’s cup [s/y seaquell].
Cocktails & Canapés at 37th America’s Cup [S/Y SEAQUELL] Thursday, August 29th | 19:00-21:00 Denison Yachting cordially invites you to an evening of cocktails and canapés aboard the Sailing Yacht SEAQUELL during the 37th America’s Cup Round Robins at Port Forum. Enjoy a relaxed gathering on board, set against

Newport International Boat Show [Brokerage Boats On Display]
Newport International Boat Show [Brokerage Boats On Display] Thursday-Sunday | September 12-15, 2024 Denison invites you to view a number of available brokerage boats at the 2024 Newport International Boat Show. The Newport International Boat Show, set for September 12-15, 2024, in Newport, Rhode Island, is one of

NEWS | August 19, 2024
85′ azimut 2006 sold by florent moranzoni [eva].
85′ Azimut 2006 Sold by Florent Moranzoni [EVA] EVA, an 85′ (26.82m) Azimut built in 2006, was sold by Florent Moranzoni, who represented the Seller. Special thanks to James von Eiberg of Bluebnc, who represented the Buyer. EVA can accommodate ten guests in four comfortable cabins, including a
The Only 50 Sailing Terms You'll Need To Know (With Pictures)
Ever get confused by all those odd sailing terms? Starboard, tack, jib… Well, no worries. In this article, I'll go over the most important sailing terms for beginners.
This is a great resource for beginning sailors that need an overview of the most important sailing terms without drowning in it . For a comprehensive list, check out this Wikipedia glossary of nautical terms . There are A LOT of nautical terms there. But no one in his or her right mind will read through that entire page (it has 48.434 words!). There are a lot of obscure words listed that no one really uses anyways. So in this article, I've filtered out the most important ones to get you up to speed quickly. I've also added pictures so you'll know what we're talking about.
Let's jump straight in. For the sake of good manners, I have categorized them by topic. If you are looking for a specific term, just ctrl+f your way directly to it.
Here are the only 50 sailing terms you'll need to know:

Orientation
Parts of the boat, parts related to sails, other terms.
...because it isn't as easy as 'left', 'right', 'front' and 'back'. No, no.
Port is the left side of the boat. It's as simple as that. I'm not entirely sure why don't they just call it 'left' these days. The name came to existence because centuries ago, you always docked your big boat with the harbor (port) being on the left side. And the word stuck with us till today.

Starboard is the right side of the boat. If in a car, you say 'look to your right', on a boat, you say 'look to the starboard'. Again, you might as well just call it 'right'. Oh, wait… you wouldn't seem as cool if you did. Alright, let's keep calling it starboard.

The bow is the front of the boat. The word likely comes from the Middle Dutch 'boech' (nowadays spelled 'boeg'). If you call it 'front' instead, you will get your message across just as well. But it won't get you the admiring looks from those around you.

Stern is the back of the boat. That is where you, as a captain, will spend most of your time. Whether you will force your crew to call it 'stern' or let them use the word 'back', like the dry land creatures they are, is up to you. After all, you are the captain.

The windward side of the boat is the side facing into the wind. So if the wind is coming from the right side, the windward side is on the right. Unlike some of the previous ones, this term actually makes sense - at times you need to talk about a direction not fixed in relation to the boat, but rather relative to the direction of the wind.

Leeward side of the boat is the lee side. If the wind is coming from the right side, the leeward side is on the left. Note that neither windward nor leeward specify the angle of the wind. Thus even if the wind was coming 20 degrees right off of the direction of the boat, so almost from the front, left would still be considered the leeward side.

Since there are gadgets and parts on the boat that you won't see anywhere else, it only makes sense they all have their own special name. You want to know these because unlike the direction terms where you can do with 'left' and 'right', you don't want to call a tiller 'that stick thing back there'.
Helm is the boat's steering wheel. In this case, I forgive those who came up with this name, since it is shorter than 'steering wheel' and thus saves valuable time that we can spend on sailing. Though I doubt linguistic economy was the reason.

Tiller is the long stick that operates your boat's rudder. A steering stick, if you will. It has the same function as a helm does, but it is usually used on smaller boats, where a helm would take up too much space. Or by people who prefer it to a helm, since a tiller offers a bit more in terms of response.

The rudder is the long, flat piece of metal or wood that sits underwater below the back of your boat. Connected to a tiller or a helm, it is used to control the direction of your exciting voyage. By the way, since aerodynamics and hydrodynamics work in similar ways, a plane is also operated by a rudder. Though that one isn't underwater. Hopefully.

Hull is the boat's body. Whatever the shape or size, whether opened on top (like a dinghy) or closed by a deck, (like a traditional sailboat) it's all called a hull. Structures sitting on top of the deck, like a deck salon or cabins, aren't considered a part of the hull anymore.

The keel is an underwater fin below the boat's belly. The sizes and shapes vary, sometimes it is relatively short and goes deep, (fin keel) sometimes it runs from the front all the way to the back (full keel or ballast keel). It is there mainly for stability and to help maintain forward direction when sailing.

The cockpit is the area where a boat is operated from. On sailboats, it is usually in the back and it is an open area without a roof, though this varies. You will find the rudder control and winches there. In 'smaller' (below 70 ft or so) sailboats this area oftentimes doubles as a deck dining place with a table and seating.

The bimini is a sun roof or shade that is covers the cockpit, and is generally attached to a steel frame which runs over the cockpit.
This is where things tend to get confusing. There are a whole lot of parts and a whole lot of names for them. It pays off for you and your crew to know them though, as during the stormier moments, you all want to be on the same boat (ha, ha) linguistically, as every second counts.
Lines are ropes. Not much more to add here. I suppose a 'line' sounds a bit fancier than a 'rope'. One thing this article will teach you is that if there is the slightest crack in the wall of your boat, linguistic elitism will leak its way in.
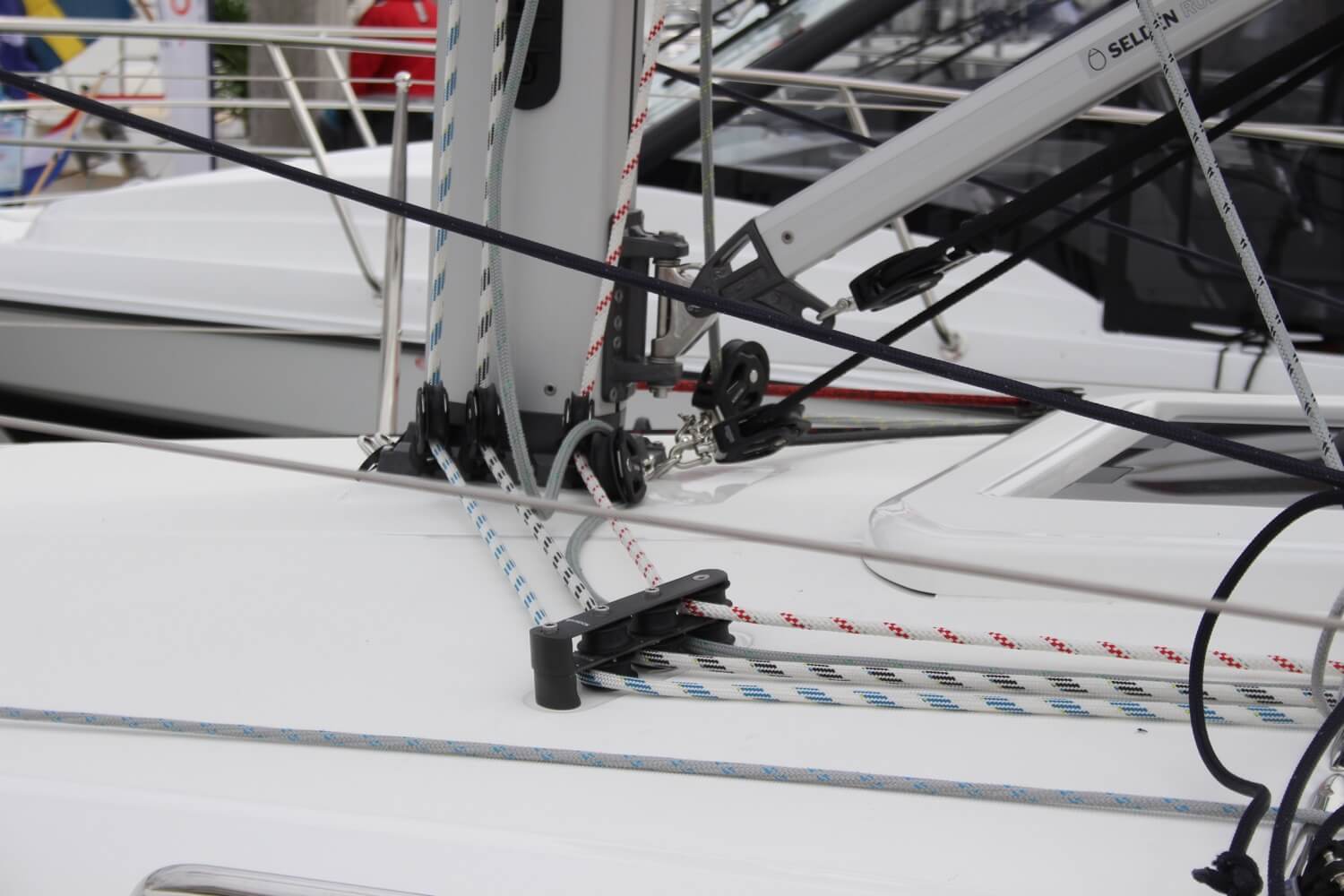

This one is quite self-explanatory. The mainsail is the main, largest sail of the boat, attached to the mast on the side and the boom at the bottom. It has a triangular shape and serves as the most important sail, the first one you should get acquainted with if you are just starting out.

The jib is the front sail of your boat, sometimes also called the genoa. That is as long as you are sailing on the traditional sloop - the classical two sail setup you see the most often. The jib is wrapped around the line that goes from the top of your mast to the boat's bow.

Spinnaker is the third type of sail you are the most likely to encounter on your travels. It goes in front of your boat and has a half balloon or kite-like shape. This is because it is constructed specifically for sailing downwind. Its purpose is to grab as much backwind as it can and drag your boat forward. It is not attached to the boat most of the time like the mainsail or the jib, instead, it is stored separately and used only when needed.

The mast is the tall, vertical pole that goes from the floor of your salon, through the deck, meters above your boat. All the sails are attached to it, also radars and lights, giving sailboats radio and visual visibility far greater than that of equally sized motorboats. Take that, ya noisy stinkies!

The boom is the horizontal pole right above the deck, attached to the mast at the right angle. The bottom of the mainsail is attached to it, it is used to determine its shape and direction. It is also where the mainsail is often stored, folded and covered with a protective sheet. The boom is also among the top causes of injuries on a sailboat, as in certain winds it tends to swing with force powerful enough to knock a few grown men overboard. Stay away from its reach at all times when under sail.

The forestay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very front of the bow. It is there to hold the mast in place. Sometimes you will find people refer to it as the 'headstay'. It is often made of steel, so it is safe to hold on to it when you are pretending to be Jack on the bow of the Titanic's, the boat hits a wave and you lose your balance.
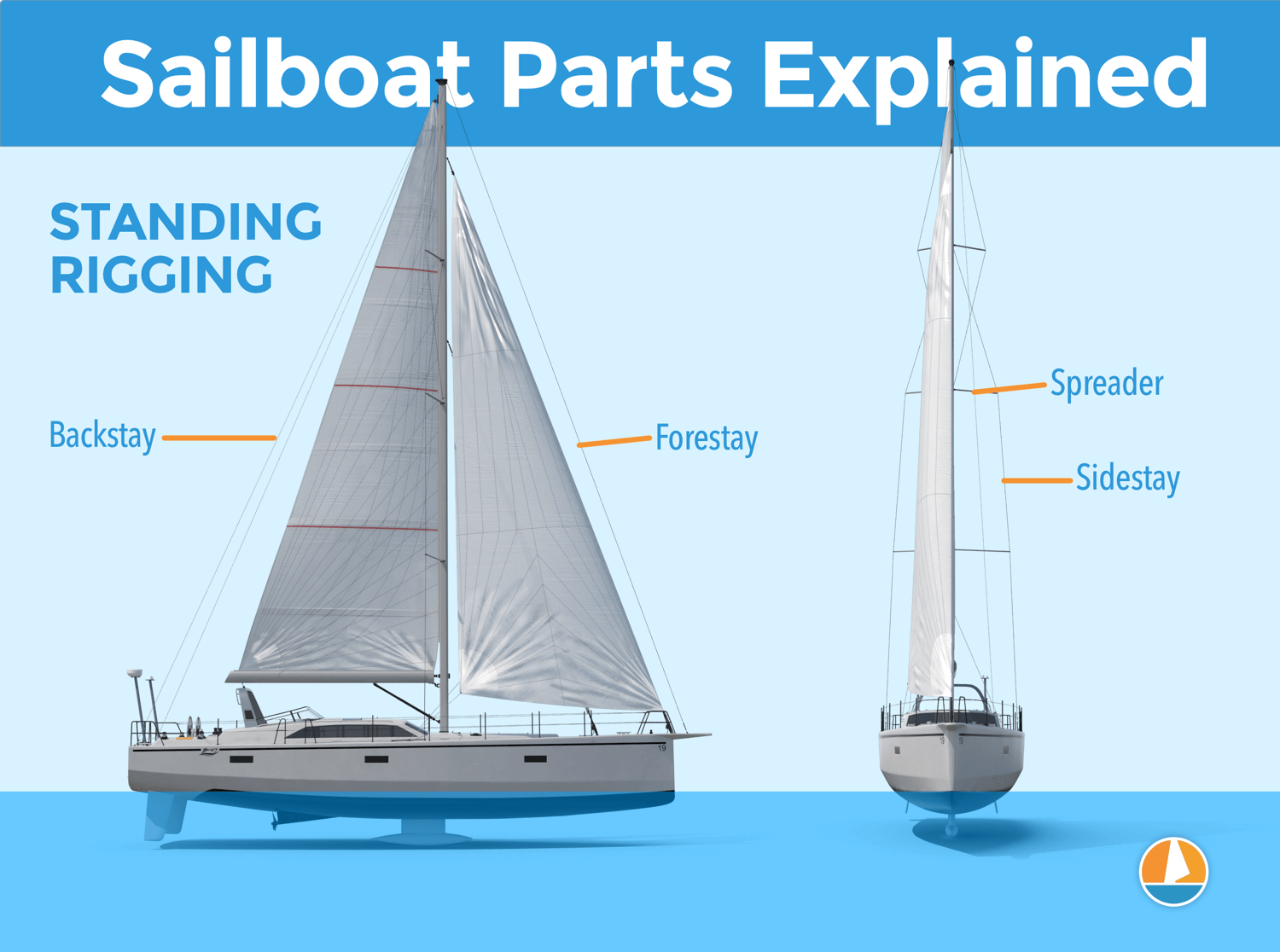
This diagram is from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. It walks you through all the most important sailboat parts in normal words.
The backstay is the cable going from the top of the mast to the very back of the boat. In many cases it is doubled at the bottom, each end attached to one corner of the back of the boat so that they don't interfere with space and provide more stability for the mast. Just as with forestay, these are made of steel.
Shrouds are the cables going from the top of the mast to the left and right side of the boat. Sometimes there are four, two on each side. Together with forestay and backstay, they make sure your mast withstands all the forces exerted on it when the wind pushes the sails.
The foot of a sail is its bottom edge. If you imagine a sail as a triangle, the base is called the foot. You probably won't use this term while sailing, but when researching proper sail trim, it is likely you will stumble upon it.
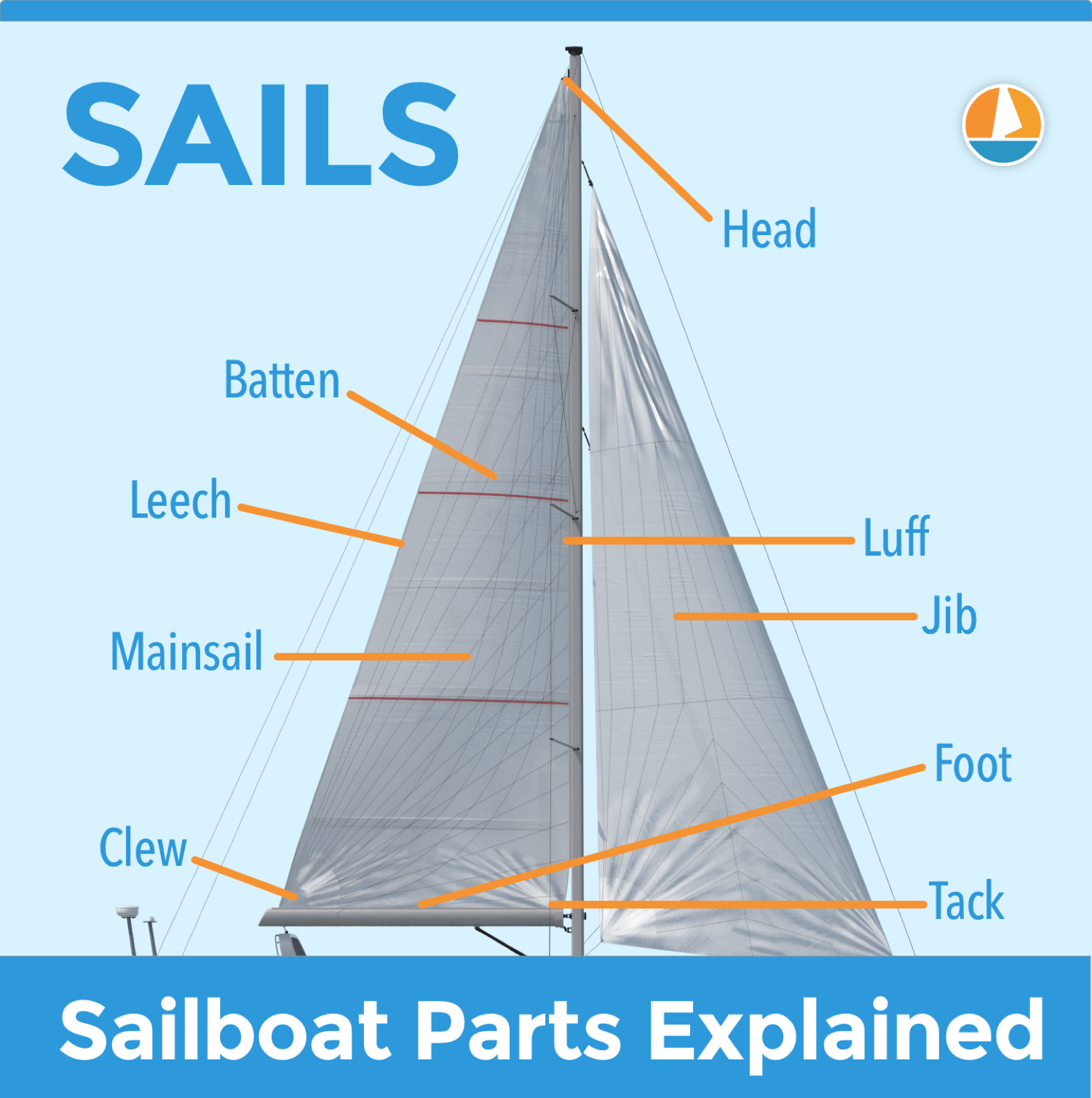
This diagram is again from our guide on sailboat parts , which I really recommend for beginners. If you're looking for a good starting point to learn your sailboat ins and outs, this article is perfect for you.
Leech of a sail is its back side edge. Thus it is the part closest to you when you are standing at the helm. Just as with the foot, this is a term quite often used when describing sail trimming techniques, since the shape of the leech determines the shape of the whole sail.
Luff of a sail is its front side edge. Thus the part the furthest from you when you are standing at the helm. For mainsail, it is the edge that is right next to the mast, for the foresail it is the edge right next to the forestay. Just as with foot and leech, the shape of these edges determines the overall shape of the sail so you will most likely encounter these terms in trimming lessons and tutorials.
The head of a sail is its top corner. On a traditional sloop, you will have the 'main head' and the 'jib head'. There is usually a reinforcing patch of some kind on these corners, as you will find a hole in them to which a line is attached.
It's also something else entirely, but more on that later ...
Halyard is the line attached to the sail head. On your boat, you will most likely have two. The 'main halyard' which is what you use to hoist your mainsail if it is folded on the boom, and the 'jib halyard' which holds the jib head up.
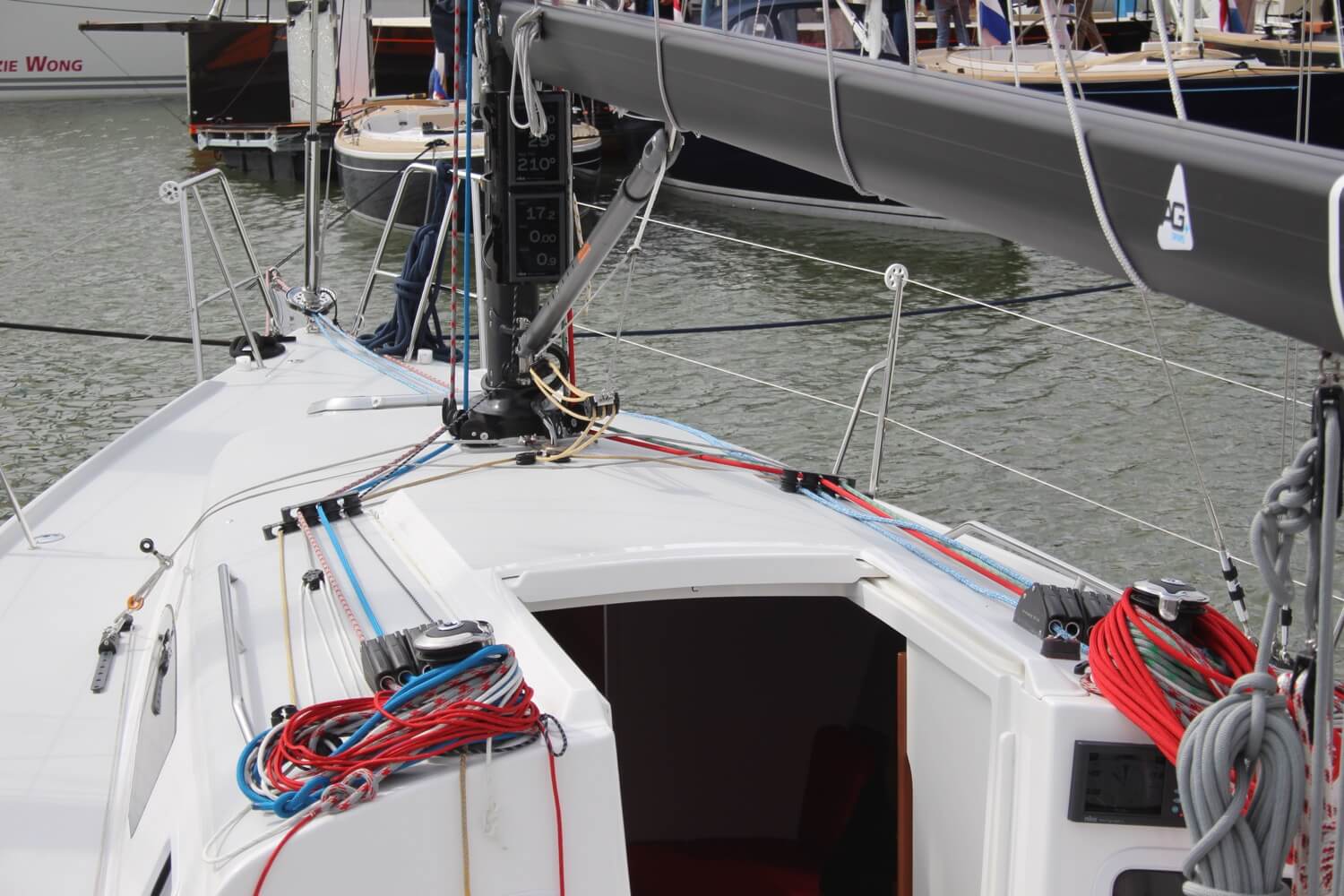

Clew of a sail is its back corner. The line attached to the 'main clew' will be used to hoist your mainsail if it is wrapped inside of the mast. The line attached to the 'jib clew' will be used to open the jib on most sailboats since jibs are most often wrapped around the luff.
Telltales are light, usually cotton or wool pieces of ropes attached to a sail, showing you the airflow around it. These are important because they help you determine if your trim is effective or not. Because of the material they are made of, you might sometimes encounter them being called 'woolies'.
Vang, or a 'boom vang' is a device pulling the boom down. This is important because it controls the tension of the mainsail, influencing its shape greatly. You won't find it on every boat though. Holiday cruisers often don't have it, as it is a piece of equipment focused on performance and thus not necessary for your average trip.

Topping Lift
The topping lift is a line that is attached to the aft (back) end of the boom and runs to the top of the mast. It supports the boom whenever you take down the mainsail.
Also referred to as a 'horse', the traveler is a side to side track to which the boom is attached, allowing the control of the extent to which the boom goes off the centerline. This is important especially if the wind is blowing from behind and you need to control the angle of the mainsheet.

Outhaul is the line attached to the mainsail or the jib clew, allowing the control of the foot tension. This is important for determining the sail shape - for instance in stronger winds, you want the foot to be more tense to achieve a more effective airflow as opposed to slower winds where you can allow the foot to arch more.

Reefing is reducing the sail area to lessen the power exerted on it by the wind. You may want to reef if the wind is getting too strong for your boat, or if it is changing too rapidly, as an overpowered boat is difficult to control. Fun fact: they say that when you feel you need to reef because the wind got too strong, it is already too late to reef.

A batten is a slat placed horizontally in the body of the sail to support its shape. You will not find them on all sailboats, it is a performance-enhancing element that many cruisers lack. It helps tremendously as without it, sails tend to belly out and lose their shape under certain conditions.
The cleat is a piece of fitting where a line can be secured and immobilized, even if under great tension. It usually consists of two cogwheel-like pieces fastened close to each other, in the middle of which the rope is placed, unable to move thanks to friction. This type is great as it allows for a quick release. Sometimes though, it is a simple piece of metal or plastic where the rope is tied.
...and then there are all those things that just float around you when sailing, those little things that are the reason for you having to carry a dictionary in your pocket.
Fenders are bumpers allowing some contact with other boats or piers while docked, without scraping the paint. They are often balloon-shaped, made of rubber or some relatively soft material. They are usually attached to the boat's railing and you move them around as you need.

The beam is the width of the boat. Could be just called width, I know. The word comes from the fact that there are transverse reinforcing beams in the boat hull and deck. Next time you are choosing your charter boat for holidays, you will know what this attribute means.
True wind is the actual direction and speed of the wind. This is different than the apparent wind, which is wind direction and speed relative to the boat. Apparent wind is a combination of the true wind and the headwind, which is the wind the boat experiences solely by being in motion.
The berth is a sleeping space on a boat. Thus if a boat has eight berths, it means eight people can comfortably sleep on it. Note that this often includes the salon couches, so a berth is not necessarily a space in an actual bed for one person.

Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
Tacking is zig-zagging towards your destination. It is necessary in case your destination is in the direction of the wind since sailboats can not go directly into it. Since the closest to the wind direction you can sail is around 45 degrees, you have to change direction left and right from your desired course.

This diagram is from our guide on sailing into the wind for beginners , which explains in 7 simple steps how to get good upwind sailing performance.
Bareboat is a boat without a skipper. You will encounter this term in boat charters and it means you rent the boat without any crew, thus you need to operate it yourself. It is the best way to sail unless you enjoy living in close proximity to a sea wolf who you also have to feed.
The chart is a nautical map. It differs from classical maps as it depicts information relevant for a sailor - water depth, navigational hazards, seabed material, anchorages and so on. Formerly made of paper, these days made of ones and zeros. As is everything in this digital world.
We have a guide that explains all the different chart types clearly for beginners - read it here .
Galley on a boat is its kitchen. Also a medieval warship, but if you find this term in a boat's description, war is not likely what they have in mind.

Heads on a boat is the bathroom. Though in all my years of sailing I have never ever heard anybody use this term instead of a 'bathroom'. I suppose saying that you are going to use the heads just sounds odd.

A knot is the unit of speed of boats. It is equal to one nautical mile per hour. That is 1.852 kilometers per hour or 1.5078 miles per hour. Though a bit confusing and annoying at times, you will have to get used to this, since most of your boat's instruments will use this unit. It dates all the way back to the seventeenth century when boat's speed was measured with a rope with knots tied on it.

Mooring is attaching the boat to a buoy that is anchored to the seabed. This is usually a cheaper option to docking in a marina. It also means larger space between the boats anchored in the same area, thus more privacy. Though you will have to use your dinghy to get to shore instead of just stepping on the pier directly from your deck.

A salon on a boat is its living room. On smaller boats, it is usually in the same room as the boat's kitchen and the captain's corner with navigation instruments.

A skipper is the captain of a sailboat. If you ask me, the word 'captain' is much better than a skipper, which to me sounds like a small boy who sits on the shore the whole day, skipping stones. But hey, who am I to talk.

A monohull is a classical boat with a single hull. A boat with two hulls is called a catamaran, or a 'cat'. Although rare, there are also trimarans, boats with three hulls. Multihulls with four or more hulls do happen but they are an unnecessary freak of nature.

So there you have it. Fifty sailing terms you will encounter the most when traveling or learning. I know you might think some of them are a bit unnecessary since they have a perfectly fine 'real world' equivalent. I agree. But until the tradition changes, you might want to get some of these under your skin.
A boat's freeboard is the distance from the upper deck to the waterline. Classic yachts have low freeboards, so they appear to lay deeper in the water, as opposed to more modern yachts, which have a higher freeboard. It literally means 'free-board' : the amount of visible board.
The lunch hook is a light anchor setup that is used to moor small yachts temporarily. It typically uses a lightweight anchor on a short scope that takes little effort to set. The lunch hook is only used when the crew is on board and will be monitoring the anchor.
In naval architecture and ship design: “Head” = WC = Bathroom. A toilet is still a toilet. The toilet is in the head. In olden day, the toilet was a hole in the head.
Hi Rich, you’re absolutely right. I’ve corrected the error. Thanks for pointing it out.
A nautical mile is one minute of a degree, so if you travel 60 nautical miles that means you have gone 1 degree around the “globe”. (Note: arc length not actual length.) This is the original definition. As such the average was agreed upon and the lengths given a standardization. Which you mentioned.
As such 1 knot is to travel one nautical mile in an hour.
Also 1.5078. I think you made a mistake as it should be 1.1508 miles to a nautical mile.
Thanks for the information. Sorry about being a pedantic mathematics teacher.
So, where is the “nautical mile” calculated from, the equator or one of the tropic lines?
Just to clarify a nautical mile. If you draw an imaginary line from the North Pole or South Pole to the center of the Earth and draw another line from the center of the Earth to any point on the equator, it forms a right angle, which is 90 degrees. This equates to latitude. The equator is 0 degrees and the poles are 90 degrees. Your latitude is the angle that you are north or south of the equator. Each degree of latitude is divided into 60 minutes. A minute of latitude is the same distance matter where you are on Earth. It is 6,076 feet. This is the length of a nautical mile. A statute mile is 5,280 feet, so a nautical mile is 1.1508 statute miles.
Thank you very clear and well explained. Hopefully I’ll remember The Fifty
KöhnSharkösz
Really? No gunwale? No transom? Those or basic terms to the Washington State Boater Education Card required to operate watercraft here. Definitely more of a “need to know” than bimini.
Thank you, those definitions and explanations were clear, thorough, and helpful. I’m really glad I found my way (somehow) to your webpage.
Leave a comment
You may also like, 17 sailboat types explained: how to recognize them.
Ever wondered what type of sailboat you're looking at? Identifying sailboats isn't hard, you just have to know what to look for. In this article, I'll help you.

How Much Sailboats Cost On Average (380+ Prices Compared)

The Ultimate Guide to Sail Types and Rigs (with Pictures)

Sailboat Parts Explained: Illustrated Guide (with Diagrams)

How To Live On a Boat For Free: How I'd Do It
latest in US News

90-year-old grandma celebrates birthday by skydiving from 13K...

Liquor store worker pulls gun on mob of bicyclists surrounding...

Patriotic student banned from flying American flag on his truck...

NYPD hunts for antisemitic suspect who spit on 65-year-old man's...

Democrats distance themselves from megadonor who allegedly posed...

Baby left in hot car rescued by roper at fair while mother was...

Inmates whip up five-course meal from prison garden for 60...

Cigarette butt helps crack cold case murder of Boeing instructor...
Morgan stanley international chair jonathan bloomer among 6 missing after yacht, the bayesian, sinks off italy.
Morgan Stanley International chairman Jonathan Bloomer and his wife are among the six people still missing after a mega-yacht sank off the coast of Italy Monday morning, according to officials and reports.
Bloomer remains unaccounted for after the Bayesian, a 184-foot luxury sailboat, capsized with 22 people aboard off the port of Porticello after it was struck by a tornado, said Salvatore Cocina, head of the civil protection agency in Sicily.

His wife is also missing, the Daily Mail reported .
British tech tycoon Mike Lynch, 59, and his 18-year-old daughter, Hannah, have also not been found since the ship wrecked.
The Italian agency also confirmed that Chris Morvillo, an attorney at British law firm Clifford Chance, which represented Lynch in a massive fraud case in California earlier this year, is also missing, the Guardian reported .
Morvillo served as an assistant US attorney for the Southern District of New York from 1999 to 2005.
The Post has reached out to Morgan Stanley and Clifford Chance for comment.
The ship’s chef, Canadian-born Thomas Recaldo, was confirmed dead by Italian officials and his body was recovered.

Bloomer, reportedly a close friend of Lynch’s, is also the chairman of insurance provider Hiscox and was formerly the chief executive of Prudential, according to his LinkedIn profile.
Fifteen others onboard, including Lynch’s wife, Angela Bacares — who owns the ship — and a 1-year-old girl, managed to escape the superyacht before it went down. The boat was carrying a crew of 10 people and 12 passengers when it sank.
Eight of those rescued were taken to local hospitals, officials said.

Charlotte Golunski, 36, saved her 1-year-old daughter , Sophia, from the sinking ship by keeping her afloat in the rough waters.
Domenico Cipolla, a chief physician at the Di Cristina hospital in Palermo, said the mother and daughter are recovering.
“The baby is doing well,” he said. “The mother is also in good condition, albeit with some minor abrasions. The father will also be discharged from the hospital soon.

What to know after a tornado sank the yacht Bayesian off the coast of Sicily:
- A superyacht capsized off the coast of Sicily after a tornado hit the area early Monday, killing seven passengers.
- British tech tycoon Mike Lynch was identified as one of the bodies pulled from the wreckage. His teenage daughter, Hannah, was the final one to be recovered.
- Lynch — known as “Britain’s Bill Gates” — had invited guests from Clifford Chance, a legal firm that represented him, and Invoke Capital, his own company, on the voyage, according to the Telegraph .
- Security camera footage shot from 650 feet from where the Bayesian sank Monday shows it disappearing.
- A rare and unexpected “black swan” weather event may have led to the Bayesian’s speedy demise , maritime experts say.

“They have said that most of them were colleagues who worked for Lynch. They are deeply traumatized,” he continued. “As time passes, they realize more and more that this morning they lost many friends.”
The Italian coast guard deployed divers to the wreckage to search for survivors some 160 feet deep.
Authorities believe some of the missing passengers may have been trapped inside their rooms when the yacht sank, BBC reported.

Lynch, a billionaire once dubbed the UK’s answer to Steve Jobs, was acquitted just two months ago by a San Francisco jury of fraud charges linked to the sale of his software company, Autonomy, to Hewlett-Packard for $11 billion in 2011.
The trip had been organized by Lynch to celebrate his legal victory, the Daily Mail reported.
In a shocking twist, Lynch’s co-defendant in the case, Stephen Chamberlain, died on Monday after he was struck by a car in Cambridgeshire, UK, Reuters reported . Chamberlain, the former vice president of finance at Autonomy, was 52 years old.

The Bayesian was built by Italian shipbuilder Perini in 2008 and was last refitted in 2020. It is owned by a firm called Revtom Limited — of which Bacares is named as the sole shareholder.
The captain of a boat that was anchored next to the Bayesian told Reuters he had turned on his engine to keep control of his vessel and avoid a collision with the giant yacht when strong winds suddenly rolled in.
“We managed to keep the ship in position and after the storm was over, we noticed that the ship behind us was gone,” Karsten Borner told reporters. The other boat “went flat on the water, and then down,” he added.
He said his crew found some of the survivors on a life raft — including Golunski and her baby — and took them on board before the coast guard picked them up.

Advertisement

100 Basic Yachting & Sailing Terms You Need To Know
- No Comments
Yachting is an increasingly popular activity that involves exploring and enjoying bodies of water aboard sailboats or motorboats. It doesn’t matter if you’re a seasoned sailor or brand-new to the sport; knowing the language used in yachting is crucial for efficient communication and secure navigation. We’ll look at some of the most often used terminology and expressions in the world of yachting in this list of 100 fundamental yachting terms, from boat parts to navigation and safety gear, and more. This list is an excellent place to start whether you’re seeking to brush up on your yachting terminology or are just beginning into the sport.
Aft – Toward the back of the boat
Anchor – A heavy object used to keep a boat in place
Ballast – Weight added to the bottom of a boat to improve stability
Beam – The width of a boat at its widest point
Bilge – The lowest point inside the boat where water collects
Bimini – A type of sunshade or canopy used on boats

Bow – The front of a boat
Buoy – A floating marker used to mark channels, hazards or anchorages
Cabin – An enclosed space on a boat used for sleeping and living quarters
Capsize – To tip over or turn upside down
Cleat – A metal or plastic fitting used to secure ropes or lines to the boat
Cockpit – The open area in the back of the boat where the steering and controls are located
Compass – A navigational tool used to determine the direction
Crew – The people who work on a boat, assisting with sailing or other duties
Deck – The top surface of a boat where people can stand or walk
Dock – A platform or structure where boats can be tied up or moored
Draft – The depth of a boat below the waterline
Fender – A cushion or bumper used to protect the boat from damage when docking
Flag – A piece of fabric used to signal or communicate on a boat
Galley – The kitchen area on a boat
Genoa – A type of sail that is used for cruising and racing
GPS – Global Positioning System, a navigational system that uses satellites to determine the location
Halyard – A rope or line used to hoist or lower a sail
Hatch – An opening in the deck or cabin of a boat
Head – The bathroom on a boat
Hull – The main body of the boat, typically made of fiberglass or wood
Jib – A small triangular sail located forward of the mast
Keel – A fin-shaped object located under the boat that provides stability and helps prevent drifting
Knot – A measure of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour
Lanyard – A short cord or rope used to secure equipment or gear on a boat
Latitude – A measure of distance north or south of the equator
Leeward – The side of the boat sheltered from the wind
Lifeline – A line or rope used to provide safety and support on the deck of a boat
Log – A device used to measure speed and distance traveled
Mast – A vertical pole or spar that supports the sails
Mooring – The process of securing a boat to a dock or anchor
Nautical – Relating to or involving ships, sailors, or navigation on water
Navigation – The process of planning and controlling the course of a boat
Oar – A long pole with a flat blade used for rowing a boat
Outboard – A motor located on the outside of the boat
Port – The left side of a boat when facing forward
Propeller – A device that uses rotating blades to provide forward motion to a boat
Pulpit – A railing or fence located on the bow of the boat
Rudder – A flat object located at the back of the boat used to steer
Sail – A piece of fabric used to catch the wind and propel the boat
Sailing is the practice of using the wind to power a vessel through the water
Sheet – A line or rope used to control the angle of the sails
Skipper – The person in charge of operating a boat
Stern – The back of the boat
Tack – The direction of a boat when it is sailing upwind
Throttle – The control used to increase or decrease engine speed
Tiller – A handle or lever used to steer a boat
Transom – The flat, vertical surface at the back of the boat where the outboard motor is mounted
Trim – The adjustment of the sails and other equipment to optimize performance
Wake – The waves created by a boat as it moves through the water
Windward – The side of the boat facing into the wind
Winch – A device used to pull or hoist heavy objects on a boat
Yacht – A larger, more luxurious type of boat typically used for pleasure cruising
Bilge pump – A device used to pump water out of the bilge
Boom – The horizontal pole or spar that extends from the mast to support the bottom of the sail
Bowline – A knot used to secure a line to a fixed object
Cam cleat – A device used to secure a line under tension
Catamaran – A type of boat with two parallel hulls
Centerboard – A movable fin located underneath the boat that helps improve stability and maneuverability
Chafe – The wearing away or damage to a rope or line caused by friction against another surface
Clew – The lower corner of a sail
Current – The flow of water in a particular direction
Dinghy – A small boat used to transport people or supplies to and from shore
Fairlead – A device used to guide a line or rope in a particular direction
Flotation device – A piece of equipment used to keep a person afloat in the water
Forestay – The wire or rope that supports the mast at the front of the boat
Gaff – A spar used to support the upper edge of a sail
Headway – The forward motion of a boat
Inboard – A motor located inside the boat
Jibsheet – The line or rope used to control the jib sail
Keelboat – A type of sailboat with a fixed keel for stability and maneuverability
Luff – The forward edge of a sail
Masthead – The top of the mast where the highest sails are attached
Navigation lights – Lights used to signal other boats of the position and direction of a boat at night
Outhaul – The line or rope used to control the tension of the bottom of the sail
Planing – The state of a boat when it is moving quickly across the water and partially out of the water
Powerboat – A type of boat that is powered by an engine rather than sails
Ratchet block – A device used to reduce the effort required to pull a line under tension
Reefing – The process of reducing the size of the sails in high wind conditions
Rigging – The system of ropes and wires used to support and control the sails and mast
Rudderpost – The vertical post or shaft that the rudder is attached to
Scow – A type of sailboat with a flat bottom and squared-off ends
Shackle – A metal fitting used to connect two pieces of rope or chain
Spinnaker – A large, lightweight sail used to catch the wind when sailing down
wind 90. Spreaders – The horizontal struts on a mast that help to support and spread the shrouds
Standing rigging – The fixed parts of a boat’s rigging system, such as the mast and shrouds
Stern light – A white light on the back of a boat used to signal other boats at night
Stowaway – A person who hides on a boat in order to travel without permission
Tiller extension – A device used to extend the length of the tiller to make steering easier
Topside – The upper part of a boat, above the waterline
Transom door – A door in the back of a boat that provides access to the water
Traveler – A device used to move the mainsail along the boom
Waterline – The level at which a boat floats in the water
Winch handle – A handle used to turn winches to control the sails and lines
Yawl – A type of sailboat with two masts, the smaller of which is located aft of the rudder post.
Leave a Review Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
You may also like
Sailing spots.

Where to Rent a Yacht in Winter: An Expert’s Guide

A Yachter’s Guide to Australian Customs and Immigration Procedures
Yachting basics.

When to Change Your Anchor Chain and How to Choose the Right One

Sailing for beginners – 10 Questions and Concerns
Sailing routes.

Sailing Route in Spain: from Barcelona along the Costa Brava

Sailing Route in Thailand from Phuket
Yacht events.
No listings were found matching your selection. Something missing? Why not add a listing? .
Sailing News

International Charter Expo (ICE) 2023: Get Ready for the Ultimate Yacht Charter Event!

Navigating 2023: A Calendar of the Year’s Remaining Major Sailing Races and Regattas
Faces in yachting.

Laura Dekker: The Youngest Circumnavigator – A Voyage of Resilience and Dreams

John F. Kennedy: The Yachtsman President
Boat reviews.

| Sailing Click - search best yacht rental deals worldwide, discover new sailing destinations, find new yacht marinas. |
- TOP Charter Deals (updated)
- Advertising and Promotion
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Please note that some links on our site are affiliate links. This means we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you if you click on them and make a purchase. We recommend products because we believe they add value, not because of the commission we receive. Your support helps keep our site running. If you have questions, please reach out to us.
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Change Location
Find awesome listings near you.

Urban Thesaurus
Urban Thesaurus finds slang words that are related to your search query.
Click words for definitions
- sailing mishap
- root chakra
- yacht clubbin' it
- yacht bounce
- videoservices
- unicorn mayonaise
- whatever floats your yacht
- pirate mike
- cookie gate
- porta potty
- fairfield county
- hiring freeze
- vineyard vine
- yachtacious
- wolf blitzer
- on the dock
- vancouverite
- shelter island
- the bulgarian
- dupont registry
- porta potties
- amx duder 343cid
- prep star millionaire
- lilly pulitzer
- smooth sailor
- congressional
- camden yacht club
- bridge stare
- iraqi freedom
- motor-yacht
- westchester
- making trees
- mantoloking
- allenhurst beach club
- lighthouse point
- marlinbelter
- post-yacht rock
- abercrombie
- montgomery county
- big ed moustapha
- supermodelz
- white trash bloody mary
- cheddar beakley
- manhattanite
- coral gables
- deck jewellery
- che guevara
- viking ship
- motoryachting
- south dartmouth, ma
- mahone bay, nova scotia
- gentleman's cocoa
- osterville, ma
- brofreshional
- lynn university
Popular Slang Searches
Slang for yacht.
As you've probably noticed, the slang synonyms for " yacht " are listed above. Note that due to the nature of the algorithm, some results returned by your query may only be concepts, ideas or words that are related to " yacht " (perhaps tenuously). This is simply due to the way the search algorithm works.
You might also have noticed that many of the synonyms or related slang words are racist/sexist/offensive/downright appalling - that's mostly thanks to the lovely community over at Urban Dictionary (not affiliated with Urban Thesaurus). Urban Thesaurus crawls the web and collects millions of different slang terms, many of which come from UD and turn out to be really terrible and insensitive (this is the nature of urban slang, I suppose). Hopefully the related words and synonyms for " yacht " are a little tamer than average.
The Urban Thesaurus was created by indexing millions of different slang terms which are defined on sites like Urban Dictionary . These indexes are then used to find usage correlations between slang terms. The official Urban Dictionary API is used to show the hover-definitions. Note that this thesaurus is not in any way affiliated with Urban Dictionary.
Due to the way the algorithm works, the thesaurus gives you mostly related slang words, rather than exact synonyms. The higher the terms are in the list, the more likely that they're relevant to the word or phrase that you searched for. The search algorithm handles phrases and strings of words quite well, so for example if you want words that are related to lol and rofl you can type in lol rofl and it should give you a pile of related slang terms. Or you might try boyfriend or girlfriend to get words that can mean either one of these (e.g. bae ). Please also note that due to the nature of the internet (and especially UD), there will often be many terrible and offensive terms in the results.
There is still lots of work to be done to get this slang thesaurus to give consistently good results, but I think it's at the stage where it could be useful to people, which is why I released it.
Special thanks to the contributors of the open-source code that was used in this project: @krisk , @HubSpot , and @mongodb .
Finally, you might like to check out the growing collection of curated slang words for different topics over at Slangpedia .
Please note that Urban Thesaurus uses third party scripts (such as Google Analytics and advertisements) which use cookies. To learn more, see the privacy policy .
Recent Slang Thesaurus Queries


- How to , INFLATABLE BOATS AND RIBS , MOTOR BOATS , News , SAILBOATS
Yacht : modern meaning of the term and types of boats
- Luca D'Ambrosio
- February 25, 2023
The etymology of the term yacht comes from the Dutch word ‘jacht’, which was used in the past to define the fast sailing vessels used to hunt down pirates along the coasts of northern Europe.
Today, the term ‘yacht’ is used to describe all recreational vessels, whether sailing or motor-powered, with at least one cabin that allows the crew to sleep on board.
There is no established definition for the length of this family of boats, but common usage tends to define a yacht as a vessel longer than 33 feet, or about 10 meters.
As mentioned above, a yacht may be equipped with sailing, motor or mixed propulsion. It can have more than one hull, and if it exceeds 25 meters it also deserves the definition of superyacht . When a yacht is over 50 meters it is called a megayacht and, more and more frequently, when it exceeds 100 meters it becomes a gigayacht.
A yacht normally flies a flag that corresponds to the country where the vessel is registered, not least because, if it does not, it may be captured and taken to the nearest port for ‘flag survey’. As far as international maritime law is concerned, the yacht is considered in all respects to be the territory of the country of the flag it flies, to whose sovereignty the crew is subject.
A yacht flying the flag of a country, unless there is well-founded suspicion of illegal activity, can only be stopped for inspection by the military vessels of that country. When a yacht enters the territorial waters of a country other than that of its flag, it is obliged to fly a courtesy flag.
This is tantamount to a declaration of submission to the navigational laws of the country in which it is sailing.
Sailing and motor-powered yachts
The first major distinction is between sailing yachts and motoryachts. The current worldwide spread of these two families has shifted decisively towards motor yachts, which make up about 75% of the total sailing fleet.
Progress and design have produced many different categories of motor yachts, so let’s discover them together.
Motoryachts
Seen from the stern, a flybridge yacht is often equipped with a “beach club”, a platform that facilitates access to the sea and on which water toys are placed or simply used for diving. A staircase, or even two symmetrical staircases, leads from this platform to the main deck. Sometimes there is a “garage” between these two staircases to house the engine room, a tender and other on-board equipment.
The main deck is characterized by the presence of a helm station, inside of which a large open-space salon houses settees and a galley. The helm station often leads below deck, also known as the lower deck, where the sleeping quarters, or cabins, are normally located.

The foredeck often has a large sundeck bordered by a “bowplate” for hauling anchor. The bow is often “fenced in” by the handrails, which are vital grips for safety at sea.
Let’s get to why a yacht is called a flybridge. The flybridge is an upper deck, open 360 degrees and often covered by a hard-top, a roof usually made of fibreglass. The flybridge usually has an additional helm station to steer from a more panoramic position. An additional galley is often located on the flybridge, as well as additional lounge seating and sun decks.
Open Yachts
An open yacht has no flybridge and its main deck is commonly all open. The helm station can frequently be sheltered by a T-Top. Below deck, depending on the length of the yacht, there are living spaces for the crew which may include dinette, cabins and facilities. Open yachts can be walk-around, i.e. with the possibility for passengers of walking freely around the perimeter of the boat, or they can have an enclosed bow and thus have a raised deck.

A coupe yacht is a yacht without a flybridge, characterized by a sporty design, with the main deck open aft. Very often it has a sunroof and is always equipped with side-decks connecting the stern to the bow. It is a vessel that, depending on its size, is suitable for medium to long-distance cruising.

This is an important type of yacht, which has its origins on the American East Coast where it was used to catch lobsters. It has a romantic, sometimes vintage aesthetic, and is endowed with sinuous lines that, for some, are evocative of the 1950s. Very suitable for cruising and conviviality, thanks also to a large sofa in the cockpit, the lobster is an iconic boat that offers plenty of comfort and space below deck for at least one cabin and one head.

The trawler is essentially a yacht for owners who want to spend a lot of time on board. This is why interior volumes are maximized and the upper deck is always present. Also part of the trawler family are the famous Menorcan boats, inspired by the llaüts of the Menorca island..
Increasingly popular among motor yachts, too, is the multihull, due to its inherent features of stability and capacity. In most cases it is a catamaran designed for long stays at sea.
Sailing yacht
Sailing yachts are vessels where propulsion should mainly rely on the power transmitted by the wind. In the past, sailing yacht engines were low-powered and mainly used for entering and leaving ports, but today, for obvious reasons of practicality and ease of use, they have enough power to make the sailing yacht cruise at a speed at least equal to its theoretical hull speed. This means that sailing yachts can be used efficiently even in the total absence of wind.
A sailing yacht can be rigged in many different ways, these being the most common in modern times:
Sloop : this is the most common rigging on modern boats, characterized by the presence of a single mast with a mainsail and a jib or genoa. Sloop rigging has become popular over the years because it is the easiest to handle with a small crew and also offers the best ease of use/sailing performance ratio.
Cutter : Widely used for long distance sailing, it is characterized by the presence of a mainsail and two jibs rigged on a single mast. Normally the two jibs are a genoa and foresail that are used individually, depending on the weather conditions.
Ketch : this is the most commonly used rig on two-masted sailing yachts, with a mainmast, rigged with a mainsail and genoa, and a mizzenmast, forward of the rudder shaft, rigged with a single mainsail. The splitting of the sails makes this type of yacht suitable for sailing in bad weather.
Yawl : exactly the same as a ketch but with the mizzen mast located aft of the rudder shaft.
Sailing yachts can be monohulls or multihulls, i.e. catamarans or trimarans, but in all cases they can be divided into these categories:

Easy to handle and with plenty of space above and below deck, this type of yacht is normally characterized by an unbalanced length/width ratio favouring the latter, a small sail area and more powerful than average engines.
The interiors are fully equipped and sophisticated, with each cabin often having its own en-suite head.
The deck plan and sailing equipment are simplified, often electrified and minimal.
Cruiser-Racer

This yacht, while still featuring a luxurious and complete interior, also has all the equipment needed for sail fine-tuning and a generous sail area.
This is a category where special attention is paid to both the overall weight of the boat and the hull shape.
The hull lines are in fact designed to enhance performance and, inevitably, this results in a slightly smaller interior than that of pure cruising yachts of the same length.
Racer-Cruiser

The owner who buys this type of yacht has already competed in club competitions and now wants to engage in higher level racing. The hulls are light and can sometimes be made of carbon, and all the sail adjustments are fine-tuned to achieve maximum performance.
The deck plan is definitely designed for crewed racing and the sail area/displacement ratio is unbalanced in favour of the former, making this yacht more difficult to handle with a smaller crew but, conversely, capable of performance similar to a pure racing yacht.
A pure racing yacht is a sailing yacht built exclusively for racing. Free from any commercial constraints, it is built according to the type of race to be competed in and, above all, the rating to be obtained. The interiors of this boat are minimal. This yacht is capable of planing and sailing upwind at very low wind angles, but is almost never used for recreational purposes.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Language switcher
Browse categories.

You might be interested in

RS21 CUP: the Innovative Sailing World Championship takes place in Porto Rotondo

Rio Yachts: the new Le Mans 45 and 50 in world premiere at Cannes and Genoa

The golden September of Scanner Marine, introducing the new Envy 1500

ICE YACHTS: at the Cannes Yachting Festival with two out-of-the-ordinary sailing yachts

© 2021 – THE INTERNATIONAL YACHTING MEDIA Designed by BLive Communication
ABOUT YACHTINGNEWS.COM
Yachting News is an interactive multimedia magazine dedicated to the world of boating.
The International Yachting Media is the worlds most widely read boating magazines network. Whit its portal It broadcast its original contents in five languages and in more than 200 countries developing 950,000 views a week. Our web portals are the main source of information for yacht and boat owners, the place where they can find anything about their boating passion.
THEINTERNATIONALYACHTINGMEDIA.COM | SUPERYACHTS.NEWS | YACHT DIGEST
VIRTUAL BOAT SHOW | TUTTTOBARCHE | TOUSLESBATEAUX | TODOSLOSBARCOS
BOATING NEWS FREE APP
To provide the best experiences, we and our partners use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us and our partners to process personal data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site and show (non-) personalized ads. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
Click below to consent to the above or make granular choices. Your choices will be applied to this site only. You can change your settings at any time, including withdrawing your consent, by using the toggles on the Cookie Policy, or by clicking on the manage consent button at the bottom of the screen.
Subscribe For Latest Updates
Sign up to receive the best of Yachting News, sea trials, boat review and world premieres .
The only ADVERTISING FREE newsletter
Superyacht sinks latest: Investigators reveal where bodies were found as probe looks at 'crew's responsibility'
Italian officials revealed at a news conference there could be "a question of manslaughter" as they opened a shipwreck investigation and said the probe is also looking at the "crew's responsibility".
Saturday 24 August 2024 18:33, UK
- Superyacht sinking
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Prosecutor: There 'could be a question of manslaughter'
- Probe 'concentrating' on crew's responsibility
- Seven bodies recovered after five-day search of superyacht wreckage off Sicily
- Saturday's papers pay tribute to youngest victim Hannah Lynch
- Hannah's sister pays tribute to 'my little angel'
- Explained: Inside the superyacht | What challenges have faced divers?
- Eyewitness: Sombre scenes greet rescue teams as final body is brought ashore
- Live reporting by Niamh Lynch
We're ending our live coverage for this evening but here is a recap of what we know:
- Prosecutors have opened a manslaughter investigation into the Bayesian sinking;
- Officials have revealed more details on their investigation and the difficult five-day rescue mission;
- The six bodies found during the search in recent days were all in cabins on the left-hand - and highest - side of the ship. Five were found in the first cabin and the sixth was found in the third;
- Prosecutors said the six passengers were most likely asleep when the boat sank;
- The probe is now focusing on the crew and their responsibilities, with the captain set to undergo more questioning.
Monday 19 August
The Bayesian yacht, flying a British flag, sinks at around 5am local time when the area was hit by a tornado.
Fifteen people are rescued from the 56 metre vessel - including a mother and baby - but another seven remain missing.
One body, later confirmed to be the yacht's chef Recaldo Thomas, is found near the wreck.
It emerges that British technology tycoon Mike Lynch and his 18-year-old daughter Hannah are among six people that remain missing.
Tuesday 20 August
The search continues for the six tourists missing.
It is reported that among those missing are Morgan Stanley International chairman Jonathan Bloomer; his wife, Judy Bloomer; Clifford Chance lawyer Chris Morvillo; and his wife, Neda Morvillo.
Police divers try to reach the hull of the ship, resting at a depth of 50 metres.
Italy's fire brigade Vigili del Fuoco say early inspections of the wreck were "unsuccessful" because of limited access to the bridge and furniture obstructing passages.
The operation is later described as "complex", with divers limited to 12-minute underwater shifts.
Tributes pour in for Mr Thomas, with his friend Gareth Williams saying: "I can talk for everyone that knew him when I say he was a well-loved, kind human being with a calm spirit."
Wednesday 21 August
The search for the six people unaccounted for enters a third day, with crews carrying out inspections of the yacht's internal hull.
A team of four British inspectors from the Marine Accident Investigation Branch (MAIB) arrive in Porticello to look at the site of the sinking.
A helicopter is drafted in to help with the search effort and remotely controlled underwater vehicles are being used, with naval units and cave divers also taking part in the search.
Five bodies are found inside the yacht on Wednesday afternoon. Only four of them are brought to shore.
Body bags are seen being taken to Porticello in the afternoon where dozens of emergency services staff wait.
Searches finish for the day just before 7.30pm.
Thursday 22 August
The search resumes for the remaining missing person.
The body of the fifth missing person, found but not recovered the previous day, is brought to shore.
A fire service boat with flashing blue lights returns with a blue body bag to the port of Porticello just after 8.45am local time on Thursday.
Tributes pour in for Mr Lynch and Mr and Mrs Bloomer after they are identified as having died.
The search is called off at around 8pm in Sicily, with divers expected to begin again at 6.30am on Friday.
Friday 23 August
The search continues for the final person missing from the wreck of the Bayesian, Hannah Lynch.
Vincenzo Zagarola, of the Italian Coastguard, says the search for Hannah has not been "easy or quick", comparing the sunken yacht to an "18-storey building full of water".
The coastguard confirms in the late morning that her body has been found.
A green body bag is brought to the port of Porticello from the site of the sinking.
A spokesperson announces on behalf of the Lynch family that they are "devastated" and "in shock" after the deaths of Mike and Hannah.
Hannah's sister Esme pays tribute to her "little angel".
Saturday 24 August
A press conference is held in the court of an Italian town, Termini Imerese.
Public prosecutor Ambrogio Cartosio tells reporters that his office has opened an initial investigation against unknown persons into manslaughter and negligent shipwreck.
As the focus now turns to the manslaughter investigation, here's another reminder of the seven victims of the sinking and the 15 people who survived.
A close friend of the Lynch family has added to the chorus of tributes for British tech tycoon Mike Lynch, who died in Monday's superyacht sinking.
Susannah Gurdun, who lives in Suffolk, recalled being "daunted" when she first met Mr Lynch at a dinner party, before discovering he was "so much more than the corporate cliche".
"He was riveting. He was funny, and kind, and endlessly interesting; capable of talking about anything and everything," she said.
Ms Gardun said the businessman also had a "thrilling ability" to make complicated subjects "accessible to those of us less blessed with a science acumen".
"In particular, he was wonderful with children. I will never forget hearing him explain to a group of them - including our ten year old son - the physics of why the sky went pink at sunset," she said.
She went on describe Mr Lynch as a "true genius" and "phenomenal creative".
Ms Gardun said his daughter Hannah was also showing "serious literary promise", and added that it was "beyond tragic that we will never know where her own particular brilliance might have led".
"I still feel blessed to have shared that time with them in Spain. Not just because I witnessed Mike’s incredible storytelling; but because I was given a chance of understanding what that moment said about all four of them as a united vibrant loving family," she said.
"He was an extraordinary human being and it was - truly - a privilege to have known him."
A yacht crew member who survived the sinking has paid tribute to Hannah Lynch, calling her a "diamond in a sea of stars".
Sasha Murray, chief stewardess of the Bayesian, has released a statement after divers recovered the final missing body from the wreckage, which is believed to be 18-year-old Hannah.
"Those who knew her will know that Hannah was a diamond in a sea of stars," she said.
"Bright, beautiful and always shining. What most people may not have seen was the extraordinarily strong, deep and loving relationship she shared with her parents, whom she adored more than anything.
"While swimming with them she often said, if anything ever happened she would save them.
"I have no doubt that the Irish, Latina fire that burns in her soul kept that spirited determination alive."
Ms Murray's statement comes as a new image of Hannah Lynch and her father Mike Lynch is released:
Prosecutors announced in this morning's news conference that they have opened a manslaughter and negligent shipwreck investigation.
Officials were unable to answer several queries from the media, saying they needed time to establish the facts, but what are the key questions facing prosecutors?
Why weren't passengers who remained on board the vessel warned about escaping from the yacht?
The prosecutor in charge of the case, Raffaele Cammarano, suggested that some passengers may have been asleep when others were awake.
Asked why they were not woken up or alerted, he said that is something investigators are trying to work out from the statements of the survivors.
He called it an "essential" part of the inquiry.
Why were several of the passengers in one cabin?
The press conference heard several bodies onboard the sunken yacht were found in a single cabin which was not theirs.
Mr Cammarano said investigators currently do not know the reason for them being discovered in the same cabin.
The chief of the Palermo fire service, Bentivoglio Fiandra, said the yacht pinned to the right and suggested people tried to go on the other side, taking refuge in cabins in the higher part of the wreck.
Why did the boat sink?
The vessel had been deemed "unsinkable" by its manufacturer - Italian shipyard Perini Navi.
The Bayesian was hit by a downburst, according to Mr Cammarano, which are powerful winds that descend from a thunderstorm and spread out quickly once they hit the ground.
Officials will look into the safety equipment on the sunken vessel.
Mr Cammarano was asked about whether there is a black box and if the hatches were left open.
He said investigators do not have exact information about the black box and that the first phase of the inquiry will look into it.
Why were nearby vessels not similarly affected?
Another yacht, the Sir Robert BP, was about 150 to 200 metres from the Bayesian when extreme weather hit.
Its crew helped to rescue 15 people from the stricken vessel.
Italian officials said they would be looking at how the downburst could affect one vehicle and not other nearby vessels.
What weather warnings was the Bayesian alerted to?
Maritime director of western Sicily, Rear Admiral Raffaele Macauda, said the weather at the time of the yacht's sinking was abnormal and there was nothing to suggest such an extreme situation would arise.
He said there were forecasts of winds and a storm alert, but there was no warning of a tornado.
"Given that the conditions were such, there wasn't anything to suggest there could be an extreme situation arising," he said.
"There are vessels that can monitor, after all, these events and one would have thought that the captain had taken precautions."
How long will it take to recover the sailing vessel?
Mr Macauda could not confirm how long it would take to retrieve the shipwreck of the sunken yacht.
"Everything depends on the availability of the owners and the timeframe of the retrieval of the wreck and of course all that has to be submitted to the port authorities and in parallel of course there will be the inquiry results and it's only really then that we will be able to authorise the operation," he said.
"I can't say, like some experts who have already spoken on the subject, [said] that it will be eight weeks."
He made clear that the owners will bear the full cost of retrieval, although he could not estimate the figure.
Italian authorities detailed the challenging and meticulous rescue operation to recover the six missing people from the Bayesian wreck (see 9.18am post).
But why was the five-day search so difficult?
Read more below...
More on this morning's press conference.
One of the main updates from prosecutors was that they have opened manslaughter and shipwreck investigations after the deaths of seven people in the Bayesian sinking.
Watch the announcement below...
Prosecutors have given a lengthy news conference this morning on their investigation into the sinking of the Bayesian.
Read the full report on the prosecutors' probe below...
Marine investigator James Wilkes has been speaking to Sky News after this morning's press conference.
"Naturally, there are more questions than there are substantive answers at the moment - that's the nature of investigative work.
"Something forced that yacht to roll beyond its nominal stability limits, such that it wasn't able to right itself with the ingress of a certain amount of seawater that was coming into the yacht.
"So the investigators are going to ask themselves one initial question - what must the conditions have been for this to happen?
"Then they are going to look at the contributing factors to the yacht, sinking, and, and the unfortunate loss of life."
Prosecutors said this morning that the future of the investigation is reliant on recovering the wreck.
Mr Wilkes said the yacht is a "major piece of physical evidence in and of itself."
"It's lying at 50 metres, which is a recoverable depth.
"If it was significantly deeper, then I'm not sure they'd be considering salvage at this stage or certainly, the salvage question would be a lot more complicated to answer.
"But if there was the ability to raise that yacht in one piece safely, then it gives the investigators physically more to look at."
Mr Wilkes said he was unsure if the yacht would have a "black box" - called a voyage data recorder in shipping.
"It would record things like GPS position, heading speed, engine telemetry, whether the radars were on, what they were recording, alarms, communications from the yacht itself, any audio on the bridge.
"But more often than not, these are on merchant ships. The yacht was a commercial yacht in the sense that it could be chartered out so it's quite possible it has a voyage data recorder on, but I'm not sure that it does. I don't know that as a matter of fact," he said.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Email
- Subscribe to our Newsletter

Celebrities Accused Of 'Yachting' In Hollywood — And What Being A 'Yacht Girl' Really Means
Rumors suggest some women are paid to play..
- Micki Spollen
Written on Jan 11, 2022

It’s easy to be envious when seeing the Instagram photos of young, carefree celebrity women seemingly having the time of their lives on yachts floating in exotic waters and in the VIP sections of the most exclusive clubs.
However, rumor has it there is much more than meets the eye when it comes to these ‘yacht girls’ and their extravagant lifestyles.
What is a yacht girl?
According to Urban Dictionary , a yacht girl is “an attractive young woman who finds ways to get access to luxurious surroundings by being available to wealthy men.”
For example, you may follow a woman or two on Instagram who always seems to be partying or vacationing somewhere expensive (notably without ever showing who she’s actually with). This is a person you could potentially describe as being a yacht girl.
And it’s not just those Instagram models and wannabe stars that are considered yacht girls. As you work up the wealth chain, you may be surprised to recognize some celebrity names synonymous with yachting.
RELATED: Director Who Saw Robin Thicke Allegedly Grope Emily Ratajkowski Says He Only Did It Because He Was Drunk
What is 'yachting' in Hollywood?
In Hollywood, the term yacht girl essentially means a woman who works as an escort for high-end clientele , not just on yachts but for any social event.
While the practice has only somewhat recently gained mainstream notoriety, if you think back on the many tabloid photos of models and actresses on yachts from years past, it appears to be something that's gone on in Hollywood “for 60 years,” according to Elie Nahas, who ran a Beirut-based modeling agency before being arrested on charges of running a prostitution ring in 2007.
In 2013, "The Hollywood Reporter" ran a feature describing this so-called yachting during the Cannes Film Festival.
“Every year during the festival there are 30 or 40 luxury yachts in the bay at Cannes, and every boat belongs to a very rich person. Every boat has about 10 girls on it; they are usually models, and they are usually nude or half nude,” Nahas told THR.
At the end of the night, each woman would receive a “gift,” a generous amount of money that the client would put in an envelope for her.
And while many of these women were self-proclaimed local prostitutes and escorts, the Cannes Film Festival is, of course, known for its celebrity attendees — and it’s rumored that celebrity women trying to fast-track a name for themselves in Hollywood become yacht girls, too.
“Women installed on yachts in Cannes during the film festival are called ‘yacht girls,’ and the line between professional prostitutes and B- or C-list Hollywood actresses and models who accept payment for sex with rich older men is sometimes very blurred, explains one film industry veteran,” Dana Kennedy wrote for THR.
RELATED: What Is Instagram Face — And Which Celebrities Have It?
Some women in Hollywood have accused their celebrity peers of being yacht girls.
A 2017 blind item (celebrity gossip that doesn’t outwardly name the celebrity) allegedly written by a struggling actress describes being lured by another actress into the world of yachting :
“The actress I was talking to made it sound super easy and that she only had [sex] a few times with guys while yachting and that it was mostly partying and being arm candy,” she writes, explaining that eventually she agreed to try it for $25,000 upfront, but admitting that the experience was less than glamorous.
Blind item readers guessed that Canadian actress Vanessa Lengies wrote the blind item and further surmised that it may be one of the Glee actresses Naya Rivera or Heather Morris that introduced her to yachting. None of these claims have ever been substantiated.
If you believe the rumors, it would seem that yachting is a rite of passage for women hoping to “make it” in Hollywood, and even some celebrities we now consider A-List are thought to be former yacht girls.
In an excerpt from her 2021 memoir , “My Body,” Emily Ratajkowski details being paid $25,000 at the start of her career to go to the Superbowl with now-disgraced Malaysian financier Jho Low, who "‘just liked to have famous men and women around,’” she explains her manager told her at the time.
She writes about attending the star-studded Coachella on someone else’s dime, having drinks paid for at clubs, and attending afterparties with Oscar-winning actors before actually becoming a celebrity herself.
One could infer from this recollection that, in order to be able to tell these stories, Ratajkowski was herself a yacht girl. “My Body” suggests as much, and in it, she subtly gives away the identity of another celebrity woman who yachted alongside her.
Ratajkowski describes watching as Low gave shots to a Victoria’s Secret model. While she doesn’t name drop, Ratajkowski gives just enough information for readers to figure who that model likely was.
“Now she kept her eyes locked on him as he took his shot, throwing her head back dramatically as he did, only to quickly toss the alcohol over her shoulder,” Ratajkowski writes. “When he faced her again, her eyes sparkled and the famous dimples appeared on her cheeks.”
Low has since become a fugitive wanted for allegedly running an international money laundering scheme, and in 2017, Reuters reported that model Miranda Kerr — known for her dimples — was being ordered to return “diamond pendants, earrings and other jewelry worth about $8 million” that Low allegedly gifted her to government agents.
In 2017, Ratajkowski also posted a video on Instagram potentially outing Bella Hadid and Hailey Bieber as yacht girls as they danced aboard a yacht during that year’s Cannes Film Festival.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Emily Ratajkowski (@emrata)
Many people have also accused Meghan Markle of yachting (but then again, what haven't people accused Markle of at this point).
People have pointed to an old photo of Markle on a yacht as proof that she’s a former yacht girl.
RELATED: How Meghan Markle Is Related To Prince Harry
Another old blind item also suggested the former actress was available to “rent.”
"If you see B actress post scantily clad photos of themselves on Social Media, this is often a Comm to [them] that this person is available to ‘rent’ for a weekend of ‘yachting,’” the tweet says, including a photo of Markle in a swimsuit.
"If you see B actress post scantily clad photos of themselves on Social Media, this is often a Comm to [them] that this person is available to “rent” for a weekend of “yachting”. Typically worth $30K for the “party” - Meghan Markle @3Days3Nights https://t.co/E3WfMjnVL9 pic.twitter.com/QFv476GL0b — yacht girl (@yachtgirlmm) November 27, 2019
Markle’s close friendship pre-Harry with actress Priyanka Chopra has naturally led some to guess that Chopra once yachted as well.
Another actress that faces endless rumors of yachting is Russian actress Irina Shayk , which according to THR, is par for the course as the outlet writes that yachting your way to stardom happens with “disturbing frequency,” particularly when it comes to foreign-born actresses.
According to THR, who claims to know “of at least one now-prominent actress who made her first connections on a Cannes yacht and quickly landed her debut role in a U.S.-shot movie,” such as with Shayk’s 2014 film “Hercules,” it’s “a red flag any time you see a foreign-born actress with no credits suddenly make her way into a U.S.-shot movie.”
Of course, when it comes to yachting in Hollywood, all of these claims appear to be unfounded.
These rumors make for good gossip, whether you’re talking about low-level social media influencers or high-profile celebrity actresses.
However, nothing is proven, leaving us to wonder any time we see a photo of women on a yacht.
RELATED: Ghislaine Maxwell Facing 65 Years In Prison While Questions Remain About The Names In Epstein's Little Black Book
Micki Spollen is an editor, writer, and traveler focused on relationships, news, and pop culture. Follow her on Instagram .
Our Newsletters
Get the best of YourTango delivered straight to your inbox — the biggest stories, actionable advice & horoscope predictions!
- SI SWIMSUIT
- SI SPORTSBOOK
Angels Move Mike Trout to Long-Term IL, Promote Reliever For Potential MLB Debut
Maren angus-coombs | 10 hours ago.

- Los Angeles Angels
The Los Angeles Angels made a handful of moves on Tuesday afternoon, including transferring outfielder Mike Trout to the 60-day injured list from the 15-day IL more than
The Angels also selected the contract of right-hander Ryan Miller from Triple-A Salt Lake and placed left-hander Matt Moore on the 15-day IL.
Trout's season ended after tearing his meniscus for a second time. Transferring him to the 60-day IL is a procedural move that allows the Angels to bring Miller onto their major league roster.
Trout was initially injured on April 29 against the Philadelphia Phillies and underwent surgery on May 3, leading to months of rehab. He began a rehab assignment with Triple-A Salt Lake on July 24 but was pulled after just two innings due to knee discomfort.
Describing Trout's injury struggles over the past five years as significant would be an understatement. Last season, he missed 80 games with a fractured left hamate. In 2021, a right calf strain limited him to just 36 games. This year, knee issues have again kept him under 50 games played, with only 29 appearances.
Moore's trip to the IL comes after he exited the game against the Blue Jays on Sunday with an elbow injury after giving up two runs in the seventh inning. It was his first appearance in six days and the first time he had allowed multiple runs since mid-July.
The Angels have not confirmed the severity of his injury.
#Angels transactions: •Selected the contract of RHP Ryan Miller •Placed LHP Matt Moore on 15-day injured list •Transferred OF Mike Trout to 60-day injured list — Angels PR (@LAAngelsPR) August 27, 2024
Moore's performance this season has been inconsistent, with his earned run average fluctuating from 6.03 to 4.69 before Sunday’s outing, which then pushed it back up to 5.03.
Moore returned to the Angels on a one-year, $9 million deal in January. The 35-year-old pitcher is 71-66 with a 4.39 ERA in his career. He started 164 games before transitioning to full-time relief work in 2022, and has enjoyed two separate stints with the Angels since.
The 28-year-old Miller is set to make his MLB debut more than six years after being drafted by the Diamondbacks in the sixth round of the 2018 draft. He joined the Angels through the minor league phase of last year’s Rule 5 Draft and has performed impressively since. Over 62.1 innings, he’s posted a 2.45 ERA.
Miller played collegiately at Clemson. In two seasons with the Tigers, he compiled an 8-1 record with a 2.59 ERA, striking out 75 batters and walking 19 over 81.1 innings. He was drafted by the Arizona Diamondbacks in the sixth round (No. 189) of the 2018 MLB Draft.
Miller also had stints with the New York Yankees and Boston Red Sox organizations before being selected by the Angels in last December’s Rule 5 Draft.
MAREN ANGUS-COOMBS
Queensland man given 22-year jail term for role in importing half a tonne of cocaine into WA
By Tabarak Al Jrood
Topic: Courts and Trials
The 560 kilograms of cocaine seized at a house in Kalbarri last year. ( ABC News: David Weber )
Siosifa Kolomatoagi Faiva was one of three men charged after half a tonne of cocaine was seized at a property in Kalbarri last year.
The arrest was made after a group retrieved the drugs from waters off WA's coast, with the cocaine estimated to be worth more than $250 million.
What's next?
Faiva has been sentenced to 22 years in jail, and must serve 14 years before he is eligible for parole.
A Queensland man involved in the importation of more than half a tonne of cocaine into WA has been sentenced to 22 years in prison.
Siosifa Kolomatoagi Faiva was one of three men charged in August last year after retrieving more than 560 kilograms of cocaine from waters off the state's mid-west coast.
The District Court was told on Friday the 34-year-old had struggled with alcohol and drug use following the death of his brother.
He had also accumulated a drug debt of around $130,000 which prompted him to accept an offer of $300,000 to help retrieve the drugs.
The court heard Mr Faiva was initially contacted by a co-accused asking if he wanted to be involved in the operation, in which he replied that he was "keen" and was "in need of cash".
The drugs and cash were found at a proeprty in Kalbarri. ( Supplied: Australian Federal Police )
Both men flew from Brisbane to Perth on August 9, where they purchased a vehicle in Kenwick for $20,000 in cash.
They then bought some equipment from a store in Mosman Park and a boat in Jandakot for $85,000 in cash, before beginning their journey to Kalbarri, about six hours north of Perth.
They arrived the next day at the coastal town, where they launched the vessel into the water and began their search.
Faiva then began communicating with a co-accused via encrypted messages and informed him that he had found the bags.
After arriving back on shore, the men drove to an Airbnb home where they began unloading the large plastic-wrapped packages.
But less than 20 minutes later the Australian Federal Police (AFP) raided the property and arrested the men.
Officers seized the 560-kilogram stash of cocaine, estimated to be worth up to $250 million, along with mobile phones, and about $30,000 in cash.
The agency said the drugs were dumped into the water by a bulk carrier operating as part of a criminal network targeting Australia.
'Remorseful and ashamed'
Faiva's lawyer, Tim Ryan KC, told the court while his client's involvement was "essential in importing the drugs," it fell at a "lower level of criminality than the organisers".
"There is a proper distinction between the people who organised this and those who were recruited," Mr Ryan said.
The drugs were allegedly dropped into the water in large plastic-wrapped packages. ( ABC News: David Weber )
Mr Ryan asked Judge Belinda Lonsdale to take into account his client's cooperation with authorities and his early guilty plea.
"He is remorseful and ashamed of his behaviour," Mr Ryan said.
"He acknowledges it was a very poor decision on his part and one that he is very ashamed of."
Mr Ryan said his client had a good prospect of rehabilitation with the support of his family and friends, as well as the Tongan community in Queensland.
Faiva's partner, who he shares three children with, sat in the back of the court room and appeared visibly distressed as she awaited his sentencing.
The cocaine haul was one of the largest ever seen in WA. ( ABC News: David Weber )
Mr Ryan told the judge a long sentence would place a burden on his partner and would have a "significant impact" on his children.
Anthony Eyers, acting on behalf of the Crown, said those factors did not outweigh the seriousness of the offence.
"The offender acted on instructions and was aware he was collecting approximately 500 kilograms of drugs," Mr Eyers said.
"He travelled to WA … and was willing to play a role in the pre-planned importation by collecting drugs from the sea."
'Colossal' operation
When handing down her sentence, Judge Lonsdale acknowledged Faiva's personal circumstances
"It hardly needs to be said, Mr Faiva, that your offending was extremely serious," she said.
"The value of the cocaine, was to put it bluntly, colossal."
Judge Londsdale said Mr Faiva was "fully aware" of what he was asked to do and that he was a "trusted and crucial participant in the enterprise".
Mr Faiva will be eligible for parole after serving 14 years.
'An extremely disruptive person' : H.R. McMaster says he won't serve in second Trump term
Former National Security Adviser H.R. McMaster, who served under Donald Trump , said he would not join the former president's second administration if he is reelected this fall.
As November draws closer, the former Army lieutenant general describes his time working for Trump as a "tour of duty" in his new book “At War with Ourselves: My Tour of Duty in the Trump White House." Describing him as "very offensive" and "brash," McMaster said he would not serve under the former president again in a CNN interview Monday.
"I will work in any administration where I feel like I can make a difference, but I’m kind of used up with Donald Trump,” McMaster told CNN's Anderson Cooper.
McMaster succeeded Michael Flynn as Trump's national security adviser in February 2017. Former White House press secretary Sarah Sanders said McMaster and Trump had a "good working relationship" in March of 2018, but Trump announced he would replace McMaster with John Bolton the same month.
McMaster said although it was a "privilege" to serve, he also does not see himself working in a Kamala Harris administration if she wins in November.
Sign-up for Your Vote: Text with the USA TODAY elections team.
In his new book, McMaster claims Trump pitted members of his administration against one another. He told Cooper other former presidents did the same, but that "everything was magnified" under Trump.
“He’s an extremely disruptive person,” he said. “I saw it as my job, you know, not to try to constrain him, but to help him disrupt what needed to be disrupted.”
He added that he hopes Trump learns from his first four years in office, particularly that Russian President Vladimir Putin is not his friend.
He hypothesizes in the book that Trump figured if he was accepted by strongmen like Putin, he could convince himself and others that he was also strong.
Rachel Barber is a 2024 election fellow at USA TODAY, focusing on politics and education. Follow her on X, formerly Twitter, at @rachelbarber_
The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
Tv ratings: democratic convention closes with 26m viewers, edging rnc final night.
Vice President Kamala Harris accepted her party's nomination to lead the ticket.
By Rick Porter
Rick Porter
Television Writer
- Share on Facebook
- Share to Flipboard
- Send an Email
- Show additional share options
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Pinterest
- Share on Reddit
- Share on Tumblr
- Share on Whats App
- Print the Article
- Post a Comment

The closing of the Democratic National Convention drew a big audience Thursday — topping both the final night of the party’s gathering four years ago and that of the Republican convention in July.
Related Stories
'chimp crazy' on pace for multiyear viewer highs for hbo doc series, 'megalopolis' star laurence fishburne was busy watching the dnc when trailer drama unfolded.
Thursday’s total is up substantially over the first three days of the Democratic convention, which averaged 20.33 million viewers and were very consistent night to night: Monday averaged 20.03 million viewers, Tuesday brought in 20.78 million and Wednesday drew 20.18 million across broadcast and cable networks. Adding in Thursday’s total, the convention as a whole averaged 21.8 million viewers in primetime, a slight improvement the 2020 convention’s four-night average of 21.59 million viewers.
The DNC’s four-day average also topped the July Republican convention in TV viewers by a 14 percent margin; the RNC averaged 19.07 million viewers over four nights.
As it did throughout the week, MSNBC drew the biggest audience for any single network on Thursday. It averaged 6.53 million viewers from 9-11:30 p.m. ET Wednesday, well ahead of second-place ABC (4.23 million). CNN came in third with 3.94 million viewers, followed by NBC at 3.01 million. Fox News (2.45 million) narrowly beat CBS (2.42 million).
Those six networks made up about 86 percent of the total TV audience on Thursday; the remaining 3.62 million viewers were spread across PBS, Scripps News, Telemundo, Univision, BET, CNNe, Fox Business, Newsmax and NewsNation.
MSNBC also led all comers Thursday in the core news demographic of adults 25-54 with 1.28 million such viewers. CNN (1.13 million) grabbed second in the demo, and ABC was third with 1.05 million adults 25-54. NBC had 857,000 viewers in the demo, followed by CBS at 607,000 and Fox News at 358,000.
Aug. 23, 2:48 p.m. An earlier version of this story misstated the all-network audience for the Democratic convention on Thursday.
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
Aubrey plaza reveals why she hasn’t watched ‘white lotus’ yet, how to watch the paris 2024 paralympic games, ‘chimp crazy’ on pace for multiyear viewer highs for hbo doc series, where and when to watch emmy-winning series ‘only murders in the building’ season 4 online, ‘yellowstone’ eyeing surprise season 6 starring kelly reilly and cole hauser, ‘the rings of power’ creators on the steps they took to level up season 2.

COMMENTS
This is an acronym meaning: Young And Coming Home Tonight. It means that you scored and some fly ass coochie is going to come home with you!
A person describing a boat they saw might say, "It wasn't the most elegant boat, more like a floating barge.". 3. Ditch crawler. A "ditch crawler" is a slang term for a small boat, typically used for navigating narrow waterways or shallow areas. The term emphasizes the boat's ability to maneuver in tight spaces.
The maritime world is a treasure trove of fascinating expressions related to knots and ropes. From "tying the knot" to "left in the lurch," we'll unravel the meanings behind these captivating sayings. Let's explore more nautical phrases related to knots, rigging, and seamanship. Each saying carries a unique history, often reflecting the ...
The term log-book has an interesting derivation in itself. An early form of measuring a ship's progress was by casting overboard a wooden board (the log) with a string attached. The rate at which the string was paid out as the ship moved away from the stationary log was measured by counting how long it took between knots n the string.
Yachting is considered to be an open secret within the industry. The term yachting gained media traction in 2013, when The Hollywood Reporter published an investigation into the culture at the ...
It originates from a sailing maneuver whereby a boat would take the wind (and power) out of an opponents sails by sailing to windward of the opponent, causing the other boat to slow. : This term is now used to mean "the whole lot" or "everything.". It's thought this expression comes from square-rigged sailing vessels that had three ...
Here's a list of fundamental yachting terms and slang words that are essential for efficient communication and secure navigation in the world of yachting and sailing: Aft - Toward the rear (stern) of the boat. Ahoy - A call used to greet someone or draw attention. Aloft - Up in the rigging. Anchor - A device used to hold a vessel in ...
A boat or yacht's speed measured in nautical miles per hour (see below). Megayacht. A large luxury yacht typically measuring over 70m. Monohull. A boat with a single hull. May be a sailing yacht, motor yacht, luxury super- or megayacht. See Catamaran above for comparison. Motor yacht (or M/Y) A yacht which is powered with engines. Nautical mile
A term used to hail a boat or a ship, as "Boat ahoy!". Ahull: With sails furled and helm lashed to the lee-side. Aid to Navigation: (ATON) Any device external to a vessel or aircraft specifically intended to assist navigators in determining their position or safe course, or to warn them of dangers or obstructions to navigation.
As a noun, "ship" refers to the pairing of said people or characters. The term dates back to an "X-Files" fan forum in 1996, Merriam-Webster reports. Users who were fans of the romantic pairing of ...
The term "shipping" likely originates from the term "relationshipper," with both words being used interchangeably in Usenet Newsgroups back in the 1990s. One of the earliest archives examples of the word "shipping" being used can be traced back to a May 1996 post on a small X-Files newsgroup, where someone complained about "relationshippers ...
Draft. Boat's draft is the distance from the water surface to the deepest point of the boat. In other words, the draft is the minimum water depth you can go to and not scrape your hull or keel. Better double this number when sailing, just to be safe, as hitting the seabed can have disastrous consequences.
Morgan Stanley International chairman Jonathan Bloomer and his wife are among the six people still missing after a mega-yacht sank off the coast of Italy Monday morning, according to officials and
Stern - The back of the boat. Tack - The direction of a boat when it is sailing upwind. Throttle - The control used to increase or decrease engine speed. Tiller - A handle or lever used to steer a boat. Transom - The flat, vertical surface at the back of the boat where the outboard motor is mounted.
Salon or Saloon - Both terms mean the largest enclosed, common area of a yacht (essentially the "living room" in the terms of a land-based home). Most modern boaters use the term salon to avoid confusing it with a bar found in the old west. Old salts and those who sail with the wind prefer the old-school term, saloon.
A yacht with one hull, as opposed to a multihull or catamaran that has pontoons. While most motor yachts are monohulls, the term typically refers to sailing yachts. Motorsailor. A yacht built to sail and cruise under power with equal efficiencies, such as a Gulet.
According to the algorithm behind Urban Thesaurus, the top 5 slang words for "yacht" are: skiff, sailing mishap, klomy, pimp nautical, and root chakra. There are 124 other synonyms or words related to yacht listed above. Note that due to the nature of the algorithm, some results returned by your query may only be concepts, ideas or words that ...
February 25, 2023. The etymology of the term yacht comes from the Dutch word 'jacht', which was used in the past to define the fast sailing vessels used to hunt down pirates along the coasts of northern Europe. Today, the term 'yacht' is used to describe all recreational vessels, whether sailing or motor-powered, with at least one cabin ...
1. ( galley (kitchen)) The compartment of a ship where food is cooked or prepared; a ship's kitchen. 2. ( galley) A type of ship propelled by oars, used especially in the Mediterranean for warfare, piracy, and trade from the 8th century BC to the 16th century AD, with some in use until the early 19th century. 3.
The yacht was a commercial yacht in the sense that it could be chartered out so it's quite possible it has a voyage data recorder on, but I'm not sure that it does. I don't know that as a matter ...
According to Urban Dictionary, a yacht girl is "an attractive young woman who finds ways to get access to luxurious surroundings by being available to wealthy men. ...
Defence firm Thales won a £223m order for an anti-tank missile system from the UK After years of declining defence spending in many Western countries, the war in Ukraine since 2022 has led to a ...
The Los Angeles Angels made a handful of moves on Tuesday afternoon, including transferring outfielder Mike Trout to the 60-day injured list from the 15-day IL more than The Angels also selected ...
A boat's displacement is equal to its weight at any given time, with any given load. Draft: The total distance a boat penetrates the water, from waterline to keel or appendage bottom. "The Schenectady 54 has a draft of four feet, six inches.". Dry Weight: The weight of a boat without fuel or water onboard.
After the ship sank just before 5 a.m. local time, 15 people, including a 1-year-old, were pulled from the water. Some were rescued from a life raft by the crew of a ship docked nearby.
Three Queensland men are charged over the alleged importation of more than half a tonne of cocaine to Western Australia by boat. After arriving back on shore, the men drove to an Airbnb home where ...
The Associated Press is an independent global news organization dedicated to factual reporting. Founded in 1846, AP today remains the most trusted source of fast, accurate, unbiased news in all formats and the essential provider of the technology and services vital to the news business.
ROGERS, Ark. — With the uptick in short-term rentals, Beaver Lake would be a prime location for an owner to open up their home to people visiting Arkansas. However, for property owners with boat ...
Former National Security Adviser H.R. McMaster, who served under Donald Trump, said he would not join the former president's second administration if he is reelected this fall. As November draws ...
Vice President Kamala Harris accepted her party's nomination to lead the ticket. By Rick Porter Television Writer The closing of the Democratic National Convention drew a big audience Thursday ...